Question: Java Program for the following question: Source Code is provided You must implement the methods specified below according to the specifications below. You may chose
Java Program for the following question: Source Code is provided
You must implement the methods specified below according to the specifications below. You may chose to use these existing methods in the source code; however, you cannot rely on the existing methods as a reason your code does not work. You can also create your own helper methods.

************************************
Source Code:
package LabExam1;
import java.util.*;
class Node{
private char letter;
private Node next, prev;
public Node(char c){
letter = c;
next = prev = null;
}
public char getLetter(){
return letter;
}
public Node getNext(){
return next;
}
public void setNext(Node n){
next = n;
}
public Node getPrev(){
return prev;
}
public void setPrev(Node p){
prev = p;
}
}
public class TemplateLabExam1 {
Node head, tail;
public TemplateLabExam1(){
head = tail = null;
}
public boolean isPalindrome(){
if(head == tail) return true;
else{
Node currB = head;
Node currE = tail;
while(currB!=null && currE!= null){
if (currB.getLetter() ==
currE.getLetter()){
currB = currB.getNext();
currE = currE.getPrev();
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
////////////////
public void deleteLetter(char c){
if(head ==null) return;//empty linked list
Node curr = head;
while (curr!=null){
if(curr.getLetter() == c){
if(head == tail )
head = tail = null;
else if(curr == head){
head = head.getNext();
head.setPrev(null);
}
else if(curr == tail){
tail = tail.getPrev();
tail.setNext(null);
}
//internal node
else if(curr.getPrev()!=null &&
curr.getNext()!=null){
curr.getPrev().setNext(curr.getNext());
curr.getNext().setPrev(curr.getPrev());
}
}
curr = curr.getNext();
}
}
public void removeFirstLast(){
if(head == tail||head.getNext()==tail)
head = tail = null;
else{
head = head.getNext();
tail = tail.getPrev();
head.getPrev().setNext(null);
tail.getNext().setPrev(null);
head.setPrev(null);
tail.setNext(null);
}
}
public void makePallindrome(){//from tail
if(tail == null || tail.getPrev() == null) return;
Node curr = tail.getPrev();
while(curr!=null){
this.insert2(curr.getLetter());
curr = curr.getPrev();
}
}
public boolean letterPresent(char l){
boolean present = false;
Node curr = head;
while(curr!=null){
if(curr.getLetter() == l){
present = true;
break;
}
curr = curr.getNext();
}
return present;
}
////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
////////////////
public String concatinateBackward(){
Node curr = tail;
String backward="";
while(curr!=null){
backward = backward+curr.getLetter();
curr = curr.getPrev();
