Question: It appeared that TECHSERV relied significantly on a regimented approach to project management. Do you believe that there was anything else the management team could
It appeared that TECHSERV relied significantly on a regimented approach to project management. Do you believe that there was anything else the management team could have done to guarantee success?
a) answer the question just like you can speak about it for 5 minutes
b) creatively develop your answers.
best presentation most creative, engaging, use of tools, etc. {tools PPT, pollev, Flipgrid, padlet, Microsoft poll, videos}
2-3 PPT slides for 3 minutes of explanation along with the answer
Introduction: The Strategic Planning Meeting
In the 2017 financial year-end strategic planning meeting, the senior leadership of TECHSERV 1 noted that this was the year of the benchmarksfor the environment, operations, content, and management. One specific learning was that management needed to be a bridge by acknowledging and connecting employee success to performance. In operations, the organization became adopters then leaders on design thinking as applied to implementations. Reflecting on implementations during 2017 so far, the senior leadership team in TECHSERV discussed the robotics process automation (RPA) rollouts as one of the ways that the organization was improving efficiency, effectiveness, and productivity in their operations. More specifically, the benchmarks for productivity in their daily operations included costs, efficiency, accuracy, and time. The organization made the strategic decision to pilot and subsequently implement projects related to RPA as a tool to support the organizations performance benchmarks. Within the next few weeks, TECHSERV needed to identify the resources, tools, and techniques for implementing the RPA projects.
After the pilot implementations earlier in 2017, the senior leadership recognized they needed to get with the project team to obtain information and make decisions about what role senior executives should play in progressing digital technologies including cognitive tools and blockchain.
Thus, the senior leadership wanted to know, what issues or challenges the project team anticipated for deploying RPA in future geographical locations?
Company Background: TECHSERV
TECHSERV is an information technology company that provides hardware, software, and related products and services including computers, printers, and computer-related accessories including, keyboards, headphones, cases, routers, and other items. The foundational platform included refusing to accept the status quo. The organization strives to achieve innovation by their products, people, and ways of doing business. The desire is to create technology that makes life better for everyone. The organization was focused on the worth of specific technologies and technology management was integral in ensuring technology was treated as an asset that could yield competitive advantage. Technology management included the planning, design, execution, and control of the processes to be digitized or automated. RPA was noted as in the current plan, with the end goal to include an enterprise-wide solution to support business innovation and profitability leading to a competitive advantage for the organization. The profitability was to be based on reducing costs, cycle times, and processing times as well as increasing efficiency.
The organization had already received several awards that included acknowledgment from the industry for their excellence in service and operations. For example, the Communication Award for excellence and for distinction and Runner-up award for excellence in culture creation. These awards were important to the senior leadership team and increasing global recognition for various initiatives continued to be a focus of the organization.
To continue to stay on the cutting edge, the companys focus was digital technology and reinvention. Automation formed part of this. The core modernization of intelligent automation that drove the digital finance agenda included using the cloud, implementing process robots, and using dashboards on the production floor to signal bottlenecks in the production process. The focus of the organization included strategic planning with annual coding and programming related to teams that include infrastructure that support projects and programs for strategic implementations. The value proposition related to RPA implementations included accuracy, audit trail, consistency, flexibility, location agnostic (geographically independent), low-risk and noninvasive technology, productivity, reliability (24/7 availability), productivity, and staff retention.
The projects related to digital implementation included RPA pilot rollouts in Spain and China for the fiscal year 2017 in the Finance business unit of the organization. (In the interests of preserving anonymity of the case site the country names have been changed.) The automation focused on repetitive processes and tasks that included rule-based practices, security checks, scalability and demand expansion, and audit trails for compliance reporting and monitoring. These repetitive automation processes and tasks may be the source of some issues and challenges as the organization continued the path forward into intelligent automation. It raised the question, What are the issues and challenges for future RPA implementation in the various geographical areas of the firm?
