Question: It is from desire2learn, Ap stat Question 10 (4 points) Which of the following is true about the degrees of freedom? a) The degree of
It is from desire2learn, Ap stat


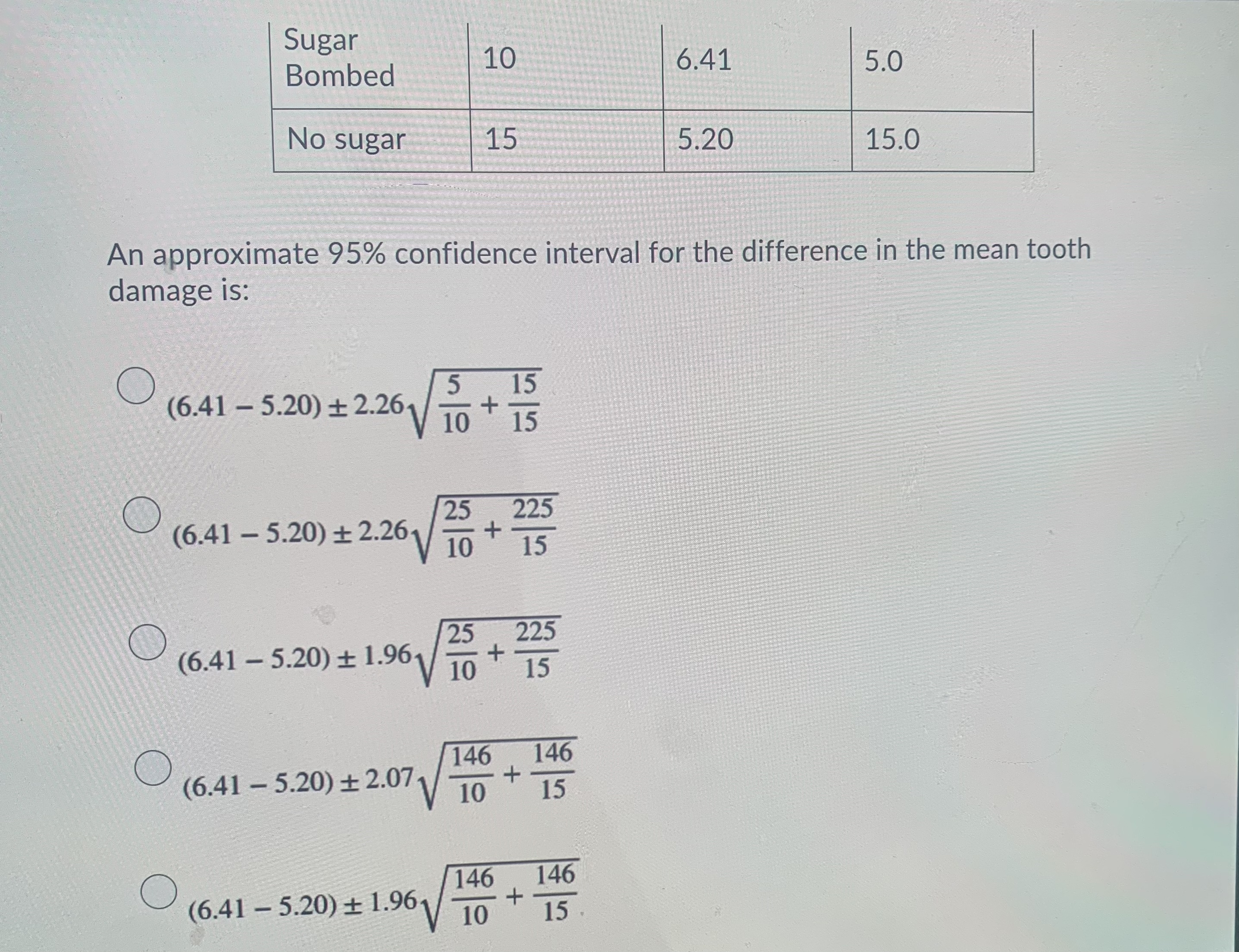


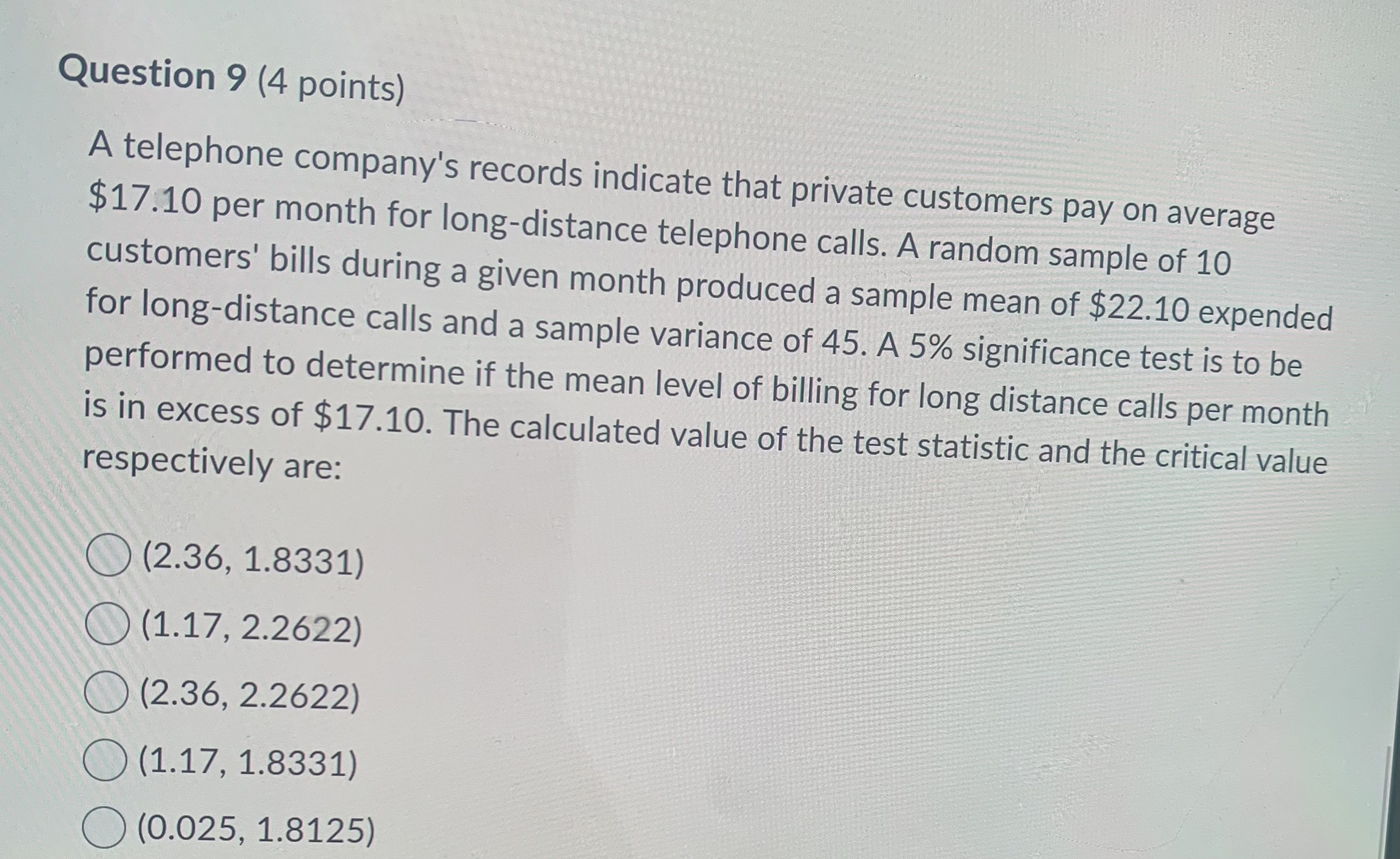
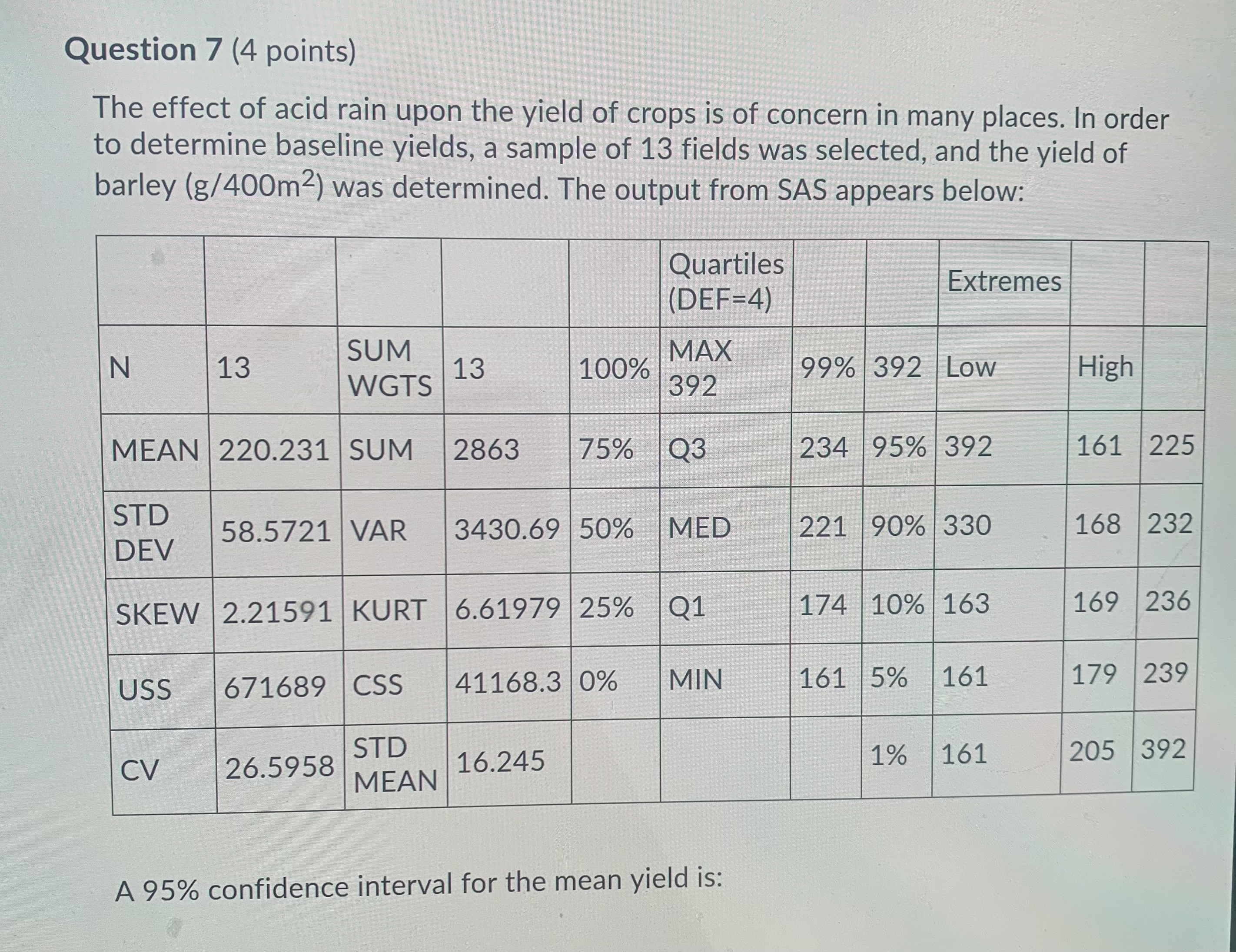


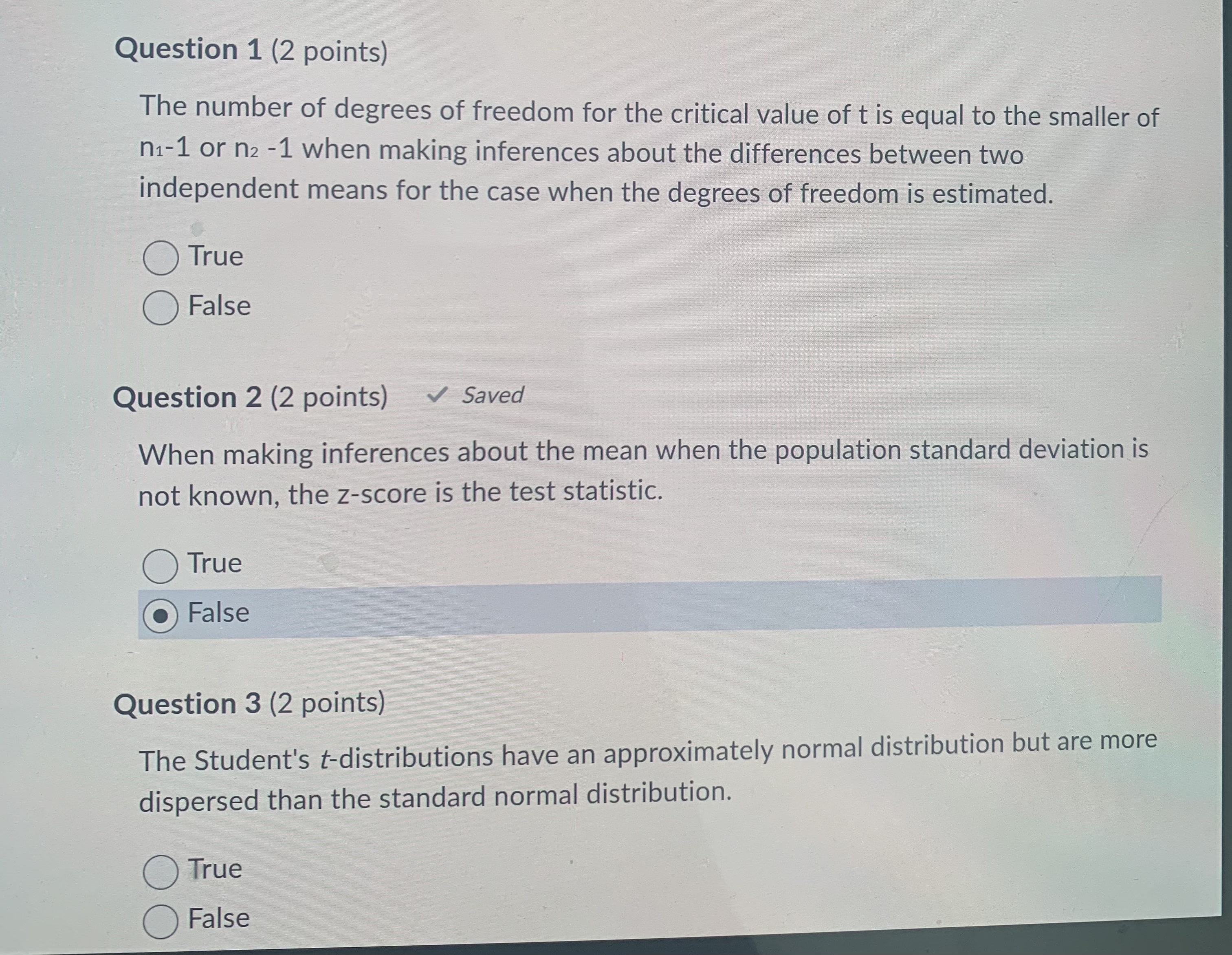
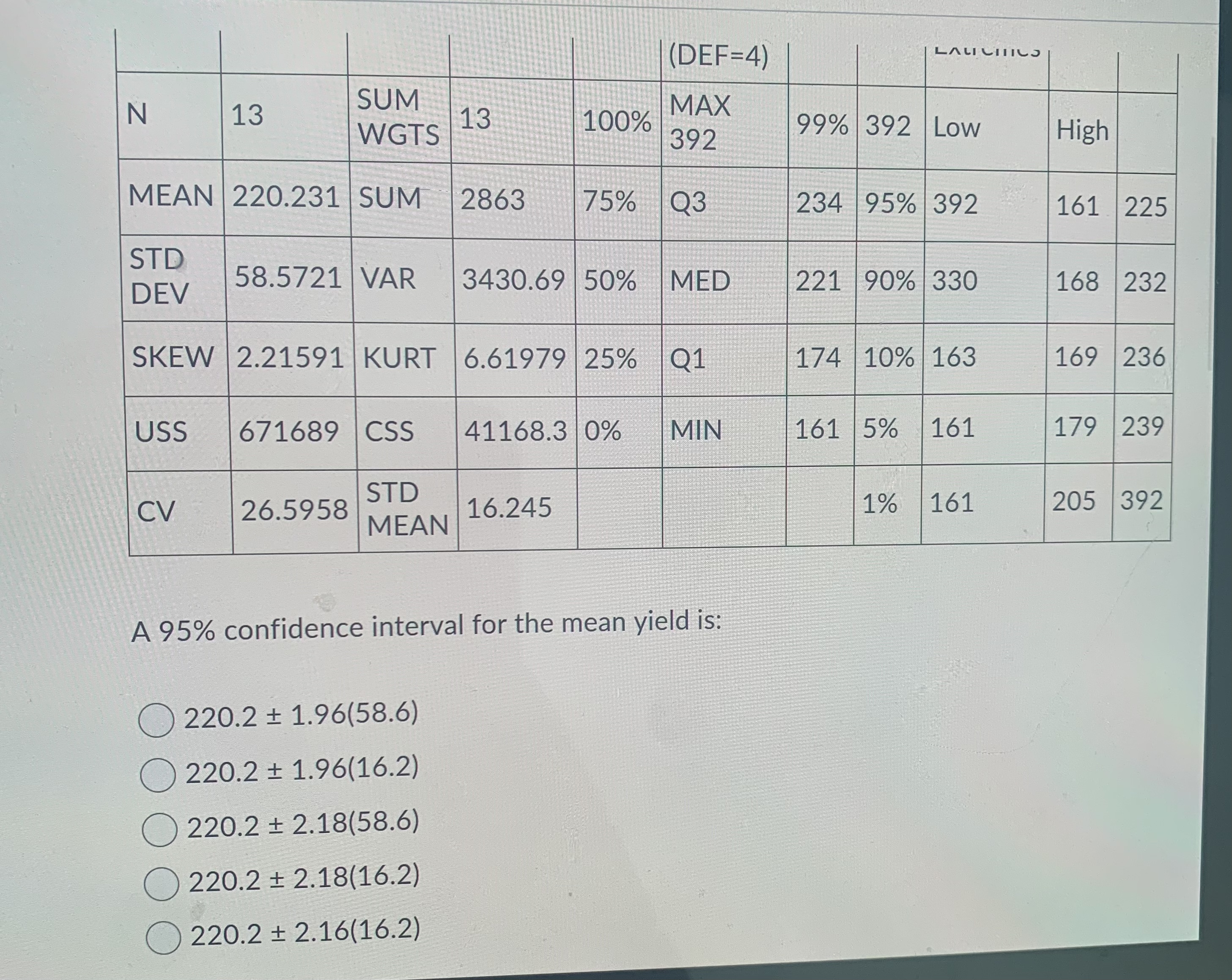


Question 10 (4 points) Which of the following is true about the degrees of freedom? a) The degree of freedom is the same as the sample size b) The degree of freedom is one less than the denominator used calculating the standard deviation (denominator - 1) c) Every time a statistic is calculated from a sample, one degree of freedom is added to the sample size to reduce variability O d) The t distribution varies from the standard normal in that its standard deviation is determined by what is known as the number of degrees of freedom. e) All of the above are trueQuestion 13 (4 points) A farmer investigated pesticide contamination at a small pond with significant run- off (meaning water runs from the nearby fields into the pond). Ten measurements of pesticide concentrations were randomly taken at the pond (assume the pesticide is normally distributed throughout the pond). The reported pesticide concentrations: 18.4, 25.8, 27.3, 19.5, 