Question: Integration: Probability Geometric Probability O Geometric probability involves using length and area to find the probability of an event. . If a point on AB

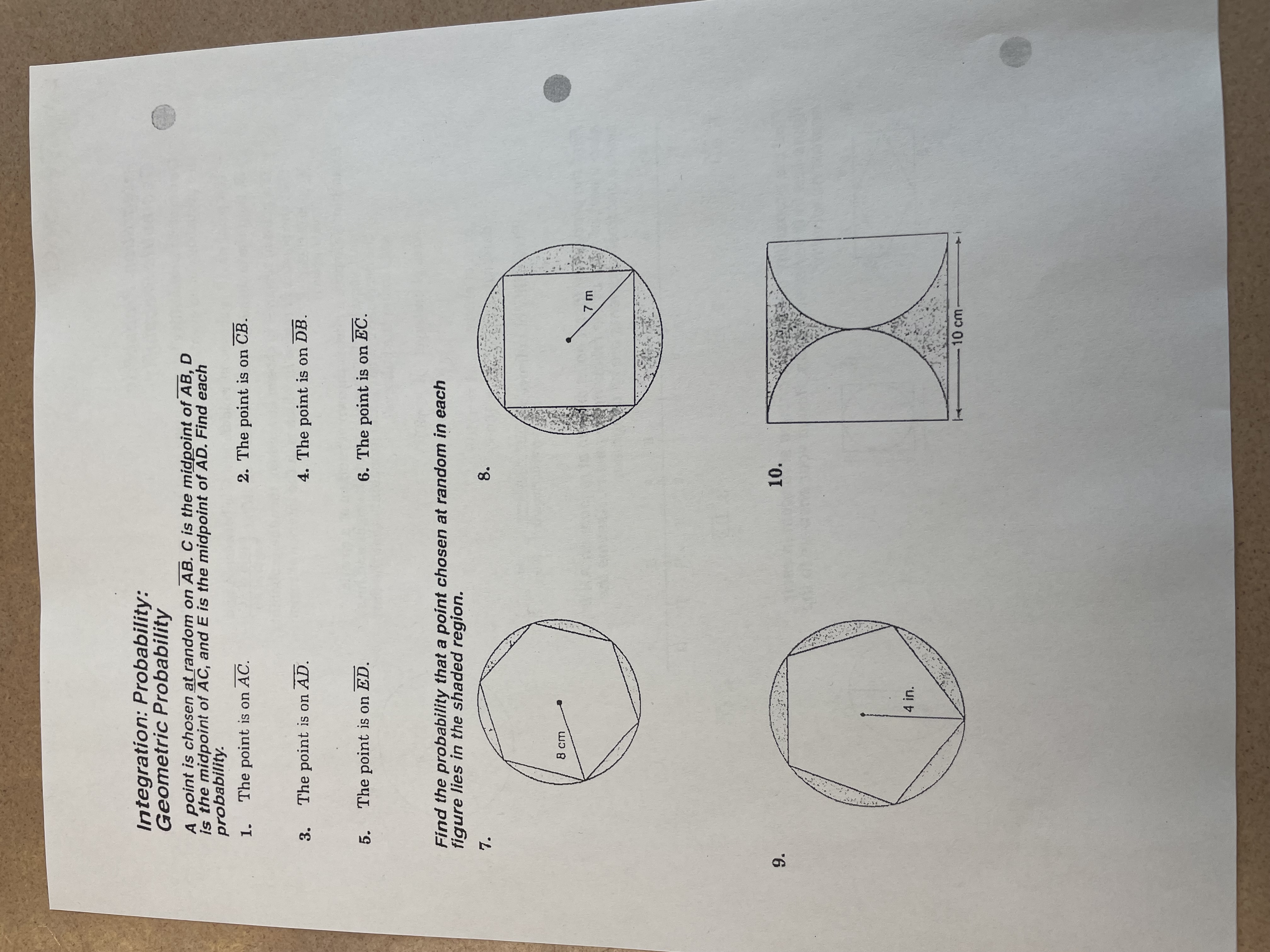
Integration: Probability Geometric Probability O Geometric probability involves using length and area to find the probability of an event. . If a point on AB is chosen at random and C is between A and B, then the probability that the point is on AC is length of AC length of AB . If a point in region A is chosen at random, then the probability that the point is in region B, which is in the interior of region A, is area of region B area of region A Example: Suppose a dart is thrown at random at a circular dartboard like the one shown at the right and hits the dartboard. What is the probability that the dart will land in the bullseye? Area of bullseye: A = T(2)2 A = 4T 10 Area of entire A = T(10)2 dartboard A = 100T Probability of bullseye = area of bullseye - = 1 area of dartboard 100T 25 Find the probability that a point chosen at random on AH is also a part of each of the following segments. Assume the twelve shortest segments are all congruent. G H 2 10 12 1. AD 2. AE 3. DE 4. CG Find the probability that a point chosen at random in each figure lies in the shaded region. Round your answers to the nearest hundredth. 5. 6. 7. 120 9.Integration: Probability: Geometric Probability A point is chosen at random on AB. C is the midpoint of AB, D is the midpoint of AC, and E is the midpoint of AD. Find each probability. 1. The point is on AC. 2. The point is on CB. 3. The point is on AD. 4. The point is on DB. 5. The point is on ED. 6. The point is on EC. Find the probability that a point chosen at random in each figure lies in the shaded region. 7. 8. 8 cm 7 m 9. 10. 4 in 10 cm
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


