Question: Introduction to Microeconomics Problem Set #17 Complete these 2 questions (questions 1 and 2) and then submit answers to questions about problem set one on




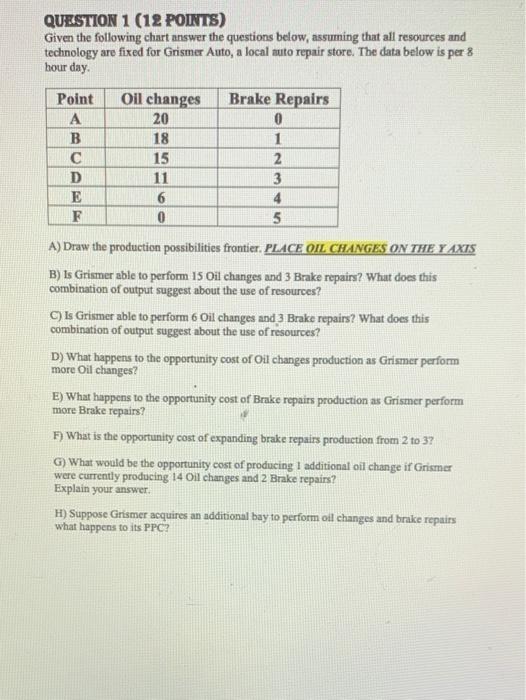

Introduction to Microeconomics Problem Set #17 Complete these 2 questions (questions 1 and 2) and then submit answers to questions about problem set one on Blackboard. You will be able to access this form Three times prior to the deadline date and time (see the Calendar). My Advice is to submit your answers once, see what you missed, and try to solve where you might have problems. I'd print out the questions the 1" time I access the form. Brake Repairs 01 A B C D E F Oil 20 18 15 11 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 Wewe LOOKINegprys Brewer shape of your PC Sungline dowwerd eping PPO Straight line upward sloping PPO Horton straight PPG Vertical right in A downwarding on how to the curve A downward sloping convex howed and from the surve 15 QUESTION 2 Can Grimer currently produce 15 l changes and braker) Yes NO Maybe 2 QUESTIONS What does the point of 15 of charges and brake repairs get about Grimer's resources They are being used efficient They are being used in They are not all being employed Cramer does not currently enough ros or the whology to produce the combination QUESTION 4 What does the output combination of all changes and 3 brate repairs suggest about Grimer's use of resources All resources are used ferty Grimer does not have the wount of resources needed to produce this combination of ovevis Grimer's technology is inefficient Grimer is using its resources or no sing them 2000 QUESTION 5 As Grismer increases the number of oil changes it performs the opportunity cost of an oil change increases remains constant decreases decreases at an increasing rato 2000 QUESTION 6 As Grismer performs more brake repairs the opportunity cost of a brake repair increases remains constant decreases decreases at an increasing rate oil changes QUESTION 7 The opportunity cost of increasing the number of brake repairs performed by Grismer from 2 to three is QUESTIONS The opportunity cost of performing an additional oil change when Grismer is currently producing 14 oil changes and 2 brake repairs nothing since the firm can produce 15 oil changes and 2 brake repairs the additional oil change some partial completion of a brake repair job It depends upon the S value of an oil change QUESTION Suppose Grismer acquires and additional bay to perform all changes and brake repairs. The PPC would relect this change by not moving since it does not impact output by becoming steeper by becoming less steep (atter) by shifting outward by shifting inward by switching from a concave curve to a convex curve QUESTION 10 Looking at your budget line or consumption possibilities curve, which of the following best describes it shape? Straight line downward sloping straight line upward sloping line bowed outward from the origin curve (concave) bowed inward towards the origin (convex) QUESTION 11 Pete can buy 2 pounds of pastrami and 0.66 pounds of corned beef True False QUESTION 12 Pete can buy 15 pounds of pastrati and 1 pound of corned beef True False QUESTION 1 (12 POINTS) Given the following chart answer the questions below, assuming that all resources and technology are fixed for Grismer Auto, a local auto repair store. The data below is per 8 hour day. Point Oil changes Brake Repairs A 20 0 B 18 1 15 2 D 11 3 E 6 4 F 0 5 A) Draw the production possibilities frontier. PLACE OIL CHANGES ON THE Y AXTS B) Is Grismer able to perform 15 Oil changes and 3 Brake repairs? What does this combination of output suggest about the use of resources? C) Is Grismer able to perform 6 Oil changes and 3 Brake repairs? What does this combination of output suggest about the use of resources? D) What happens to the opportunity cost of oil changes production as Grismer perform more Oil changes? E) What happens to the opportunity cost of Brake repairs production as Grismer perform more Brake repairs? H) What is the opportunity cost of expanding brake repairs production from 2 to 3? G) What would be the opportunity cost of producing 1 additional oil change it Grimer were currently producing 14 Oil changes and 2 Brake repairs? Explain your answer. H) Suppose Grismer acquires an additional bay to perform oil changes and brake repairs what happens to its PPC? QUESTION 2 (8 POINTS) Tom lives on a budget. He loves lunch meat, especially pastrami and corned beef. He budgets himself $25 per week for lunch meat. A price of a pound of pastrami (GB) is $10 and the price of a pound of corned beef is $7.50 A) Graph Pete's consumption possibilities curve (between the amount of pastrami and comed beef). PLACE PASTRAMI ON THE X AXIS B) Can Pete buy the following combinations of pastrami (P) and comed beef (C)? 