Finance and RPA Pilot Implementations
The Finance business unit in TECHSERV was led by Ann Anderson and responsible for ensuring that the business operated efficiently and effectively. The Financial business unit included finance, accounting, tax, and treasury activities. The business functions included managing the accounting and monitoring internal controls as well as conducting banking and financing activities and reporting to authorities. The focus of the Finance Department was to digitalize experience by enabling tools and processes that accelerate their employees ability to imagine the future, inspire the team, and make it happen.
The Finance business unit was charged with piloting rollouts in Spain and China including automating the invoicing process using rule-based processes and machine language for processing and analyzing data. The Finance business unit embraced innovation as a key enabler to drive business value and build the required capabilities for the future. Therefore, the organizations strategic plan included RPA as an integral pathway to the future success of digital technology including intelligence automation related to the cloud, process robots, visualization, cognitive computing, advanced analytics, and Blockchain. The goal with regard to RPA was to foster an inclusive environment in which the senior leadership and employees partnered to ensure successful RPA implementation.
Can We Gain Competitive Advantage? Can We Acquire RPA Skill-Sets?
Prior to making the decision to rollout RPA, Ann Anderson wondered whether there was enough data to support investing the time and effort into the RPA technology for the Finance business unit. She charged her Finance Research Staff, led by April Harris, to research the benefits of RPA including looking at other companies that had executed RPA initiatives. This research would help Ann Anderson and the Finance determine whether RPA would help maintain a competitive edge, if executed. April and the Research Staff noted that RPA was a new wave of innovation of computer software configured to perform operational tasks such as processing sales and financial transactions, consolidating and reporting data, integrating with different systems via communication, and process monitoring. 2 Thus, the goal of RPA was to take existing processes, possibly redesign them, and apply automating work packages in order to facilitate new job creation, cost reductions, quality management, and productivity enhancements. 3 The cost reductions were related to automating certain processes that previously were performed by full-time employees. The improved efficiencies were related to 24-h process capabilities and improvements in customer responses. In addition, the Research Team reported that RPA implementations reduce costs, improve service quality, increase compliance reporting, and lowers delivery times. 4 TECHSERV expected the benefit metrics and associated measurements in Table 1 based on their limited research about RPA.
To further support the decision to deploy RPA projects, the Finance research staff noted that O2 and OpusCapita Group executed RPA in their organizations. 5 The focus of the O2 implementation included transforming the back-office processes by eliminating some processes and optimizing other processes while managing the costs to continue to compete in the mobile communications industry. The organization rolled out two pilot studies focusing on high-volume, low-complexity processes to conduct the proof of concept phase. Thereafter, the organization selected a vendor to assist with implementation and used their provider to conduct the development activities within the project. The research staff further noted that the OpusCapita Group provides financial services for their clients and focuses on purchase-to-pay and order-to-cash financial processes and automated those processes using RPA, for their clients. The company implemented RPA using four stagesanalysis workshop, process assessment, business case proposal, and thereafter RPA implementation. During implementation, OpusCapita developed process libraries for the process flows which included detailed instructions for robots to execute. The information noted about the O2 and OpusCapita Group further solidified the decision to use RPA to automate business processes.
The Finance business unit in conjunction with business units within TECHSERV noted that there were other benefits from RPA including in the ways human resources, compliance, and reporting were improved. The human resource benefits included the results of automating manual processes which include 24/7 resources as well as freeing up resources to learn RPA skills as well as other higher-order jobs. The compliance benefits include the reports or logs that are recorded and available for audit purposes. In addition, the automation would support real-time data analytics. Despite these operational, human resource, compliance, and reporting benefits, TECHSERV was concerned about how difficult the task might be of implementing this technology and successfully assimilating it into the organization. There were success stories in many industries, but there were also reports throughout 2017 of 30%50% of RPA projects stalling, being rethought, or even abandoned. The organization also learned from the research that the methodology and collaboration between internal and external resources were necessary for successful executions. When the Finance business unit consulted with the Human Resources business unit, it learned that there were no full-time or part-time staff with the skill-sets needed to implement this emerging technology. How were these skill-sets going to be acquired? The Finance business unit decided that this was a question that needed to be resolved by the project team based through the project management approach adopted.
