Question: java. Complete the code that is at the bottom. For this problem, assume that MyLinkedList uses a circular doubly-linked list with a dummy head node
java. Complete the code that is at the bottom. For this problem, assume that MyLinkedList uses a circular doubly-linked list with a dummy head node as shown in the following diagrams. Recall that the size data field is declared by the MyAbstractList class and has protected access.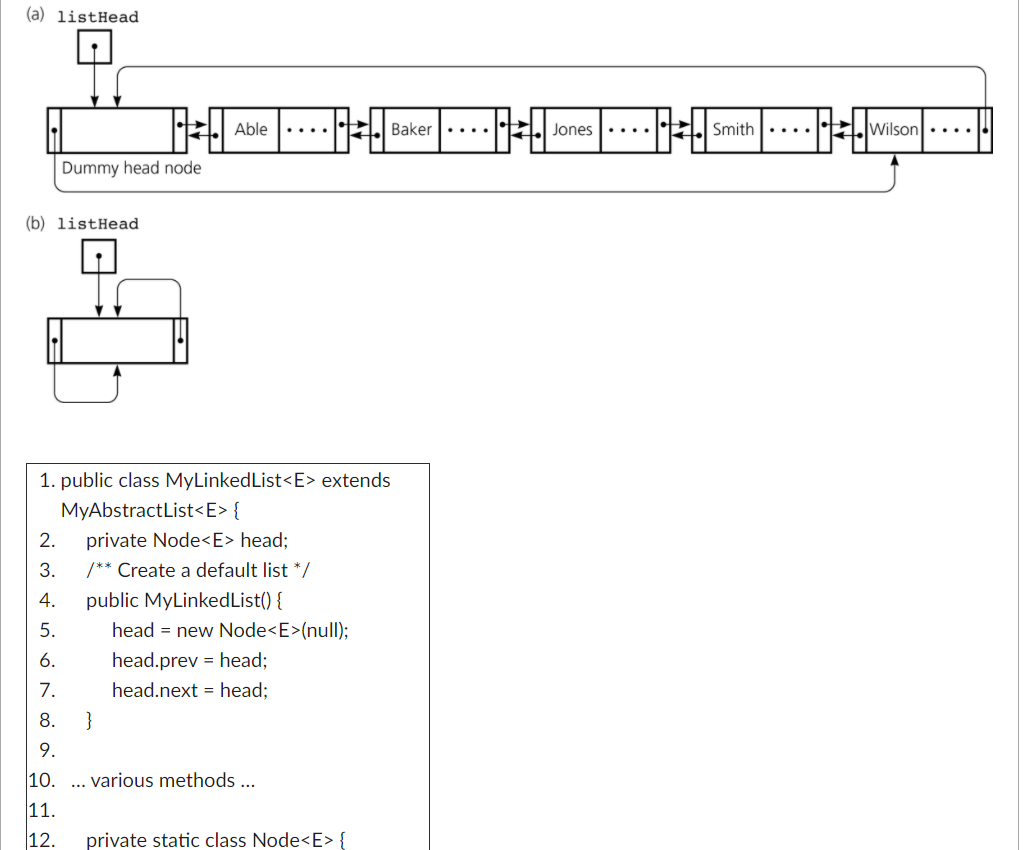
- public class MyLinkedList
extends MyAbstractList { - private Node
head; - /** Create a default list */
- public MyLinkedList() {
- head = new Node
(null); - head.prev = head;
- head.next = head;
- }
- various methods
- private static class Node
{ - E element;
- Node
prev; - Node
next; - public Node(E element) {
- this.element = element;
- }
- }
- }
Complete the implementation of the addNodes method below. The method receives an array of Node objects in the parameter, and then adds all the Node objects from the nodes array to the linked-list.
Your algorithm should require no more than O(n) time.
For instance, consider the list shown in the above diagram, with [Able, Baker, Jones, Smith, Wilson] currently in the list.
You have an array of Nodes as follows:
Node[] nodes = [Tom, Kate, Steve];
Calling addNodes(nodes) will update the current linked-list as [Able, Baker, Jones, Smith, Wilson, Tom, Kate, Steve]
Be clear and concise in your code. You should consider both cases, where the linked-list may or may not be initially empty. Do not forget to update size.
- /** Adds to the linked-list all the Node objects from the nodes array **/
- public void addNodes(Node[] nodes) {
- // YOUR CODE GOES HERE
- }
\\
(a) listHead -:| atve .... 1=sker.... 1-1.1 10.... 1=1/sman.... -.wson. Dummy head node (b) listHead 1. public class MyLinkedList
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


