Question: Java Programming Question 2 0.1 pts In an Observe implementation, we want loose coupling and not to require a Subject recompile for each additional Observer
Java Programming
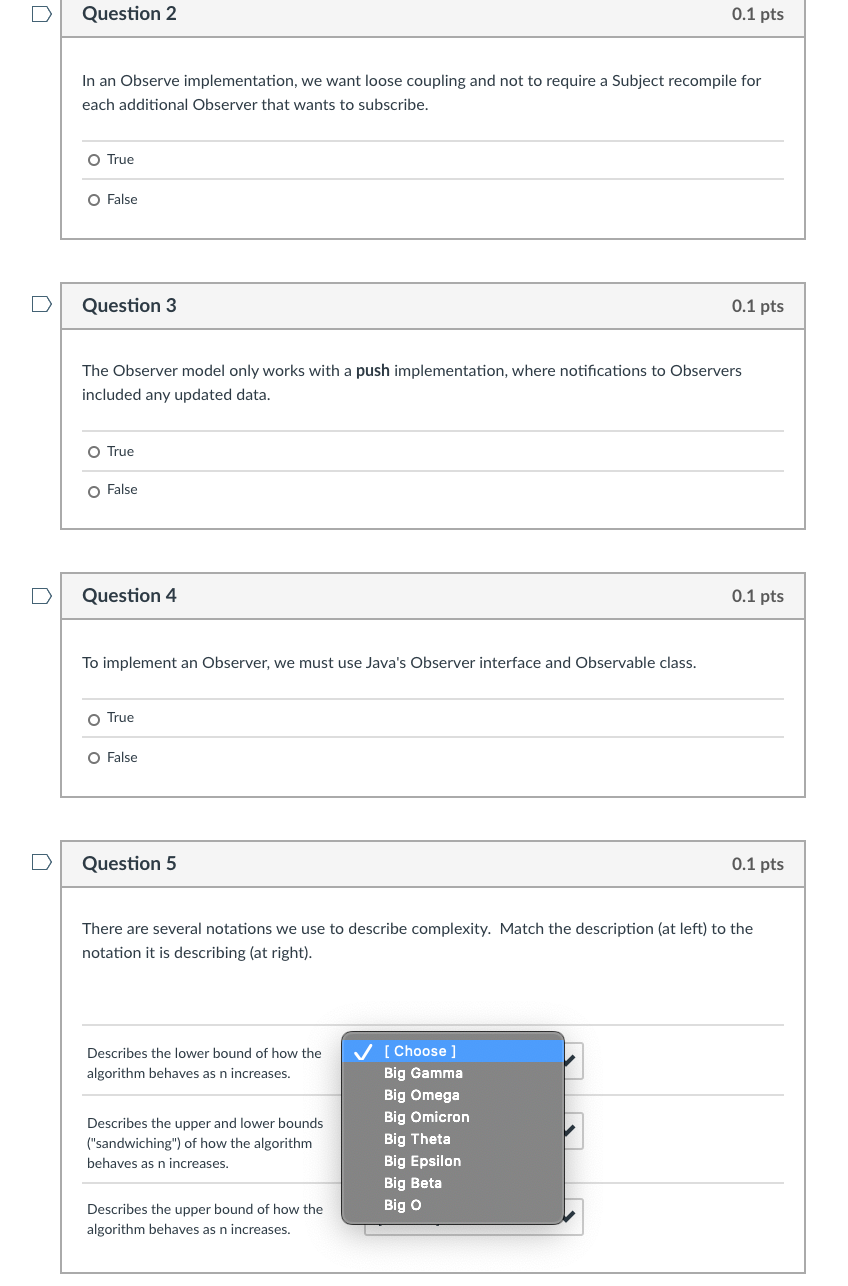
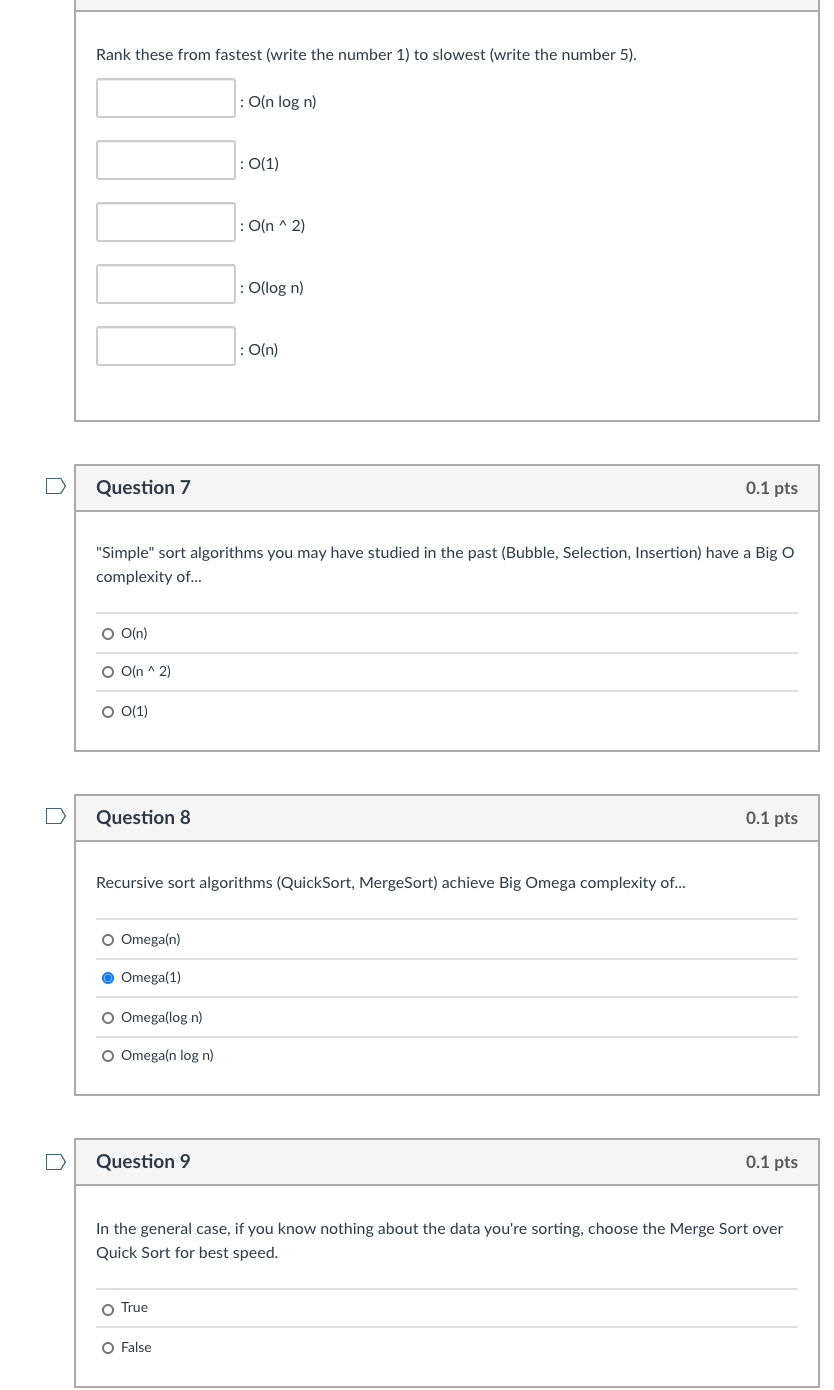

Question 2 0.1 pts In an Observe implementation, we want loose coupling and not to require a Subject recompile for each additional Observer that wants to subscribe. O True O False Question 3 0.1 pts The Observer model only works with a push implementation, where notifications to Observers included any updated data. O True False Question 4 0.1 pts To implement an Observer, we must use Java's Observer interface and Observable class. O True O False Question 5 0.1 pts There are several notations we use to describe complexity. Match the description (at left) to the notation it is describing (at right). Describes the lower bound of how the algorithm behaves as n increases. Describes the upper and lower bounds ("sandwiching") of how the algorithm behaves as n increases. [Choose ] Big Gamma Big Omega Big Omicron Big Theta Big Epsilon Big Beta Big O Describes the upper bound of how the algorithm behaves as n increases. Rank these from fastest (write the number 1) to slowest (write the number 5). : O(n log n) : 0(1) On * 2) Odlog n) O(n) n Question 7 0.1 pts "Simple" sort algorithms you may have studied in the past (Bubble, Selection, Insertion) have a Big O complexity of... O O(n) O O(n^2) O 0(1) Question 8 0.1 pts Recursive sort algorithms (QuickSort, MergeSort) achieve Big Omega complexity of... o Omega(n) Omega(1) o Omega(log n) Omegan log n) Question 9 0.1 pts In the general case, if you know nothing about the data you're sorting, choose the Merge Sort over Quick Sort for best speed. o True O False n Question 10 0.1 pts Which of the recursive sort algorithms has the lowest space complexity? O QuickSort O Merge Sort
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


