Question: JAVA PROGRAM. PLEASE USE ECLIPSE Create a class RecursiveTree that extends JPanel and implements ActionListener Create a class TestRecursiveTree RecursiveTree has an instance variable: order:
JAVA PROGRAM. PLEASE USE ECLIPSE
Create a class RecursiveTree that extends JPanel and implements ActionListener
Create a class TestRecursiveTree
RecursiveTree has an instance variable: order: int
Instance variables for the GUI components must also be written
The constructor must have one argument that assigns the instance variable order. The GUI setup should be done in the constructor of the class. Each button is of size 180 X 30 pixels. The window size is 300 X 330 pixels. Handle only button click events.
Generate getter/setter and toString() for order
Write the recursive method to create the tree with the following signature:
+drawTree(g:Graphics, order:int, x:double, y:double, branchAngle:double, branchLength:double): void
Implement the method as follows. Use the Math class for the mathematical functions:
Compute the change in the x-coordinate and y-coordinate using the following formulae:
cx = x + cos(branchAngle) * branchLength //cx should be a double
cy = y - sin(branchAngle) * branchLength //cy should be a double
//The line should be drawn before the condition for the base case is tested because lines of 0 to order //must appear in the final graphic, unlike in Recursive Snowflake where only the lines of order must //appear in the final graphic
Draw the line from coordinates (x,y) to (cx, cy) //cast the coordinates to int
Write the base case. The base case is reached when order is equal to zero. The base case requires only a return statement.
Convert 35 degrees angle to radians and assign to variable changeBranchAngle:double
Assign 0.569 to variable changeBranchLength:double
The method calls itself recursively to draw additional branches as follows:
//Adds changeBranchAngle to branchAngle in order to draw the left branch
drawTree(g, order-1, cx, cy, branchAngle + changeBranchAngle, branchLength * changeBranchLength);
//Subtracts changeBranchAngle from branchAngle in order to draw the right branch
drawTree(g, order-1, cx, cy, branchAngle - changeBranchAngle, branchLength * changeBranchLength);
In the method paintComponent, add the following code after the call to super.paintComponent(g);
//This code will set the thickness and color of the lines of the tree
//Cast the Graphics object g to Graphics2D (subclass of Graphics). This is required in order to call the //setStroke method which is implemented in the subclass.
Graphics2D g2D = (Graphics2D) g;
//Create a solid line of thickness 2.5
g2D.setStroke(new BasicStroke((float) 2.5));
//Set the color of the line to blue
g2D.setColor(Color.BLUE);
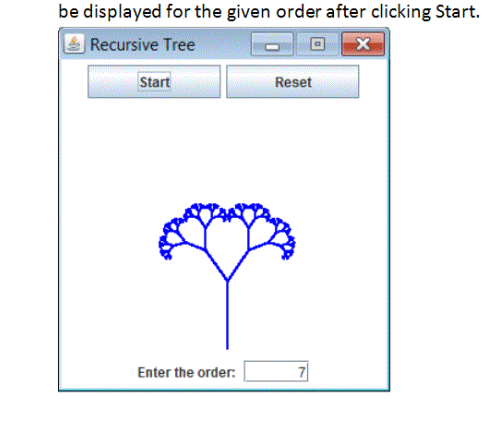
At the end of the method paintComponent, call the method drawTree to draw the initial line beginning at coordinates (150, 220) with branch angle PI/2 and branch length60
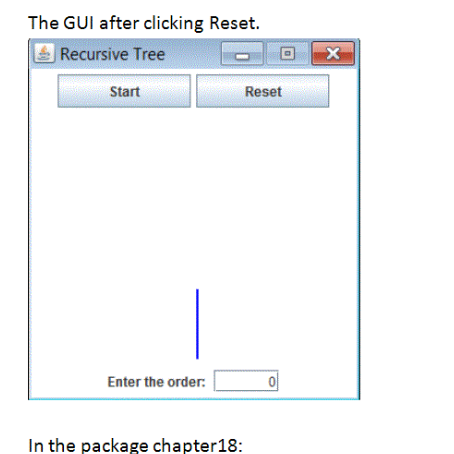
In the method actionPerformed, handle the button clicks. On Start, assign the value from the text field to order. Assign false to wait. On reset, assign 0 to order. Assign false to wait. Set the value of order to the text field. Focus should be given to the text field using the following code: textField.grabFocus(). This allows the user to begin typing in the text field without first having to click in it.
In the class TestRecursiveTree, create an object of RecursiveTree with order 0
Recursive Methods:
In the package chapter18, create a class RecursiveMethods with the following instance variables/constructor/methods. Also create a tester TestRecursiveMethods to test the methods.
computeArray (an array of int), n (an int) and order (an int).
A no-args constructor that creates an array of 10 integers and populates it with random values in the range (0-100), 100 not inclusive. Assigns random values to n and order in the range (0-10), 10 not inclusive.
Getters/setters and toString() for the instance variables.
A recursive method fibonacci that takes an int value n and returns the nth number in the Fibonacci sequence. The Fibonacci sequence is 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55 89 144 .