Enter Project Management and Start-Up
The project management of the Spain and China initiatives included the activities and tasks organized by the five process groups as defined by the Project Management Institute (2017). 6 These process groups included initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and controlling, and closing. The focus of the implementation was to automate as much as possible, in order to allow employees to spend more time interpreting the data, understanding the needs of the business, and driving more predictive outcomes.
Initiating Process and RPA Skill-Sets Acquired
The feasibility study, proof of concept, and risk identification activities were conducted in the initiating phase. Also during the initiating process, the project team defined the scope; authorized the project start; and created the project charter to document the business case and allocation of resources including human capital, equipment, and software (Project Management Institute, 2017).
The Finance charged the project team to make a decision about the RPA skill-sets. Since RPA was an emergent technology and no one in the organization had led or been involved in RPA initiatives, the project team decided to hire external consultants to provide RPA skills-sets required for the leadership and advisement related to the implementation. More specifically, the external consultants provided project leadership including project team members to provide daily project management including resolving issues, removing roadblocks, and reviewing deliverables. The external consultants worked in conjunction with the organizations internal resources including the project manager, lean six sigma quality professionals, software developers, IT staff, and RPA technical solution architects. The local controllership and tax executive business sponsors were also involved in both Wave 1 and Wave 2 implementations. After the first pilot, only the companys internal resources, local controllership, and tax executives were used to implement the project. The external consultants were not used to execute the second pilot once the internal resources were trained and understood the technical issues and challenges from the first pilot.
There were also hardware and software resources needed for successful pilots and included system and network connectivity and access; Microsoft Office Applications such as Microsoft Outlook, Excel, and Internet Explorer; Kryon (RPA software); and other tools such as FlexCard and PDF. Table 2 shows the hardware and software tools needed for RPA pilot implementation. These tools are worth noting because the integration of hardware and software tools are not only important for the RPA pilot projects but also important because of the issues and challenges for future pilot RPA sites. This raised the question, What were the future issues and challenges that the project team should identify and plan to mitigate? Would these issues and challenges be related to the integration points for the various software and hardware?
The Feasibility Study
The feasibility study was developed to establish the scope of the project including the objectives and reasons for project initiation (Project Management Institute, 2017). The feasibility study included the following activities: development of the business case, identification of the technical resources, development of a highlevel project schedule, assessment of an estimated return on investment, region of interest/regions of interest (ROI), and creation of a feasibility report. After completion of the feasibility study, April Harris and her Finance business unit decided to deploy RPA and to pilot the implementation in certain environments starting with Spain and thereafter China. In Spain, the tax section was selected for the RPA pilot due to the amount of time human workers have spent historically performing manual and repetitive tasks.
There were two tax sub-processes that were deployed in the pilot projects. The first RPA process validated third-party invoice data prior to loading the data in the Spain Tax System. The Spain Tax System is the source system and reference point for all tax transactions and thus all invoice transactions were validated via the local government website. A robot, via RPA, automatically validated both the invoice amount and access key via the government website, prior to storing the invoice in the companys tax system. During the RPA processing, errors were flagged and returned to the third-party provider via email for resolution. The second RPA sub-process included reviewing and validating customer return data prior to goods being shipped. For example, this sub-process focused on validating the product return invoice with accompanying information such as the dead-on-arrival number.