1) 2 pounds of P and 0.67 pounds of C ii) 1.5 pounds of P and a pound of C til) 0.8 pounds of P and 2.5 pounds of C C) What is the opportunity cost of Pete's? 1) First pound of pastrami ii) Second pound pastrami iii) Last pound of pastrami D) How is Pete's opportunity cost of pastrami shown in the graph you drew in part A? Introduction to Microeconomics Problem Set #17 Complete these 2 questions (questions 1 and 2) and then submit answers to questions about problem set one on Blackboard. You will be able to access this form Three times prior to the deadline date and time (see the Calendar). My Advice is to submit your answers once, see what you missed, and try to solve where you might have problems. I'd print out the questions the 1" time I access the form. Brake Repairs 01 A B C D E F Oil 20 18 15 11 6 0 1 2 3 4 5 Wewe LOOKINegprys Brewer shape of your PC Sungline dowwerd eping PPO Straight line upward sloping PPO Horton straight PPG Vertical right in A downwarding on how to the curve A downward sloping convex howed and from the surve 15 QUESTION 2 Can Grimer currently produce 15 l changes and braker) Yes NO Maybe 2 QUESTIONS What does the point of 15 of charges and brake repairs get about Grimer's resources They are being used efficient They are being used in They are not all being employed Cramer does not currently enough ros or the whology to produce the combination QUESTION 4 What does the output combination of all changes and 3 brate repairs suggest about Grimer's use of resources All resources are used ferty Grimer does not have the wount of resources needed to produce this combination of ovevis Grimer's technology is inefficient Grimer is using its resources or no sing them 2000 QUESTION 5 As Grismer increases the number of oil changes it performs the opportunity cost of an oil change increases remains constant decreases decreases at an increasing rato 2000 QUESTION 6 As Grismer performs more brake repairs the opportunity cost of a brake repair increases remains constant decreases decreases at an increasing rate oil changes QUESTION 7 The opportunity cost of increasing the number of brake repairs performed by Grismer from 2 to three is QUESTIONS The opportunity cost of performing an additional oil change when Grismer is currently producing 14 oil changes and 2 brake repairs nothing since the firm can produce 15 oil changes and 2 brake repairs the additional oil change some partial completion of a brake repair job It depends upon the S value of an oil change QUESTION Suppose Grismer acquires and additional bay to perform all changes and brake repairs. The PPC would relect this change by not moving since it does not impact output by becoming steeper by becoming less steep (atter) by shifting outward by shifting inward by switching from a concave curve to a convex curve QUESTION 10 Looking at your budget line or consumption possibilities curve, which of the following best describes it shape? Straight line downward sloping straight line upward sloping line bowed outward from the origin curve (concave) bowed inward towards the origin (convex) QUESTION 11 Pete can buy 2 pounds of pastrami and 0.66 pounds of corned beef True False QUESTION 12 Pete can buy 15 pounds of pastrati and 1 pound of corned beef True False QUESTION 1 (12 POINTS) Given the following chart answer the questions below, assuming that all resources and technology are fixed for Grismer Auto, a local auto repair store. The data below is per 8 hour day. Point Oil changes Brake Repairs A 20 0 B 18 1 15 2 D 11 3 E 6 4 F 0 5 A) Draw the production possibilities frontier. PLACE OIL CHANGES ON THE Y AXTS B) Is Grismer able to perform 15 Oil changes and 3 Brake repairs? What does this combination of output suggest about the use of resources? C) Is Grismer able to perform 6 Oil changes and 3 Brake repairs? What does this combination of output suggest about the use of resources? D) What happens to the opportunity cost of oil changes production as Grismer perform more Oil changes? E) What happens to the opportunity cost of Brake repairs production as Grismer perform more Brake repairs? H) What is the opportunity cost of expanding brake repairs production from 2 to 3? G) What would be the opportunity cost of producing 1 additional oil change it Grimer were currently producing 14 Oil changes and 2 Brake repairs? Explain your answer. H) Suppose Grismer acquires an additional bay to perform oil changes and brake repairs what happens to its PPC? QUESTION 2 (8 POINTS) Tom lives on a budget. He loves lunch meat, especially pastrami and corned beef. He budgets himself $25 per week for lunch meat. A price of a pound of pastrami (GB) is $10 and the price of a pound of corned beef is $7.50 A) Graph Pete's consumption possibilities curve (between the amount of pastrami and comed beef). PLACE PASTRAMI ON THE X AXIS B) Can Pete buy the following combinations of pastrami (P) and comed beef (C)? 1) 2 pounds of P and 0.67 pounds of C ii) 1.5 pounds of P and a pound of C til) 0.8 pounds of P and 2.5 pounds of C C) What is the opportunity cost of Pete's? 1) First pound of pastrami ii) Second pound pastrami iii) Last pound of pastrami D) How is Pete's opportunity cost of pastrami shown in the graph you drew in part A
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


