Question: Java Introduction to Recursion Assigment Note: Use the test code to check if the code works Test Code: import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.PrintStream; import
Java Introduction to Recursion Assigment


Note: Use the test code to check if the code works
Test Code:
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class RecursionIntroTest {
public static void rowColumn(String source, int offset) {
int row = 1;
int col = 1;
for (int i = 0; i
if (source.charAt(i) == ' ') {
row++;
col = 1;
} else if (source.charAt(i) == '\t')
col += (4 - (col - 1) % 4);
else
col++;
}
System.out.println("Above problem is on line " + row + "
column " + col + " (Assuming tab width of 4)");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws
NoSuchAlgorithmException {
String source = null;
try {
source = new
String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("src" + File.separator +
"RecursionIntro.java")));
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(
"Couldn't find
RecursionIntro.java! Run this from the same Eclipse project as
RecursionIntro.");
return;
}
if (source.matches("(?s).*\\sfor[\\s\\(].*")) {
System.out.println(
"Detected 'for' statement in
your program! Please remove anything that resembles a 'for'.");
System.exit(-1);
}
if (source.matches("(?s).*\\swhile[\\s\\(].*")) {
System.out.println(
"Detected 'while' statement
in your program! Please remove anything that resembles a 'while'.");
System.exit(-1);
}
if (source.matches("(?s).*\\simport\\s.*") ||
source.indexOf("import") == 0) {
System.out.println("Detected 'import'
statement in your program! Please remove any word 'import'.");
System.exit(-1);
}
if
(source.matches("(?s).*\\spublic\\s+static\\s+\\w+[^(]*=.*")
||
source.matches("(?s).*\\spublic\\s+static\\s+\\w+[^(]*;.*")) {
System.out.println("Detected static variable
in your program! Please remove static variables.");
System.exit(-1);
}
for (int dotIndex = source.indexOf('.'); dotIndex != -1;
dotIndex = source.indexOf('.', dotIndex + 1)) {
if
("System.out.println".equals(source.substring(dotIndex - 6, dotIndex +
12))
||
"System.out.println".equals(source.substring(dotIndex - 10, dotIndex + 8))
||
"length".equals(source.substring(dotIndex + 1, dotIndex + 7))
||
Character.isDigit(source.charAt(dotIndex+1))) {
continue;
}
System.out.println("Bad dot! Context: "
+
source.substring(Math.max(0, dotIndex - 20), Math.min(dotIndex + 20,
source.length())));
rowColumn(source, dotIndex);
System.exit(-1);
}
System.out.println("Passed syntax checks!");
System.out.println("If you don't see a score, your
program didn't get to the end!");
PrintStream out = System.out;
MessageDigest md5 = MessageDigest.getInstance("MD5");
int score = 0;
int eduoddScore = 0;
int fibbyScore = 0;
int stGenScore = 0;
int median3Score = 0;
try {
try { // Part 1: eduodd
long[] ns = {0, 27, 987654321, -8443,
11121113, -11, 99999999999L, -987654321, -1016548095, -458096230};
long[] eos = {1, 36, 896745230, -9552,
30002, 0, 88888888888L, -896745230, -107459184, -549187321};
System.out.println("Testing
eduodd...");
for (int i = 0; i
long eo =
RecursionIntro.eduodd(ns[i]);
if (eo != eos[i]) {
System.out.println("Expected eduodd("+ns[i]+") = "+eos[i]+" but got
"+eo);
} else {
eduoddScore++;
}
}
Random r = new Random(123456789);
long[] rando = new long[1000];
for (int i = 0; i
{
rando[i] =
RecursionIntro.eduodd(r.nextInt());
}
byte[] b =
md5.digest(Arrays.toString(rando).getBytes());
byte[] good = {-106, 111, -96, -46, -
125, 4, 30, 41, 69, -39, 87, -114, -123, -119, -12, 22};
if (!Arrays.equals(b, good)) {
System.out.println("Your
eduodd method doesn't always work. Please consult the assignment
carefully.");
if (eduoddScore == 10) {
System.out.println("It looks like you passed the above test cases!
