Question: Java Red-Black Tree Assignment (fixed) Part 3: Red-black trees Left-leaning red-black trees, as they are described in the Sedgewick and Wayne text, undergo 3 possible
Java Red-Black Tree Assignment (fixed)
Part 3: Red-black trees
Left-leaning red-black trees, as they are described in the Sedgewick and Wayne text, undergo 3 possible transformations as they grow: rotateLeft, rotateRight, and flipColors. You may refer to the text or my lecture notes for the details of each of these tree transformations.
In red-black tree diagrams, you will see 2 ways to represent color. In the first, edges are colored, either red or black. In the other version, color information is stored within each node, and edges are not colored. In this second version, the root of the tree is always black. We will use the second version, in which nodes have color, to draw red-black trees.
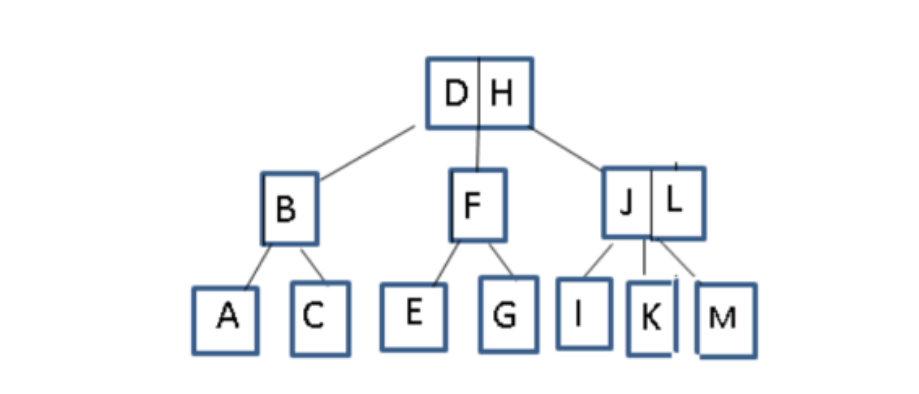
1. Draw the red-black tree that is equivalent to the 2-3 tree below.
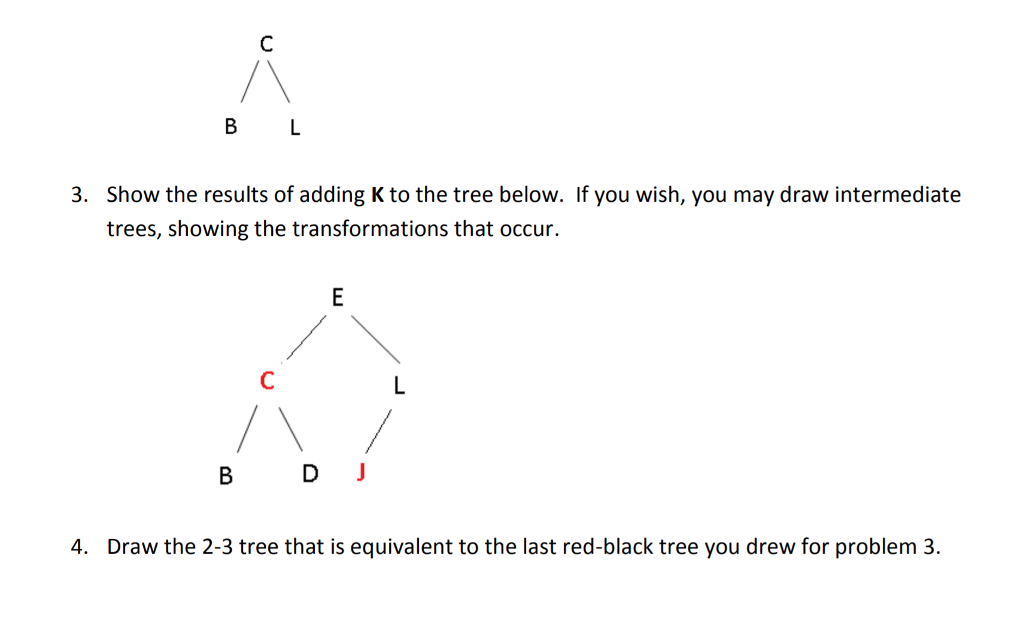
2. Show the results of adding E and then D to the tree below. If you wish, you may draw intermediate trees, showing the transformations that occur. Or, you may draw just 1 tree, reflecting the final state of the tree after both insertions are complete.
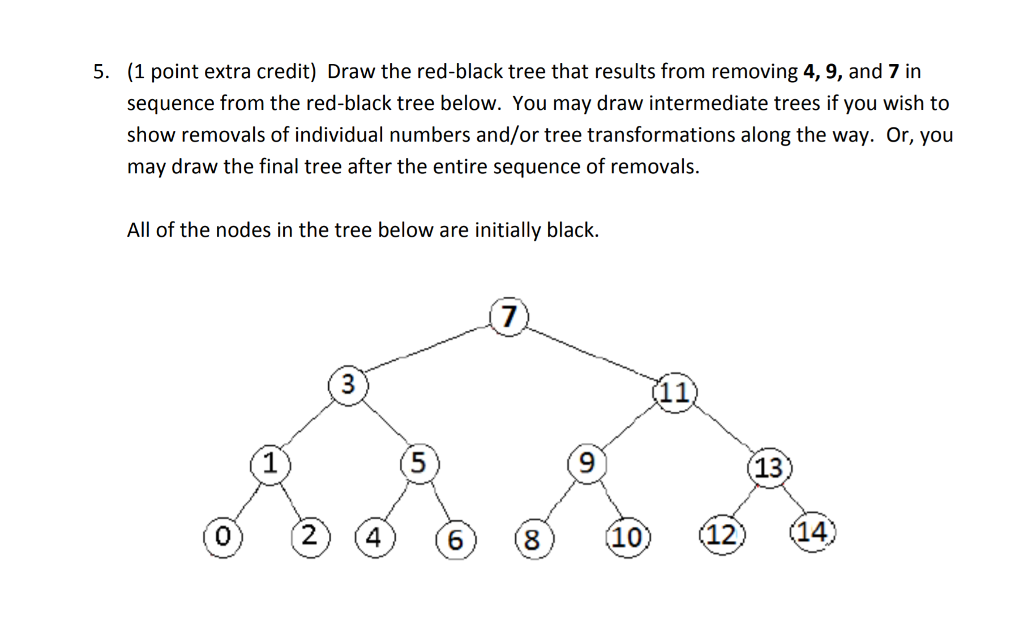
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