23.8, 29.4, 30.1, 29.1, 33.8 and 35.7 ug/L. Given that the data distribution is normal, find the t-value for a 90% confidence level. a) 1.812 O b) 1.796 O c) 1.372 d) 1.383 e) 1.833Sugar Bombed 10 6.41 5.0 No sugar 15 5.20 15.0 An approximate 95% confidence interval for the difference in the mean tooth damage is: (6.41 -5.20) +2.261 5 15 10 15 O (6.41 - 5.20)+ 2.261 25 225 10 + 15 O (6.41 - 5.20) + 1.961 25 225 10 + 15 O (6.41 - 5.20) + 2.071 146 146 10 15 O (6.41 - 5.20) + 1.961 146 146 10 + 15Question 14 (4 points) Which of the following is not true? (a) As n approaches infinity, the t-distribution table looks more like the Standard Normal table (b) Confidence intervals from the t-distribution are wider than confidence intervals from the normal distribution ( c) For hypothesis testing the t-distribution gives lower p-values than the normal distribution O d) Degree of freedom is not the same as sample size O e) The t-statistic has larger variance than the z-statisticQuestion 15 (4 points) A farmer investigated pesticide contamination at a small pond with significant run- off (meaning water runs from the nearby fields into the pond). Ten measurements of pesticide concentrations were randomly taken at the pond (assume the pesticide is normally distributed throughout the pond). The reported pesticide concentrations: 