Question: java code Consider the linked list implementation below class ListNode { private int data; private ListNode next; ListNode (int d) f data = d; next
java code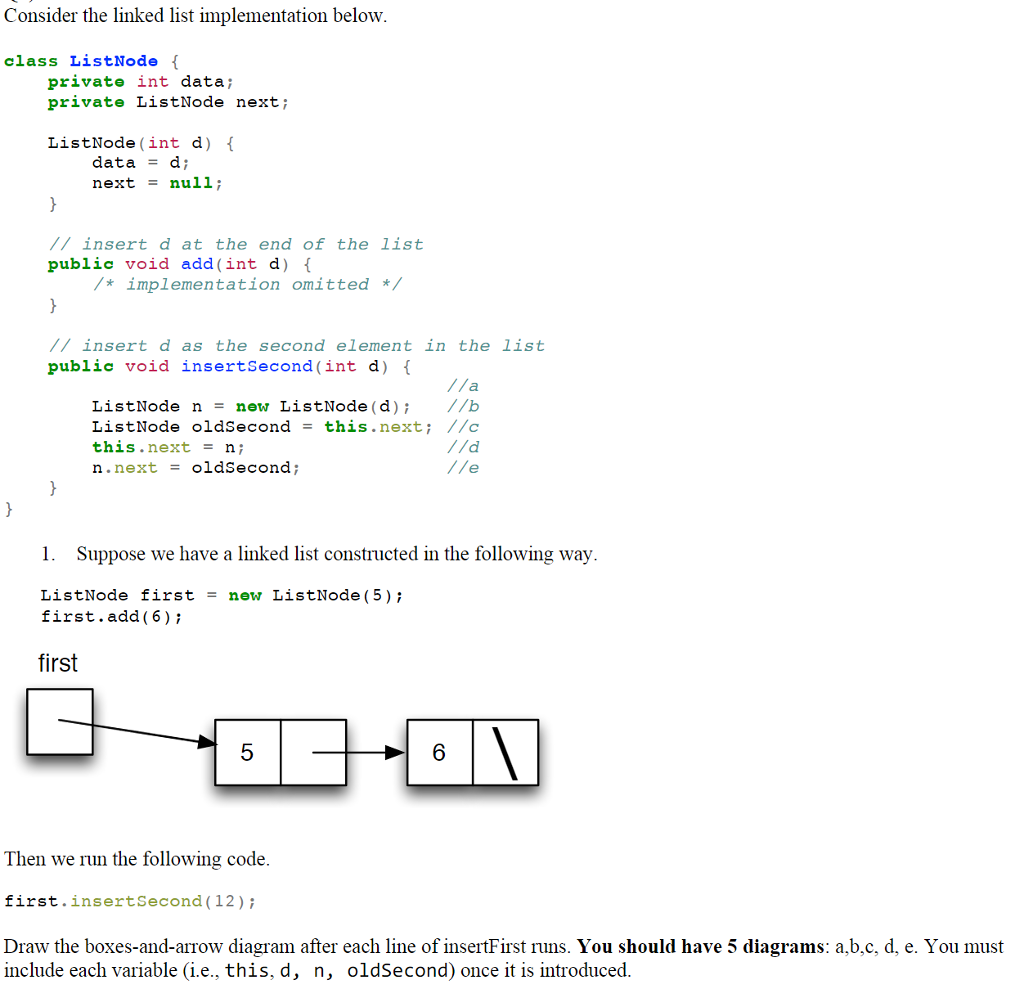
Consider the linked list implementation below class ListNode { private int data; private ListNode next; ListNode (int d) f data = d; next = null; //insert d at the end of the list public void add (int d) *implementation omitted */ /insert d as the second element in the list public void insertSecond (int d) ListNode n= new ListNode (d); //b ListNode oldSecond = this.next; //c this.nextn; n. next = o!asecond ; 1. Suppose we have a linked list constructed in the following way ListNode firstnew ListNode (5) first.add (6) ; first 5 6 Then we run the following code first.insertSecond (12) i Draw the boxes-and-arrow diagram after each line of insertFirst runs. You should have 5 diagrams: a.b.c, d, e. You must include each variable (i.e., this,d, n, oldSecond) once it is introduced
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


