Question: Is extinction probability always equal to 0? Question 10 Let (Xn)nENn be a branching process dened as in (8.1.1) in the script on page 310
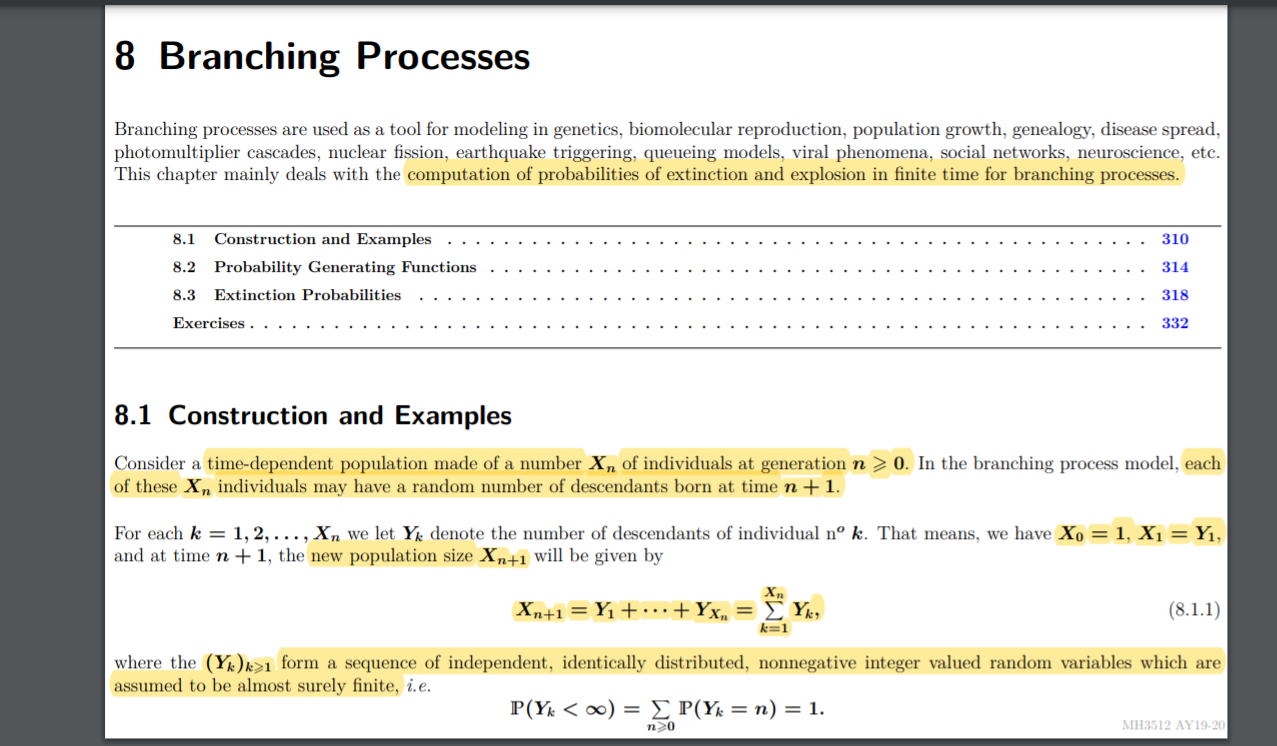
Is extinction probability always equal to 0?