You may want to ask your instructor for help!");
}
} else {
eduoddScore += 20;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
try { // Part 2a: fibby
int[] fibbys = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 6, 8,
8, 11, 11};
System.out.println("Testing fibby...");
for (int i = 0; i
{
long fib =
RecursionIntro.fibby(i);
if (fib != fibbys[i]) {
System.out.println("Expected fibby(" + i + ") = " + fibbys[i] + "
but got " + fib);
} else
fibbyScore++;
}
int[] fibbys2 = new int[10000];
for (int i = 0; i
fibbys2[i] =
RecursionIntro.fibby(i);
}
byte[] b =
md5.digest(Arrays.toString(fibbys2).getBytes());
byte[] good = {-54, -34, -99, -113, -3,
-71, -109, 113, 63, 127, 114, 95, 109, -82, 114, -108};
if (!Arrays.equals(b, good)) {
System.out.println("Your
fibby method doesn't work for some value between 0 and 9999. Please
consult the definition carefully.");
} else {
fibbyScore += 10;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
try { // Part 2b: printsparsetable
System.out.println("Testing
printsparsetable...");
int[] starts = { 1, 1000, 101 };
int[] ends = { 100, 1020, 999 };
byte[][] md5s = { { 58, 46, 104, 125, -
11, -80, -18, 110, -37, -96, 106, 87, -22, 122, 72, 64 },
{ 19, 45, 112, -
113, -33, 77, 114, 123, -71, -95, -38, 101, 59, 57, 45, -54 },
{ -87, 94, 100,
67, -96, 45, -42, -83, -84, 111, -39, 102, -87, -70, -112, -84 } };
for (int i = -2; i
i++) {
ByteArrayOutputStream ba =
new ByteArrayOutputStream();
System.setOut(new
PrintStream(ba));
if (i == -2) {
RecursionIntro.printsparsetable(5, 10);
System.setOut(out);
String expected =
"5 6 6 8 8 11 ";
if
(!Arrays.equals(expected.split("\ ?\ "),
ba.toString().split("\ ?\ "))) {
System.out.println("For printsparsetable(5, 10), expected: " +
expected + " , got: " + ba);
} else {
stGenScore
++;
}
} else if (i == -1) {
RecursionIntro.printsparsetable(13, 20);
System.setOut(out);
String expected =
"13 15 15 18 16 21 20 24 ";
if
(!Arrays.equals(expected.split("\ ?\ "),
ba.toString().split("\ ?\ "))) {
System.out.println("For printsparsetable(13, 20), expected: " +
expected + " , got: " + ba);
} else {
stGenScore
++;
}
} else {
RecursionIntro.printsparsetable(starts[i], ends[i]);
System.setOut(out);
byte[] digest =
md5.digest(Arrays.toString(ba.toString().split("\ ?\ ")).getBytes());
if
(!Arrays.equals(md5s[i], digest)) {
System.out.println(
"Didn't get expected output for printsparsetable(" + starts[i]
+ ", " + ends[i] + ")");
System.out.println("Saw this:");
System.out.println(ba);
System.out.println("MD5 sum of output seen: " +
Arrays.toString(digest));
} else
stGenScore
++;
}
}
ByteArrayOutputStream ba = new
ByteArrayOutputStream();
System.setOut(new PrintStream(ba));
Random r = new Random(918273645);
for (int i = 0; i
int start = r.nextInt(1000);
RecursionIntro.printsparsetable(start, start+r.nextInt(1000)+1);
}
System.setOut(out);
byte[] digest =
md5.digest(Arrays.toString(ba.toString().split("\ ?\ ")).getBytes());
byte[] good = {62, -87, -60, -83, -81,
99, -84, -73, -40, -24, -89, 115, 77, -82, 109, -53};
if (!Arrays.equals(digest, good)) {
System.out.println("Your
printsparsetable method doesn't always work (for starting values up to
1000 and ending values up to 1000 positions away). Please consult the
definition carefully.");
if (stGenScore == 5) {
System.out.println("It looks like you passed the above test cases!