If n=0, the method returns 0. If n=1, it returns 1. If n=2, it returns 1. If n=3, it returns 2. If n=4, it returns 3 and so on. In general:
If n
If n = 1, the method returns: 1
If n = 2 or greater, the method returns: The sum of the previous two integers
Use the following recursive formula where f(n) represents the recursive method:
f(n) = 0 if n
f(n) = 1 if n = 1
f(n) = f(n 1) + f(n 2) if n > 1
A method fibonacciHelper that prints n. Calls Fibonacci, passes n and prints the returned integer value.
A recursive method goldenRatio that takes an integer and computes and returns an approximation to the golden ratio using the following recursive formula: (Read the explanation of the golden ratio below)
f(n) = 1 if n = 0
f(n) = 1 + 1 / f(n-1) if n > 0
f(n) = -1 if n
The golden ratio is the ratio of two quantities such that their ratio is equal to the ratio of their sum to the larger of the two quantities. For example, if a line is divided into two parts and the longer part x divided by the shorter part y is equal to the sum of x + y divided by x, then the two parts are said to be in a golden ratio. The golden ratio, also known as the divine proportion, golden mean, or golden section, is a number often encountered when taking the ratios of distances in simple geometric figures. It isclosely related to the Fibonacci sequence. Note the result of dividing a Fibonacci number by the one immediately preceding it, for example 3/2=1.5. Then note the result of 5/3=1.667. Then 8/5=1.6. Then 13/8= 1.625. Then 21/13= 1.615384. If we keep going on the result will get closer and closer in value to the golden ratio which is approximately 1.6180339... The golden ratio appears in some patterns in nature, including the spiral arrangement of leaves and other plant parts and is used in art, architecture and other areas.
A method goldenRatioHelper that prints n. Calls goldenRatio, passes n and prints the return value. The greater the value of n, closer the return value to the golden ratio.
A recursive method decimalToBinary that takes a positive integer d (in decimal) and prints out its binary representation. For example, if the integer is 5, it prints 101. Use the following algorithm: Repeatedly divide the integer by 2 and read the remainders backwards until a quotient of 1 is reached. Use recursion to print the bits in the correct order.
Implement the following steps.
If d==0, print 0 and return.
Else if d==1, print 1 and return.
Else: Call decimalToBinary and pass d/2.
Print d % 2.
A method decimalToBinaryHelper that prints n. Calls decimalToBinary and passes n.
/** Method: search
* Recursively searches the array for an integer
* @param array to be searched
* @param length of the array
* @param integer to be found
* @return true if integer is found, false otherwise
*/
public boolean search(int [] a, int n, int key){
//Implement the method.
}
A method +searchHelper():void that prints computeArray. The instance variable order is the key to be searched. The method prints the value of order. Calls search, passes computeArray, the length of computeArray and order. It prints the returned boolean value.
Create an object of class RecursiveMethods and call the helpers in the tester.
screenshots of the RecursiveSnow and RecursiveTree programs for order 9, and all console output of Recursive Methods.
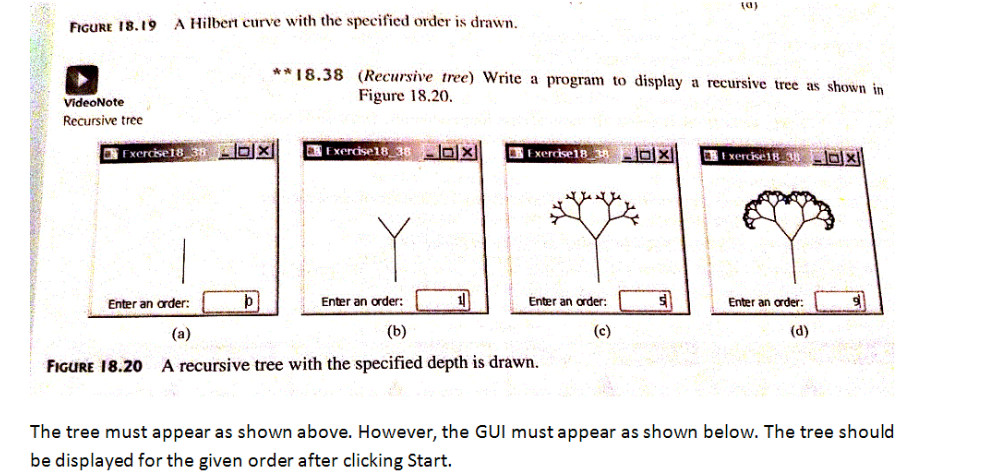
a) FIGURE 18.19 A Hilbert curve with the specified order is drawn. ** 18.38 (Recursive tree) Write a program to display a recursive tree as shown in Figure 18.20. VideoNote Recursive tree Exerdise18 35 Exercise18 38 Exerdse18 38 t xerdse18 38 Enter an arder: Enter an order: Enter an order: Enter an arder FIGURE 18.20 A recursive tree with the specified depth is drawn. The tree must appear as shown above. However, the GUl must appear as shown below. The tree should be displayed for the given order after clicking Start. a) FIGURE 18.19 A Hilbert curve with the specified order is drawn. ** 18.38 (Recursive tree) Write a program to display a recursive tree as shown in Figure 18.20. VideoNote Recursive tree Exerdise18 35 Exercise18 38 Exerdse18 38 t xerdse18 38 Enter an arder: Enter an order: Enter an order: Enter an arder FIGURE 18.20 A recursive tree with the specified depth is drawn. The tree must appear as shown above. However, the GUl must appear as shown below. The tree should be displayed for the given order after clicking Start
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