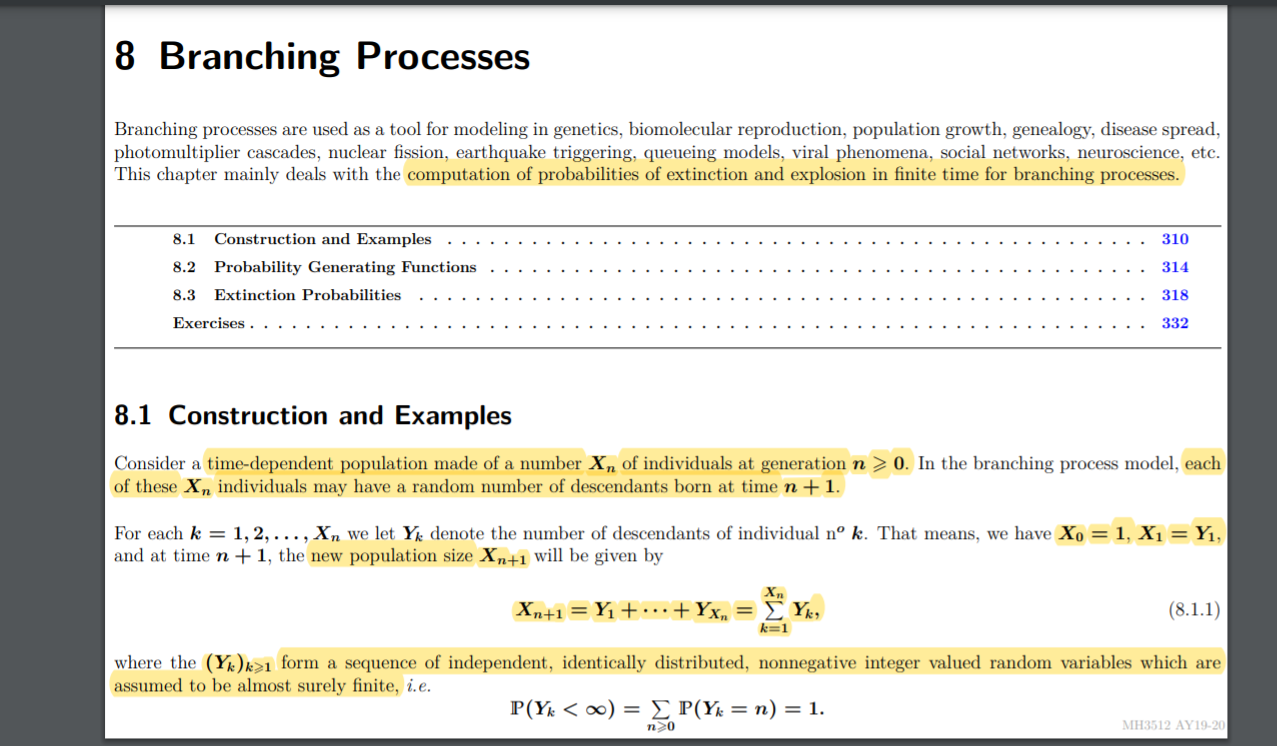
Question 10 Let (Xn)nENn be a branching process dened as in (8.1.1) in the script on page 310 with X0 = 1. Assume that the corresponding (Hikers satisfy HWY\" : 0) : Co, POI : 1) = C1, for strictly positive constants 00,01 > 0 satisfying co + cl = 1. Then the extinction probability of the branching process is equal to 1. YES NO - 8 Branching Processes Branching processes are used as a tool for modeling in genetics, biomolecular reproduction, population growth, genealogy, disease spread, photomultiplier cascades, nuclear ssion, earthquake triggering, queueing models, viral phenomena, social networks, neuroscience, etc. This chapter mainly deals with the computation of probabilities of matinction and explosion in nite time for branching processes. 3.1 Construction and Examples 3.2 Probability Generating Motions 8.3 Extinction Probabilities Exercises ................................................................ 8.1 Construction and Examples Consider a time-dependent population made of a number X\" of individuals at generation I: 2 0. In the branching process model. each of these X ,1 individuals may have a random number of descendants born at time n. -|- 1. For each is = 1, 2, . . . , X" we let Yg denote the number of descendants of individual 11' k. That means, we have X9 = 1, X1 = Y1, and at time n + 1, the new population size Kn.\" will be given by Kn Xn+1=Yi+"-+Yx,,= Z: Ya. (8.1.1) k-I where the (16,)1 form a. sequence of independent, identically distributed, nonnegative integer valued random variables which are assumed to be almost surely nite, ale. P(Yk
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