}
return backward;
}
public void insert(char c){//prepend
Node nd = new Node(c);
nd.setNext(head);
if(head != null)
head.setPrev(nd);
else
tail = nd;
head = nd;
}
public void insert2(char c){//append
Node nd = new Node(c);
nd.setPrev(tail);
if(tail != null)
tail.setNext(nd);
else
head = nd;
tail = nd;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TemplateLabExam1 myList = new TemplateLabExam1();
myList.insert('c');
myList.insert('b');
myList.insert('c');
myList.insert('c');
myList.insert('d');
myList.insert('e');
System.out.println("The list read from tail to
head:"+myList.concatinateBackward());
}
}
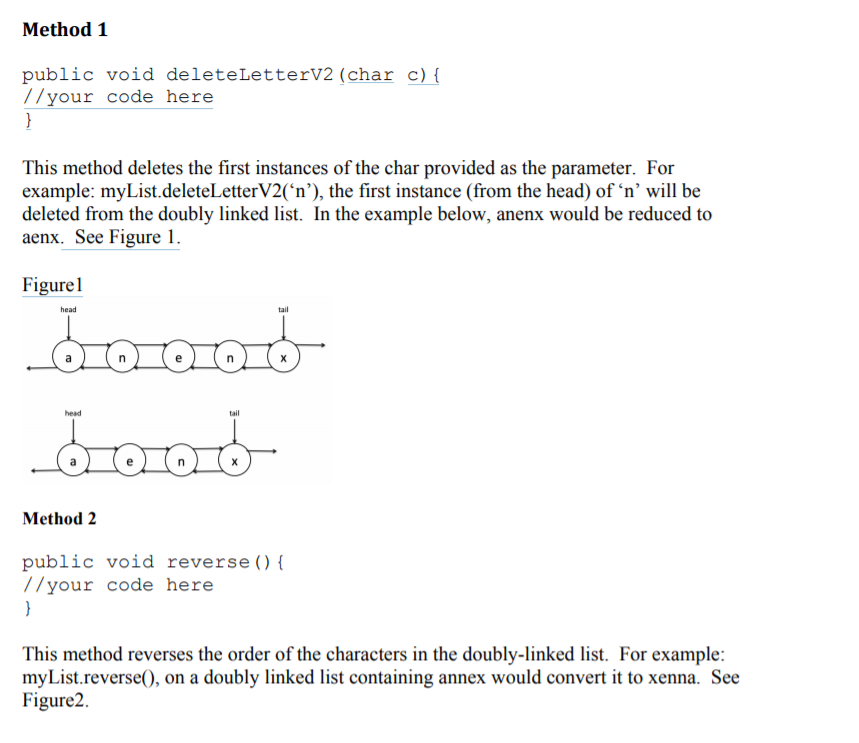
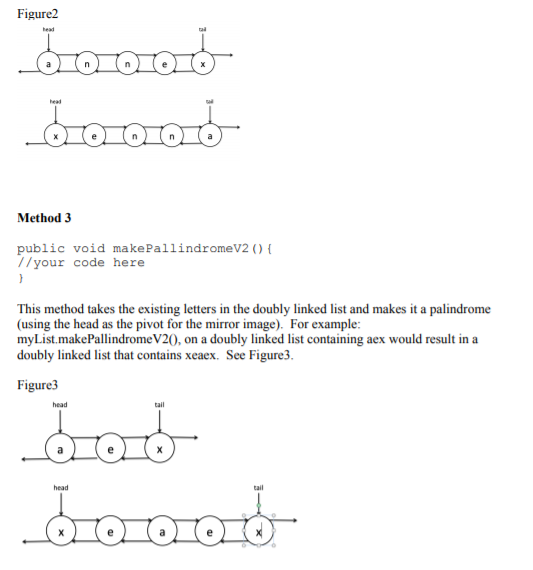
Method 1 public void deleteLetterV2 (char c) //your code here This method deletes the first instances of the char provided as the parameter. For example: myList.deleteLetterV2('n'), the first instance (from the head) of 'n' will be deleted from the doubly linked list. In the example below, anenx would be reduced to aenx, See Figure 1. Figurel tail Method 2 public void reverse ) //your code here This method reverses the order of the characters in the doubly-linked list. For example: myList.reverse), on a doubly linked list containing annex would convert it to xenna. See Figure2. Figure2 Method 3 public void makePallindromeV2 (O //your code here This method takes the existing letters in the doubly linked list and makes it a palindrome (using the head as the pivot for the mirror image). For example myList.makePallindromeV20, on a doubly linked list containing aex would result in a doubly linked list that contains xeaex. See Figure3. Figure3 head head tail Method 1 public void deleteLetterV2 (char c) //your code here This method deletes the first instances of the char provided as the parameter. For example: myList.deleteLetterV2('n'), the first instance (from the head) of 'n' will be deleted from the doubly linked list. In the example below, anenx would be reduced to aenx, See Figure 1. Figurel tail Method 2 public void reverse ) //your code here This method reverses the order of the characters in the doubly-linked list. For example: myList.reverse), on a doubly linked list containing annex would convert it to xenna. See Figure2. Figure2 Method 3 public void makePallindromeV2 (O //your code here This method takes the existing letters in the doubly linked list and makes it a palindrome (using the head as the pivot for the mirror image). For example myList.makePallindromeV20, on a doubly linked list containing aex would result in a doubly linked list that contains xeaex. See Figure3. Figure3 head head tail
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


