Question: ---------------------------------------------------------------- IntNode: public class IntNode { public int data ; public IntNode next ; public IntNode(int data, IntNode next) { this.data = data ; this.next
----------------------------------------------------------------
IntNode:
public class IntNode { public int data ; public IntNode next ; public IntNode(int data, IntNode next) { this.data = data ; this.next = next ; } }
----------------------------------------------------------------
IntLinkedList:
public class IntLinkedList {
private IntNode first; private int count;
public IntLinkedList(int[] array) { createList(array); }
public IntLinkedList() { } void add(int i) { IntNode node = new IntNode(i, first); first = node; }
void createList(int[] arr) { first = new IntNode(arr[0], null); boolean skipFirst = true; IntNode temp = first; count = 1; for (int i : arr) { if (skipFirst == true) { skipFirst = false; } else { IntNode node = new IntNode(i, null); temp.next = node; temp = temp.next; count++; }
} //first = temp; }
void remove(int index) { if (first == null) return; if (index == 0) { first = first.next; return; } if(index > count) { return; } int cnt = 0; IntNode current = first; for(;cnt
boolean empty() { return (count > 0) ? false : true; }
protected IntLinkedList clone() { IntLinkedList intList = new IntLinkedList();
IntNode temp = first; intList.first = first; IntNode inListtemp = intList.first; while (temp != null) { inListtemp.next = temp.next; inListtemp = inListtemp.next; temp = temp.next; } return intList; } public String toString() { String output=""; IntNode temp = first; while(temp!=null) { output+=temp.data+" "; temp = temp.next; } return output; }
}
----------------------------------------------------------------
TestQuestion2:
public class TestQuestion2 { public static void main(String[] args) { IntLinkedList test = new IntLinkedList(new int[]{3,5,4,6,8,2,1,4,3,2,5,3,6,3}); System.out.println("Test list: "+test); IntLinkedList oddOnes = new IntLinkedList(), evenOnes = new IntLinkedList(); test.split(oddOnes,evenOnes); System.out.println("Test list should be empty: "+test); System.out.println("Odds: "+oddOnes); System.out.println("Evens: "+evenOnes);
test = new IntLinkedList(new int[]{3,5,4,6,8,2,1,4,3,2,5,3,6,3}); System.out.println("Test list restored: "+test); System.out.println("Frequency of 3's: "+test.frequency(3)); System.out.println("Frequency of 1's: "+test.frequency(1)); System.out.println("Frequency of 7's: "+test.frequency(7)); } }
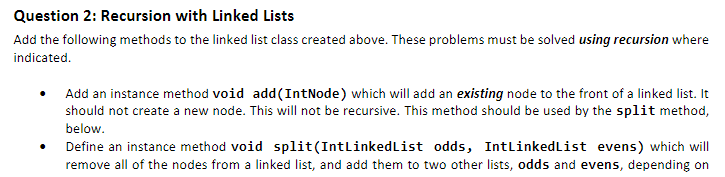
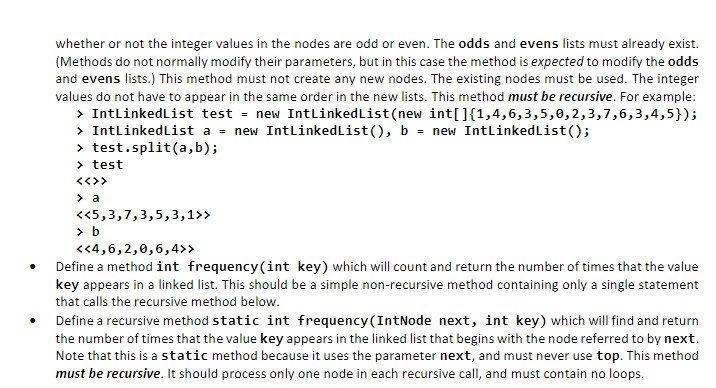
Question 2: Recursion with Linked Lists Add the following methods to the linked list class created above. These problems must be solved using recursion where indicated Add an instance method void add (IntNode) which will add an existing node to the front of a linked list. It should not create a new node. This will not be recursive. This method should be used by the split method, below Define an instance method void split (IntLinkedList odds, IntlinkedList evens) which will remove all of the nodes from a linked list, and add them to two other lists, odds and evens, depending on
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