You may want to ask your instructor for help!");
}
} else {
stGenScore += 15;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.setOut(out);
}
try { // Part 3: median3
System.out.println("Testing
median3...");
int[][] a = {{1}, {1, 2}, {3, -10,
100}, {123,234,345}, {100, 50, -1000}, {3, 100, -10}, {1, 200, 30}, {2000,
-1, 300}, {1, 2, -5, 10, 100, 6}, {1, 2, -10, 7, 20, -3, 100, 6}, {1, 2, -
20, -10, 7, 20, -3, 100, 6, 92}};
double[] rets = {1.0, 1.5, 3, 234, 50,
3, 30, 300, 2.5, 6, 1.0};
for (int i = 0; i
double ra =
RecursionIntro.median3(a[i]);
if (ra != rets[i]) {
System.out.println("Expected median3("+Arrays.toString(a[i])+") =
"+rets[i]+" but got "+ra);
} else {
median3Score++;
}
}
Random r = new Random(54321);
double[] rando = new double[2000];
for (int i = 0; i
int[] b = new
int[r.nextInt(100000)+1];
for (int j = 0; j
b.length; j++) {
b[j] =
r.nextInt()/1024;
}
rando[i] =
RecursionIntro.median3(b);
}
byte[] b =
md5.digest(Arrays.toString(rando).getBytes());
byte[] good = {29, 25, 56, -24, -17, -
68, 24, 78, -9, 25, -22, -28, -8, 123, 0, 46};
if (!Arrays.equals(b, good)) {
System.out.println("Your
median3 method doesn't always work (for arrays up to 100,000 elements).
Please consult the definition carefully.");
if (median3Score == 11) {
System.out.println("It looks like you passed the above test cases!
You may want to ask your instructor for help!");
}
} else {
median3Score += 19;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
System.out.println("eduodd: " + eduoddScore +
" / 30");
System.out.println("fibby: " + fibbyScore + "
/ 20");
System.out.println("printsparsetable: " +
stGenScore + " / 20");
System.out.println("median3: "+median3Score+"
/ 30");
score = eduoddScore + fibbyScore + stGenScore
+ median3Score;
System.out.println("Tentative score: " +
score + " / 100");
}
}
}
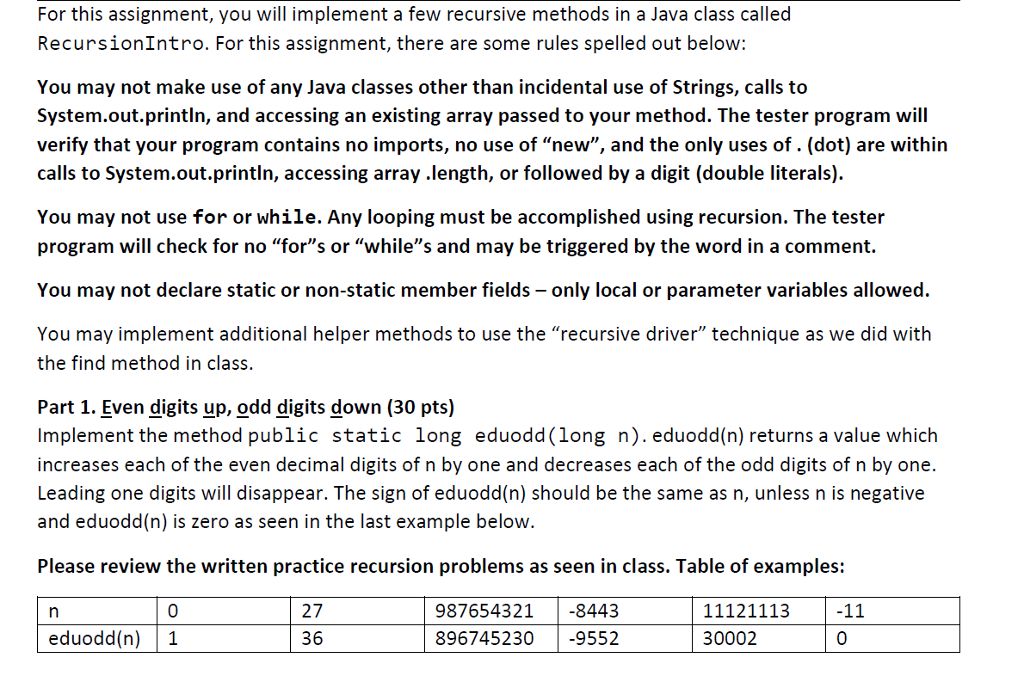
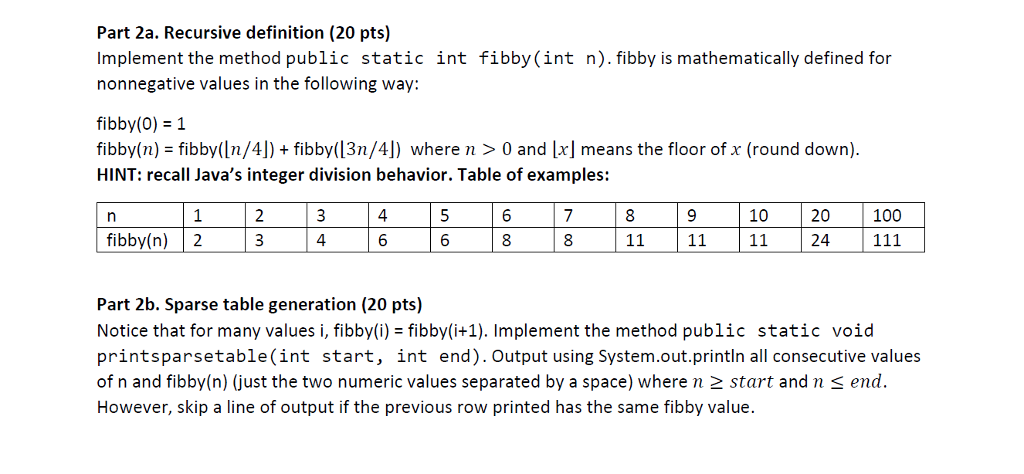
For this assignment, you will implement a few recursive methods in a Java class called RecursionIntro. For this assignment, there are some rules spelled out below: You may not make use of any Java classes other than incidental use of Strings, calls to System.out.println, and accessing an existing array passed to your method. The tester program will verify that your program contains no imports, no use of "new", and the only uses of . (dot) are within calls to System.out.println, accessing array .length, or followed by a digit (double literals). You may not use for or while. Any looping