18.4, 25.8, 27.3, 19.5, 23.8, 29.4, 30.1, 29.1, 33.8 and 35.7 ug/L. Given that the data distribution is normal, find the t-value for a 95% confidence level. O a) 2.228 O b) 2.262 c) 3.690 O d) 3.581 e) 3.250Question 9 (4 points) A telephone company's records indicate that private customers pay on average $17.10 per month for long-distance telephone calls. A random sample of 10 customers' bills during a given month produced a sample mean of $22.10 expended for long-distance calls and a sample variance of 45. A 5% significance test is to be performed to determine if the mean level of billing for long distance calls per month is in excess of $17.10. The calculated value of the test statistic and the critical value respectively are: (2.36, 1.8331) (1.17, 2.2622) (2.36, 2.2622) (1.17, 1.8331) (0.025, 1.8125)Question 7 (4 points) The effect of acid rain upon the yield of crops is of concern in many places. In order to determine baseline yields, a sample of 13 fields was selected, and the yield of barley (g/400m2) was determined. The output from SAS appears below: Quartiles (DEF=4) Extremes N 13 SUM 13 100% MAX WGTS 392 99% 392 Low High MEAN 220.231 SUM 2863 75% Q3 234 95% 392 161 225 STD DEV 58.5721 VAR 3430.69 50% MED 221 90% 330 168 232 SKEW 2.21591 KURT 6.61979 25% Q1 174 10% 163 169 236 USS 671689 CSS 41168.3 