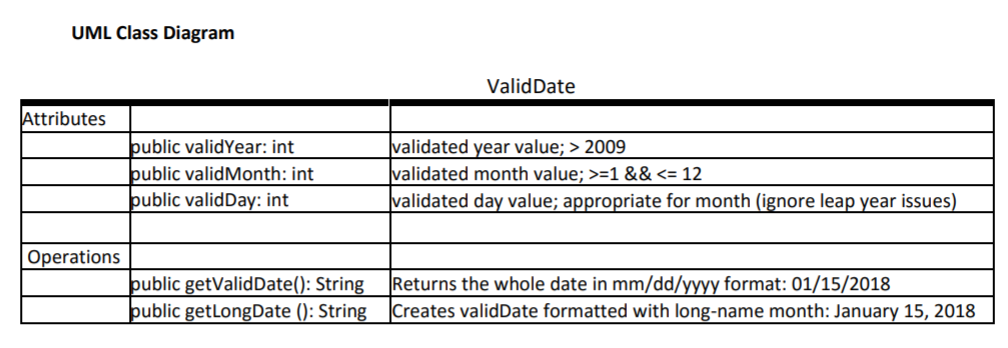
Question: JAVA Provided code: ValidDate public class ValidDate { public int validYear; public int validMonth; public int validDay; public ValidDate(String date) throws InvalidDateException { String dateArray[]

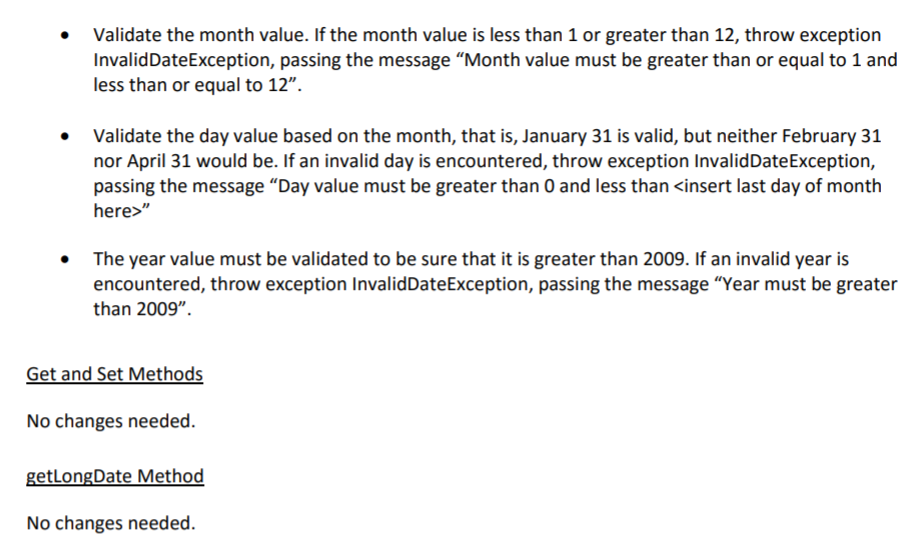
![String dateArray[] = date.split("/"); validYear = Integer.parseInt(dateArray[0]); if(validYear 12) { throw new](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.experts.images/questions/2024/09/66f303172a2f7_07066f303168c9b0.jpg)
JAVA
Provided code:
ValidDate
public class ValidDate { public int validYear; public int validMonth; public int validDay; public ValidDate(String date) throws InvalidDateException { String dateArray[] = date.split("/"); validYear = Integer.parseInt(dateArray[0]);
if(validYear 12) { throw new InvalidDateException("Month value must be greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 12"); } validDay = Integer.parseInt(dateArray[2]); if(validMonth == 1 || validMonth == 3 || validMonth == 5 || validMonth == 7 || validMonth == 8 || validMonth == 10 || validMonth == 12) { if(validDay 31)
throw new InvalidDateException("Day value must be greater than 0 and less than 32"); } else if(validMonth == 4 || validMonth == 6 || validMonth == 9 || validMonth == 11) { if(validDay 30)
throw new InvalidDateException("Day value must be greater than 0 and less than 31"); } else if(validMonth == 2) { if(validDay 28)
throw new InvalidDateException("Day value must be greater than 0 and less than or equal to 29"); } }
public final void setValidYear(int year) { validYear = year; } public final void setValidMonth(int month) { validMonth = month; } public final void setValidDay(int day) { validDay = day; } public final int getValidYear() { return validYear; } public final int getValidMonth() { return validMonth; } public final int getValidDay() { return validDay; } public final String getLongDate() { StringBuilder one = new StringBuilder(); String month = " "; switch(getValidMonth()) { case 1 : month = "January"; break; case 2 : month = "February"; break; case 3 : month = "March"; break; case 4 : month = "April"; break; case 5 : month = "May"; break; case 6 : month = "June"; break; case 7 : month = "July"; break; case 8 : month = "August"; break; case 9 : month = "September"; break; case 10 : month = "October"; break; case 11 : month = "November"; break; case 12 : month = "December"; break; } one.append(String.format("%s %d, %d",month,getValidDay(),getValidYear())); return one.toString(); } public final String getValidDate() { String date = String.format("%d/%d/%d", getValidMonth(), getValidDay(),getValidYear()); return date; }
}
InvalidDateException
public class InvalidDateException extends Exception { // The following constructor accepts a message as the only input parameter. This message will be displayed back to the user. public InvalidDateException( String message ) { super( message ); } // end one-parm constructor public InvalidDateException( String message, Throwable cause ) { super( message, cause ); } // end two-parm constuctor } // end InvalidDateException
DateConversion
// This is the test harness to use to validate/test the ValidDate class
import java.util.Scanner; // import Scanner class for retrieving user input
public class DateConversion {
public static void main (String [] args) { Scanner keyboard = new Scanner(System.in); // instantiate new object of Scanner class char answer = 'Y'; // declare & initialize variable to hold use response // assume starting point of "Yes"
while (Character.toUpperCase( answer ) == 'Y') // Test user response to continuation prompt { System.out.print("Enter a date in yyyy/mm/dd format: "); String offeredDate = keyboard.nextLine( ); // Accept & store user input
try { System.out.printf( "%nYou entered: %s", offeredDate ); // 'Mirror' input to user ValidDate inDate = new ValidDate ( offeredDate ); // Attempt to instantiate a ValidDate w/ input System.out.printf( "%nThe long form date reads: %s", inDate.getLongDate( ) ); System.out.printf( "%nThe short form date reads: %s%n%n", inDate.getValidDate( ) ); } // end try catch(InvalidDateException badDate) // if the data is 'bad' catch the exception here { System.out.printf( "%n%s%n", badDate.toString() ); } // end InvalidDateException catch catch( Exception xcptn ) // this catch block will catch ALL OTHER exceptions { System.err.printf( "%nWHAT HAPPENED?%n" ); } // end Exception catch System.out.println( "Do you want to enter another (Y/N)? "); // prompt user - additional input?
answer = keyboard.nextLine().charAt(0); // retrieve single character of user input } // end while
} // end main } // end DateConversion
Requirements ValidDate Class: Construct There will be only one constructor. It will accept a single String value. Validate the incoming String using a regular expression. Check for the following: The incoming String value must contain three groups of digits The digit groupings for month and day should be 1 or 2 digits long - The digit grouping for year must be exactly 4 digits long - The individual groupings must be separated by a slash "/) .If the user-provided String value meets the above requirements, the constructor will then parse the String into three parts (each to be stored as an int value) based on a separator character (/) a month value, a day value, and a year value. .Else, the constructor will throw an InvalidDateException with a message describing the required input
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