must be accomplished using recursion. The tester program will check for no "for"s or "while"s and may be triggered by the word in a comment. You may not declare static or non-static member fields- only local or parameter variables allowed. You may implement additional helper methods to use the "recursive driver" technique as we did with the find method in class. Part 1. Even digits up, odd digits down (30 pts) Implement the method public static long eduodd(long n). eduodd(n) returns a value which increases each of the even decimal digits of n by one and decreases each of the odd digits of n by one. Leading one digits will disappear. The sign of eduodd(n) should be the same as n, unless n is negative and eduodd(n) is zero as seen in the last example below. Please review the written practice recursion problems as seen in class. Table of examples: 27 36 987654321-8443 896745230 9552 1112111:3 30002 eduodd(n) 1 0 For this assignment, you will implement a few recursive methods in a Java class called RecursionIntro. For this assignment, there are some rules spelled out below: You may not make use of any Java classes other than incidental use of Strings, calls to System.out.println, and accessing an existing array passed to your method. The tester program will verify that your program contains no imports, no use of "new", and the only uses of . (dot) are within calls to System.out.println, accessing array .length, or followed by a digit (double literals). You may not use for or while. Any looping must be accomplished using recursion. The tester program will check for no "for"s or "while"s and may be triggered by the word in a comment. You may not declare static or non-static member fields- only local or parameter variables allowed. You may implement additional helper methods to use the "recursive driver" technique as we did with the find method in class. Part 1. Even digits up, odd digits down (30 pts) Implement the method public static long eduodd(long n). eduodd(n) returns a value which increases each of the even decimal digits of n by one and decreases each of the odd digits of n by one. Leading one digits will disappear. The sign of eduodd(n) should be the same as n, unless n is negative and eduodd(n) is zero as seen in the last example below. Please review the written practice recursion problems as seen in class. Table of examples: 27 36 987654321-8443 896745230 9552 1112111:3 30002 eduodd(n) 1 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


