Question: Java data structure You must assign the grades for a programming class. Right now the class is studying recursion, and students have been given this


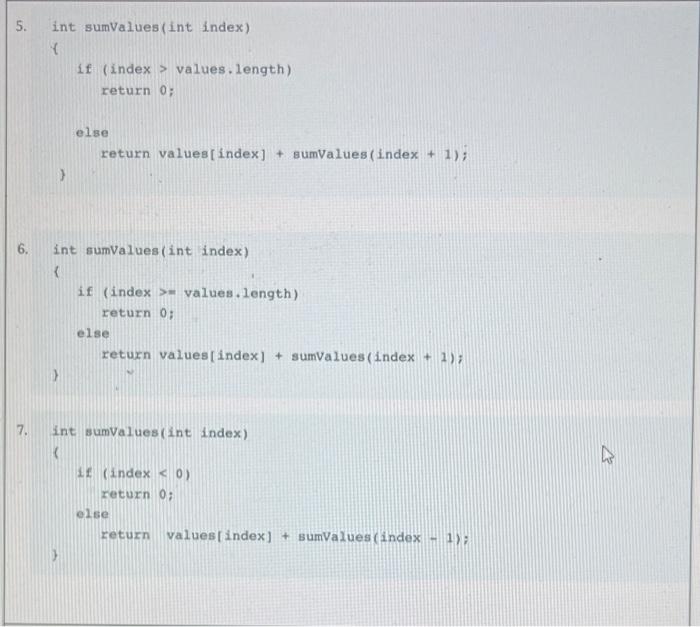
You must assign the grades for a programming class. Right now the class is studying recursion, and students have been given this assignment: Write a recursive method sumvalues that is passed an index into an array values of int (this array is accessible from within the sumvalues method) and returns the sum of the values in the array between the location indicated by index and the end of the array. The argument will be between 0 and values.length inclusive. For example, given this configuration: then sumvalues(4) returns 12 and sumValues(0) returns 34 (the sum of all the values in the array). You have received quite a variety of solutions. Grade the methods below. If the solution is incorrect, explain what the code actually does in lieu of returning the correct result. You can assume the array is "full." You can assume a "friendly" user - the method is invoked with an argument between 0 and values.length. 1. Int sumValues (int index) \{ if (index = = values. length) return 0; else return index + sumvalues (index + i); ) 2. int sumValues (int index) \{ int sum =0; for ( int i= index; i values. length) return 0; else return values [ index ]+ sumvalues ( index +1); ) 6. int sumvalues (int index) if ( index >= values.length) return 0; else return values [ index ]+ sumvalues (index +1 ); 7. Int sumvalues (int index) ( if ( index
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


