Question: Java: Previous Code: import javax.swing.JOptionPane; public class CounterTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // Display menu of choices with corresponding integer values CounterConsoleMenu
Java:
![main(String[] args) { // Display menu of choices with corresponding integer values](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/09/66dc3611b654c_79366dc36115357c.jpg)
Previous Code:
import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class CounterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Display menu of choices with corresponding integer values CounterConsoleMenu console = new CounterConsoleMenu();
console.displayChoices();
int choice = 0;
System.out.println(); console.displayCountValue();
// Allow user to increment, decrement, reset, or quit while (choice != 4) {
choice = console.getInput(); if (choice == 1) { console.incrementCounter(); } else if (choice == 2) { console.decrementCounter(); } else if (choice == 3) { console.resetCounter(); }
console.displayCountValue();
}
}
} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- public class CounterConsoleMenu {
private Counter counter;
// Default constructor: no arguments public CounterConsoleMenu() {
counter = new Counter();
}
// displays a menu of options with corresponding integer values public void displayChoices() {
System.out.println("Increment: 1"); System.out.println("Decrement: 2"); System.out.println("Reset: 3"); System.out.println("Quit: 4");
}
// returns integer value entered
public int getInput() {
int value = Input.getInt("What would you like to do? "); return value;
}
// displays value of counter
public void displayCountValue() {
System.out.println("Count: " + counter.getCountValue());
}
// increments value of counter by 1
public void incrementCounter() {
counter.increment();
}
// decrements value of counter by 1
public void decrementCounter() {
counter.decrement();
}
// resets value of counter to 0 public void resetCounter() {
counter.reset();
}
}public class CounterConsoleMenu {
private Counter counter;
// Default constructor: no arguments public CounterConsoleMenu() {
counter = new Counter();
}
// displays a menu of options with corresponding integer values public void displayChoices() {
System.out.println("Increment: 1"); System.out.println("Decrement: 2"); System.out.println("Reset: 3"); System.out.println("Quit: 4");
}
// returns integer value entered
public int getInput() {
int value = Input.getInt("What would you like to do? "); return value;
}
// displays value of counter
public void displayCountValue() {
System.out.println("Count: " + counter.getCountValue());
}
// increments value of counter by 1
public void incrementCounter() {
counter.increment();
}
// decrements value of counter by 1
public void decrementCounter() {
counter.decrement();
}
// resets value of counter to 0 public void resetCounter() {
counter.reset();
}
} -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Input { public static byte getByte( String s ) { String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( s ); return Byte.parseByte( input ); }
public static short getShort( String s ) { String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( s ); return Short.parseShort( input ); }
public static int getInt( String s ) { String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( s ); return Integer.parseInt( input ); }
public static long getLong( String s ) { String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( s ); return Long.parseLong( input ); }
public static float getFloat( String s ) { String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( s ); return Float.parseFloat( input ); }
public static double getDouble( String s ) { String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( s ); return Double.parseDouble( input ); }
public static boolean getBoolean( String s ) { String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( s ); return Boolean.parseBoolean( input ); }
public static char getChar( String s ) { String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( s ); return input.charAt(0); }
public static String getString( String s ) { String input = JOptionPane.showInputDialog( s ); return input; }
}
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- public class Counter {
private int count;
// Default constructor: no arguments public Counter() {
count = 0;
}
// returns value of count
public int getCountValue() {
return count;
}
// increments count by 1 public void increment() {
count++;
}
//decrements count by 1
public void decrement() {
count--;
}
// resets count to 0
public void reset() {
count = 0;
}
}
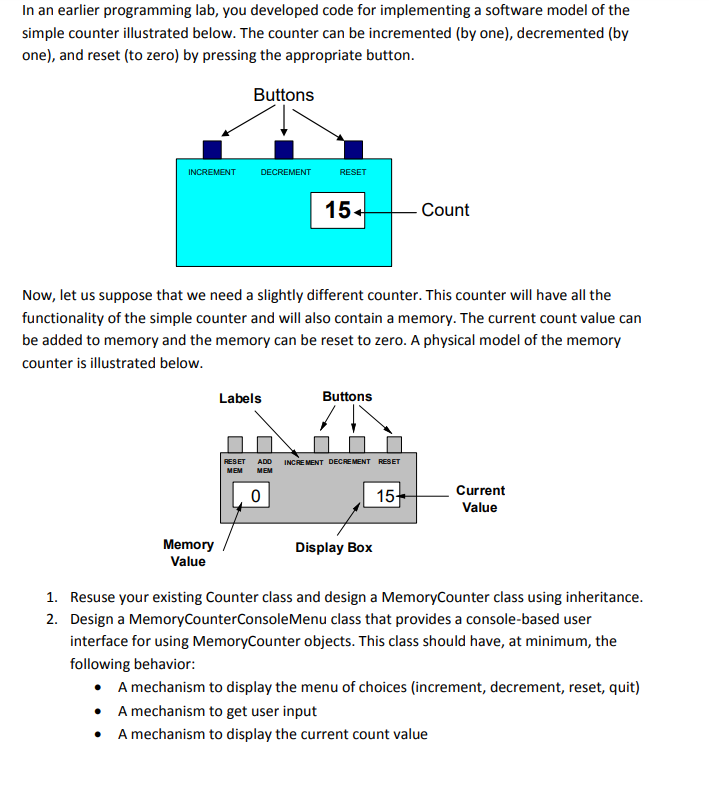
In an earlier programming lab, you developed code for implementing a software model of the simple counter illustrated below. The counter can be incremented (by one), decremented (by one), and reset (to zero) by pressing the appropriate button Buttons INCREMENT DECREMENT RESET 15 Count Now, let us suppose that we need a slightly different counter. This counter will have all the functionality of the simple counter and will also contain a memory. The current count value can be added to memory and the memory can be reset to zero. A physical model of the memory counter is illustrated below Labels Buttons ADD INCRE MENT DECREMENT Current Value 15 Memory Value Display Box Resuse your existing Counter class and design a MemoryCounter class using inheritance Design a MemoryCounterConsoleMenu class that provides a console-based user interface for using MemoryCounter objects. This class should have, at minimum, the following behavior 1. 2. A mechanism to display the menu of choices (increment, decrement, reset, quit) A mechanism to get user input A mechanism to display the current count value A mechanism to increment, decrement, and reset the current count A mechanism to display the memory count value A mechanism to add to the memory count value and reset it 3. Develop a UML class diagram illustrating the relationship between the MemoryCounter, Counter, and MemoryCounterConsoleMenu classes and show all attributes, methods, and types Implement the code for all classes and develop a program called MemoryCounterTest to test the functionality of the design solution. 4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


