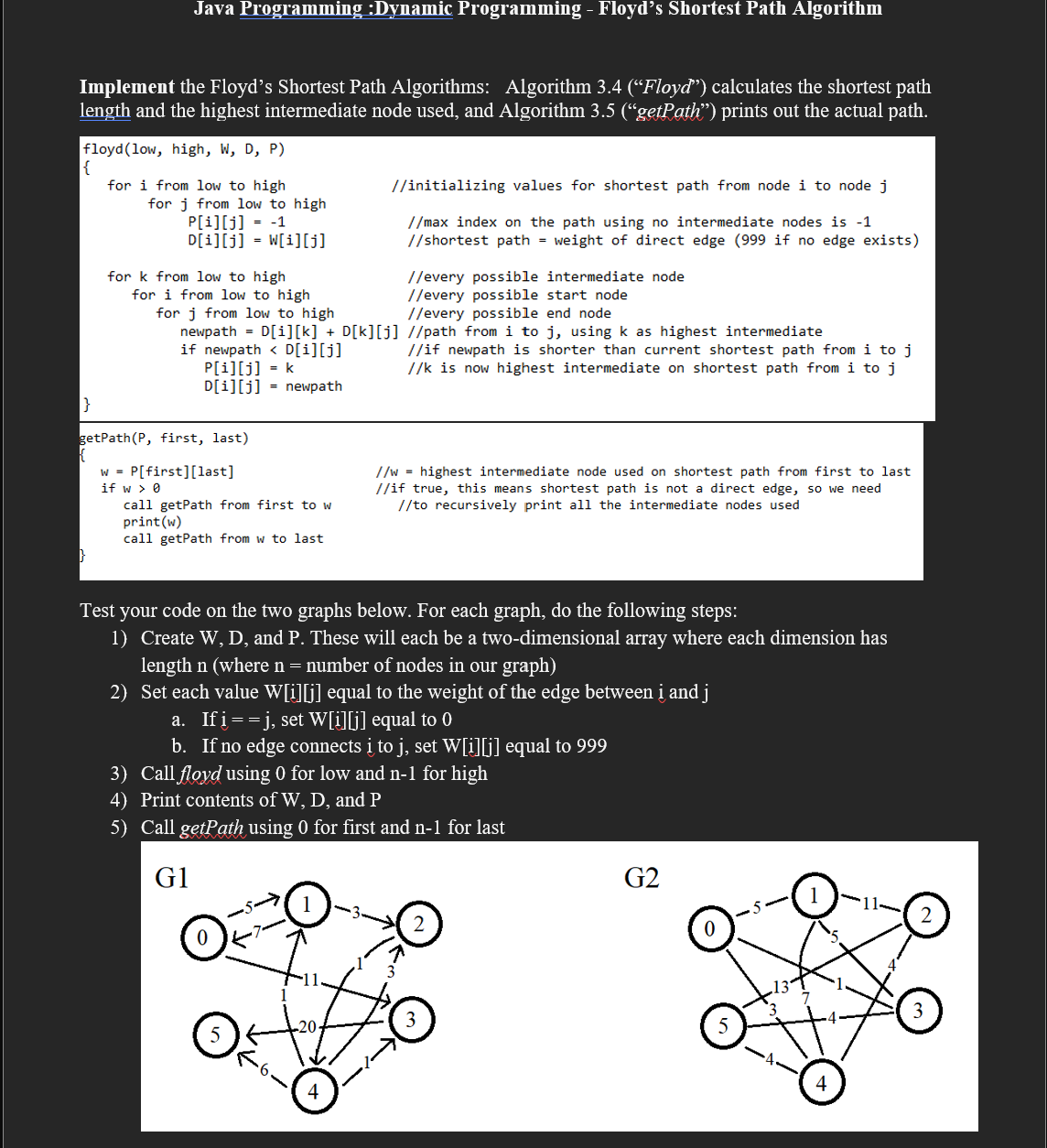
Question: Java Programming :Dynamic Programming - Floyd's Shortest Path Algorithm Implement the Floyd's Shortest Path Algorithms: Algorithm 3 . 4 ( Floyd ) calculates
Java Programming :Dynamic Programming Floyd's Shortest Path Algorithm
Implement the Floyd's Shortest Path Algorithms: Algorithm Floyd calculates the shortest path length and the highest intermediate node used, and Algorithm getPath prints out the actual path.
floydlow high, W D P
for i from low to high initializing values for shortest path from node i to node j
for j from low to high
Pijmax index on the path using no intermediate nodes is
Dij Wijshortest path weight of direct edge if no edge exists
for k from low to high every possible intermediate node
for i from low to high every possible start node
for j from low to high every possible end node
newpath Dik Dkjpath from i to j using k as highest intermediate
if newpath Dijif newpath is shorter than current shortest path from i to j
Pij k k is now highest intermediate on shortest path from i to j
Dij newpath
getPathP first, last
w Pfirstlast
if w
call getPath from first to w
printw
call getPath from w to last
Test your code on the two graphs below. For each graph, do the following steps:
Create W D and P These will each be a twodimensional array where each dimension has length n where mathrmn number of nodes in our graph
Set each value Wij equal to the weight of the edge between i and j
a If ij set Wij equal to
b If no edge connects i to j set Wij equal to
Call floyd using for low and mathrmn for high
Print contents of W D and P
Call getPath using for first and n for last
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