Proof of Concept
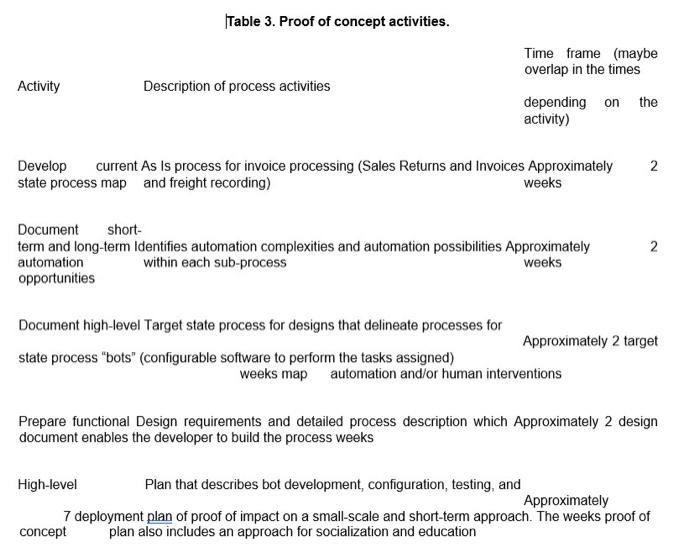
After the feasibility study, the project team collaborated to conduct the proof of concept. This phase of the projects included a review of the current state, a target future state, functional design document, targeted design, and deployment plan. The project team documented the proof of concept activities including the time frames for the activities. (See Table 3 for more details concerning the proof of concept phase.)
Project RisksIssues and Challenges
The project team, led by the external consultants, wondered what would happen if the RPA rollout disrupted normal business? This possible problem led to the need to identify other possible problems (risks) associated with the rollouts. Some of the identified risks included lack of employee buy-in to retool, robots not working as operationally intended, not managing the changes based on automation such as employee retooling, unclear new roles, and lack of communication about RPA impacts. 7 Other risks included disruption to operations during the pilot and external threats related to breaching the intranet security due to the new security methods related to the software and hardware resources. These risks were used to identify issues and challenges for future RPA implementations, and develop response plans to mitigate the impacts of the risks. For example, a response plan for mitigating the disruption of operations included the project team testing the operations in a separate environment prior to going live with the pilot sites. In addition, the project team acknowledged the need to hire IT specialist and engineers trained in security breaches to protect against external threats during and after implementations.
Planning Process
During the planning process, which was the next phase after the initiating process, the project team finalized the scope and the tasks and activities were discussed and documented (Project Management Institute, 2017). The team conducted deep dive sessions in which they discussed project scenarios and exceptions as well as information technology sizing. In addition, the organization developed a (a) change management plan, (b) process design document including the solution architect, (c) to be process map, (d) technical design document, and (e) unit testing strategy and plan.
Execution Process
The project team performed the tasks and activities per the project plan in the execution process with a focus on coordinating resources and managing project objectives (Project Management Institute, 2017). The IT and Development Team at TECHSERV used the Process Design and Technical Design documents and created the code including integration points into other systems. In addition, the project solution utilized the Leo tool from Kryon Systems to effectuate RPA. Tools and techniques such as MS Access, Scripts, and Macros were also used, and the password vault was used to store user credentials.
As a part of the development process, there were various interfaces related to enterprise systems. These high-level interfaces include the following: BOE (type of robot) tool, WRT (Web Retrieval Tool), SharePoint, SML (Extensible Markup Language) File, and SAP (Systems, Applications, and Product) systems.
TECHSERV business team members, along with the IT staff of the project team, developed user acceptance test cases and conducted user acceptance and environmental testing. These testing tasks were important; testing ensures that the systems are integrated and working properly along with the new automated software. Thereafter, the team conducted system integration testing to ensure the integration into other systems were working properly. Any issues noted during system integration testing or user acceptance testing were documented and the developers were responsible for coordinating resolutions. After the testing issues were resolved, the Finance business owners signed-off on the testing and the code was ready to migrate to production. Prior to the go-live date, a code review was conducted and collectively the team members approved the project completion. After sign-off, the code was migrated to production and communication of the migration was announced company-wide.
