Question: It turns out that the hints in Problems #10 and #11 are superfluous. Even if it was not mentioned that the 6.5% (Problem #10) and
It turns out that the hints in Problems #10 and #11 are superfluous. Even if it was not mentioned that the 6.5% (Problem #10) and 6% (Problem #11) were EARs, the only correct way to solve these problems is to treat these rates as EAR. The context itself implies that these are EAR rates. Please elaborate on why this is so. In other words, convince yourself and the reader (i.e., instructor and grader) that these are EARs.
ANSWERS ARE ATTACHED 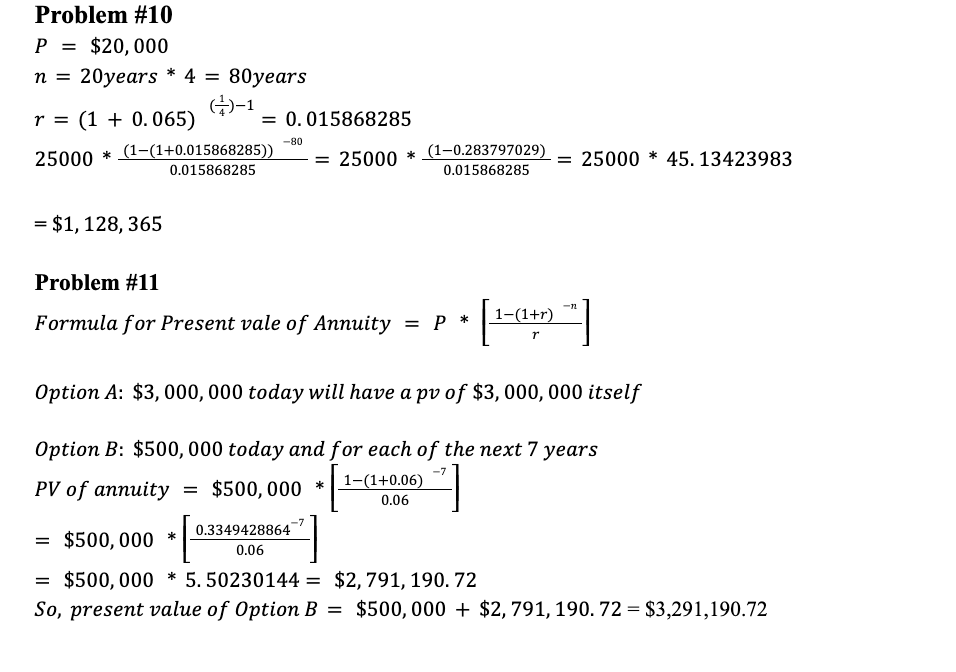

Problem #10 question:
An insurance company, Ed Nareehs Insurance, wants to sell you an annuity that pays you $25,000 per quarter for 20 years, with the first payment in one quarter from now. You want to earn a minimum rate of return of 6.5%. What is the most you are willing to pay as a lump sum today to buy this annuity? [Hint: 6.5% is an EAR.]
Problem #11question: Congratulations! As winner of the MegaThousands lottery, you can choose one of the following prizes: A: $3,000,000 today B: $500,000 today and for each of the next 7 years C: $480,000 today and $120,000 per half-year for the next 20 years D: $500,000 today and $40,000 per quarter next period forever If the interest rate is 6%, which of the above will you choose? If you were the Director of Lottery in charge of lottery payments, which of the above will you prefer? Why? [Hint: 6% is an EAR.]
Problem #10 P = $20,000 n = 20years * 4 = 80years 4)-1 r = (1 + 0.065) = 0.015868285 25000 * (1-(1+0.015868285)) = 25000 * (1-0.283797029) 0.015868285 0.015868285 -80 = 25000 * 45. 13423983 * = $1, 128, 365 Problem #11 Formula for Present vale of Annuity = p * 1-(1+r) f -12 r Option A: $3,000,000 today will have a pv of $3,000,000 itself Option B: $500,000 today and for each of the next 7 years PV of annuity = $500,000 * | 1-(1+0.06) 0.06 -7 0.3349428864 = $500,000 * 0.06 = $500,000 * 5.50230144 = $2,791, 190.72 So, present value of Option B = $500,000 + $ 2, 791, 190.72 = $3,291,190.72 = Option C: $480,000 today and $120,00 per half year the next 20 years P = $120,000 6% = 0.03 n = 20years * 2 = 40 r = -40 1-(1+0.03) So, PV of annuity = $120,000 * 0.03 = $120,000 * 23. 11477197 = $2,773.772.64 [ Option D: $500,000 today and $40,000 per quarter next period forever Present value of perpertuity Cashflow Discount rate Here, cashflow = $40,000 0.06 Discount rate = 0.015 6% = 4 4 $40,000 0.015 So, present value of perpertuity = $2,666,666.67 So, present value of OPTION D = $500,000 + $2,666, 666.67 = $3,166,666, 67 So, option (B) should be chosen as the present value of Option B is the highest of all. However, if I was the director of lottery in charge of lottery payments, I would prefer Option A as it would require the minimum discharge of payments compared to other options. Problem #12 It turns out that the hints in Problems #10 and #11 are superfluous. Even if it was not mentioned that the 6.5% (Problem #10) and 6% (Problem #11) were EARs, the only correct way to solve these problems is to treat these rates as EAR. The context itself implies that these are EAR rates. Please elaborate on why this is so. In other words, convince yourself and the reader (i.e., instructor and grader) that these are EARs. Problem #10 P = $20,000 n = 20years * 4 = 80years 4)-1 r = (1 + 0.065) = 0.015868285 25000 * (1-(1+0.015868285)) = 25000 * (1-0.283797029) 0.015868285 0.015868285 -80 = 25000 * 45. 13423983 * = $1, 128, 365 Problem #11 Formula for Present vale of Annuity = p * 1-(1+r) f -12 r Option A: $3,000,000 today will have a pv of $3,000,000 itself Option B: $500,000 today and for each of the next 7 years PV of annuity = $500,000 * | 1-(1+0.06) 0.06 -7 0.3349428864 = $500,000 * 0.06 = $500,000 * 5.50230144 = $2,791, 190.72 So, present value of Option B = $500,000 + $ 2, 791, 190.72 = $3,291,190.72 = Option C: $480,000 today and $120,00 per half year the next 20 years P = $120,000 6% = 0.03 n = 20years * 2 = 40 r = -40 1-(1+0.03) So, PV of annuity = $120,000 * 0.03 = $120,000 * 23. 11477197 = $2,773.772.64 [ Option D: $500,000 today and $40,000 per quarter next period forever Present value of perpertuity Cashflow Discount rate Here, cashflow = $40,000 0.06 Discount rate = 0.015 6% = 4 4 $40,000 0.015 So, present value of perpertuity = $2,666,666.67 So, present value of OPTION D = $500,000 + $2,666, 666.67 = $3,166,666, 67 So, option (B) should be chosen as the present value of Option B is the highest of all. However, if I was the director of lottery in charge of lottery payments, I would prefer Option A as it would require the minimum discharge of payments compared to other options. Problem #12 It turns out that the hints in Problems #10 and #11 are superfluous. Even if it was not mentioned that the 6.5% (Problem #10) and 6% (Problem #11) were EARs, the only correct way to solve these problems is to treat these rates as EAR. The context itself implies that these are EAR rates. Please elaborate on why this is so. In other words, convince yourself and the reader (i.e., instructor and grader) that these are EARs
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


