Question: Java Credit for work: /Main class class Node{ protected String name; protected Node left; protected Node right; protected int x; protected int y; protected int
Java Credit for work:

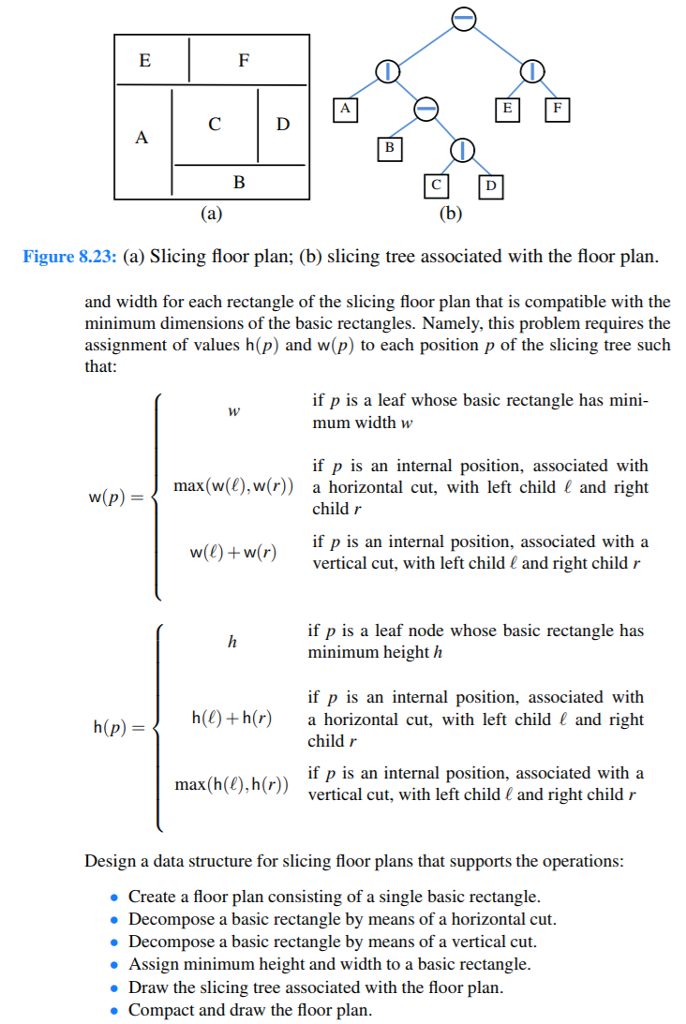
/Main class class Node{ protected String name; protected Node left; protected Node right; protected int x; protected int y; protected int height; protected int width; //Constructor public Node(){ name=""; right=null; left=null; } //Similar constructor with various parameters being passed to them can be //constructed similarly. //Function which checks if the node is a leaf node or not public boolean isLeaf() { if(right==null&&left==null) return true; else return false; } //Function to set the name of the Node public void setName(String o){ name=o; } //Function to set the top left x coordinate of the rectangle public void setX(int i) { x=i; } //Function to set the top left y coordinate of the rectangle public void setY(int i) { y=i; } //Similar function to set the width and height of the rectangle //Function to get Right Child public Node getRight(){ return right; } //Function to get Left Child public Node getLeft(){ return left; } } //Use this type of class to draw rectangles.It stores the address of the rectangle in //a linked list class Rect { protected Rect Next; protected Node Add; //Constructor public Rect() { Next=null; Add=null; } //Constructor public Rect(Node i) { Next=null; Add=i; } //Function to get Address of the Rectangle in the tree public Node getAdd() { return Add; } //Function to get the address of next rectangle and etc. } //Write the applet to draw the rectangles here.A slicing floor plan divides a rectangle with horizontal and vertical sides using horizontal and vertical cuts. (See Figure 8.23a.) A slicing floor plan can be represented by a proper binary tree, called a slicing tree, whose internal nodes represent the cuts, and whose external nodes represent the basic rectangles into which the floor plan is decomposed by the cuts. (See Figure 8.23b.) The com- paction problem for a slicing floor plan is defined as follows. Assume that each basic rectangle of a slicing floor plan is assigned a minimum width w and a min imum height h. The compaction problem is to find the smallest possible height A slicing floor plan divides a rectangle with horizontal and vertical sides using horizontal and vertical cuts. (See Figure 8.23a.) A slicing floor plan can be represented by a proper binary tree, called a slicing tree, whose internal nodes represent the cuts, and whose external nodes represent the basic rectangles into which the floor plan is decomposed by the cuts. (See Figure 8.23b.) The com- paction problem for a slicing floor plan is defined as follows. Assume that each basic rectangle of a slicing floor plan is assigned a minimum width w and a min imum height h. The compaction problem is to find the smallest possible height
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