Monitoring and Controlling Process
The project team, led by external consultants, spent a significant amount of time conducting the monitoring and controlling process during the project. This included reviewing and monitoring the status and performance of the project by updating the project plan and engaging in project communications. At various stages throughout the project, the team engaged in daily meetings. In addition, the organization used Microsoft Office tools (Outlook, Excel, Word, etc.) to manage the project for communication and issue resolution purposes. During the monitoring and closing process, the project team was not only working on the technical aspects of the project but was also managing the soft skills such as behaviors, attitudes, and motivations. These soft skills were important to manage during communication mediums and issue resolutions.
Closing ProcessWhat Lessons Did the Project Team Learn?
During the closing process, the project team verified that the tasks and activities were performed as documented in the project schedule, assessed the performance of the project, and documented the lessons learned. The maintenance and support of the RPA project was also finalized during this time. The team members decided to deploy a project retrospective customer survey in the organization to further assess the performance of the project. In addition, the project team assembled in a conference room to recap and reflect on the challenges, issues, and pitfalls related to the pilot rollout implementations. See Table 4 for some of the highlights of the lessons learned.
TECHSERV: Developments and Reflections
After completion of the pilot rollouts, during 2017, the Finance business unit implemented projects in various areas, including tax, reporting, and services. The Finance Department implemented 26 projects in various areas, including tax, reporting, and services. These projects resulted in 108 robots deployed in Finance; 110 RPA projects delivered; creation of regional finance innovation and robotics engineering labs; implementation of internship program; robust governance including IT engagement; compliance assessment and business continuity; and a culture of innovation. In addition, the rollouts included reduced cost, cycle, and processing time as well as efficiency results.
See Table 5 for the 2017 outcome information for the RPA implementations.
During 2018, the senior leadership team of TECHSERV reflected on what they felt differentiated them from their competitors and what was the key to their RPA success. This reflection led them to remember their original strategic approachdecision to rollout an all-encompassing solution including end-to-end processes with a focus on design thinking. More specifically, the organization in their pilot rollouts included validations, templates, regular tax updates into the local tax system, extraction of reports, and posting of invoices. One of the other significant RPA implementation strategies included the collaboration across multiple internal and external teams with an emphasis on coordination across processes, automation of multiple applications, and reduction of manual work to provide an end-to-end solution.
Future Geographic RPA RolloutsIssues and Challenges
As the senior leadership of TECHSERV continued to implement RPA, they questioned what risks, issues, or challenges would arise as the deployments went wider geographically and also where they engaged with other finance processes and services such as invoicing. How could they mitigate the risks, issues, and challenges once identified? Would these issues and challenges be limited to the high-level risk identified in the initiating phase, and relating to the hardware and software identified in Table 2?
RPA: robotics process automation; FTE: full-time employee.
The senior leadership also wanted to address the path forward after RPA. Other cognitive automation tools were becoming available, and other digital technologies also needed to be adopted, and possibly combined with automation technologies. In particular, they noted six intelligent automation movements that were driving the digital finance agenda. These six intelligent automation trends included cloud, process robots, visualization, cognitive tools, advanced analytics, and Blockchain.
The leadership asked the project team, what do you recommend as the path forward after implementing RPA in all geographical sites? The project team considered the six intelligent trends noted by the leadership and decided that cognitive tools could be used to build on RPA implementations related to digital technology and the invoicing process by making the robots smarter. But how could this smartness be used in the invoicing process as well as provide faster customer service?
The TECHSERV leadership also identified the cloud and blockchain technologies as vehicles for enabling cross-board payments at less costs and more real-time. This emerging technology is based on agreements between organizations because they are transacting money for services or products. 8 TECHSERV planned to move forward using cloud and blockchain for their future offerings. But how should the organization integrate RPA with block chain?




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