0% MIN 161 5% 161 179 239 CV 26.5958 STD MEAN 16.245 1% 161 205 392 A 95% confidence interval for the mean yield is:Question 11 (4 points) A farmer investigated pesticide contamination at a small pond with significant run- off (meaning water runs from the nearby fields into the pond). Ten measurements of pesticide concentrations were randomly taken at the pond (assume the pesticide is normally distributed throughout the pond). The reported pesticide concentrations: 18.4, 25.8, 27.3, 19.5, 23.8, 29.4, 30.1, 29.1, 33.8 and 35.7 ug/L. Given that the data distribution is normal, calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean amount of pesticide contained in the pond. O a) We are 95% confident that the true mean of pesticide contamination in the pond is between 27.29 and 31.3 ug/L (b) We are 95% confident that the true mean of pesticide contamination in the pond is between 23.28 and 27.29 ug/L O c) We are 95% confident that the true mean of pesticide contamination in the pond is between 23.485 and 31.094 ug/L O d) We are 95% confident that the true mean of pesticide contamination in the pond is between 23.28 and 31.3 ug/L O e) None of the above is correctQuestion 8 (4 points) Popular wisdom is that eating pre-sweetened cereal tends to increase the number of dental caries (cavities) in children. A sample of children was (with parental consent) entered into a study and followed for several years. Each child was classified as a sweetened-cereal lover or a non-sweetened cereal lover. At the end of the study, the amount of tooth damage was measured. Here is the summary data: Group n mean std. dev Sugar Bombed 10 6.41 5.0 No sugar 15 5.20 15.0 An approximate 95% confidence interval for the difference in the mean tooth damage is: O (6.41 -5.20)+ 2.261 5 15 10 15 O (6.41 - 5.20) + 2.261 25 225 10 + 15Question 1 (2 points) The number of degrees of freedom for the critical value of t is equal to the smaller of n1-1 or n2 -1 when making inferences about the differences between two independent means for the case when the degrees of freedom is estimated. True False Question 2 (2 points) Saved When making inferences about the mean when the population standard deviation is not known, the z-score is the test statistic. True False Question 3 (2 points) The Student's t-distributions have an approximately normal distribution but are more dispersed than the standard normal distribution. True False(DEF=4) LALCITIES N 13 SUM WGTS 13 100% MAX 392 99% 392 LOW High MEAN 220.231 SUM 2863 75% Q3 234 95% 392 161 225 STD DEV 58.5721 VAR 3430.69 50% MED 221 90% 330 168 232 SKEW 2.21591 KURT 6.61979 25% Q1 174 10% 163 169 236 USS 671689 CSS 41168.3 0% MIN 161 5% 161 179 239 CV 26.5958 STD MEAN 16.245 1% 161 205 392 A 95% confidence interval for the mean yield is: 220.2 + 1.96(58.6) 220.2 + 1.96(16.2) 220.2 + 2.18(58.6) 220.2 + 2.18(16.2) 220.2 + 2.16(16.2)Question 12 (4 points) To calculate the two-sample z statistic: (a) Subtract the hypothesized mean of differences (in most cases 0) from the sample mean of differences and then divide by the standard deviation (b) Estimate the z-score using the Empirical Rule, then standardize the estimate by dividing it by its standard error (c) observed difference, 1- 2 divided by the standard error ( d) Subtract the hypothesized mean of differences (in most cases 0) form the sample mean of the differences and then divide by n-1 e) None of the aboveQuestion 4 (2 points) The use of paired data often allows for the control of unmeasurable or confounding variables because each pair is subjected to these confounding effects equally. True False Question 5 (2 points) In comparing two independent means when the population standard deviations are unknown, we need to use the standard normal distribution. True False Question 6 (2 points) When the means of two unrelated samples are used to compare two populations, we are dealing with two dependent means. True False
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


