Question: java The LCS Algorithm The definition of Lj,k satisfies subproblem optimization, for we cannot have a longest common subsequence without also having longest common subsequences
java

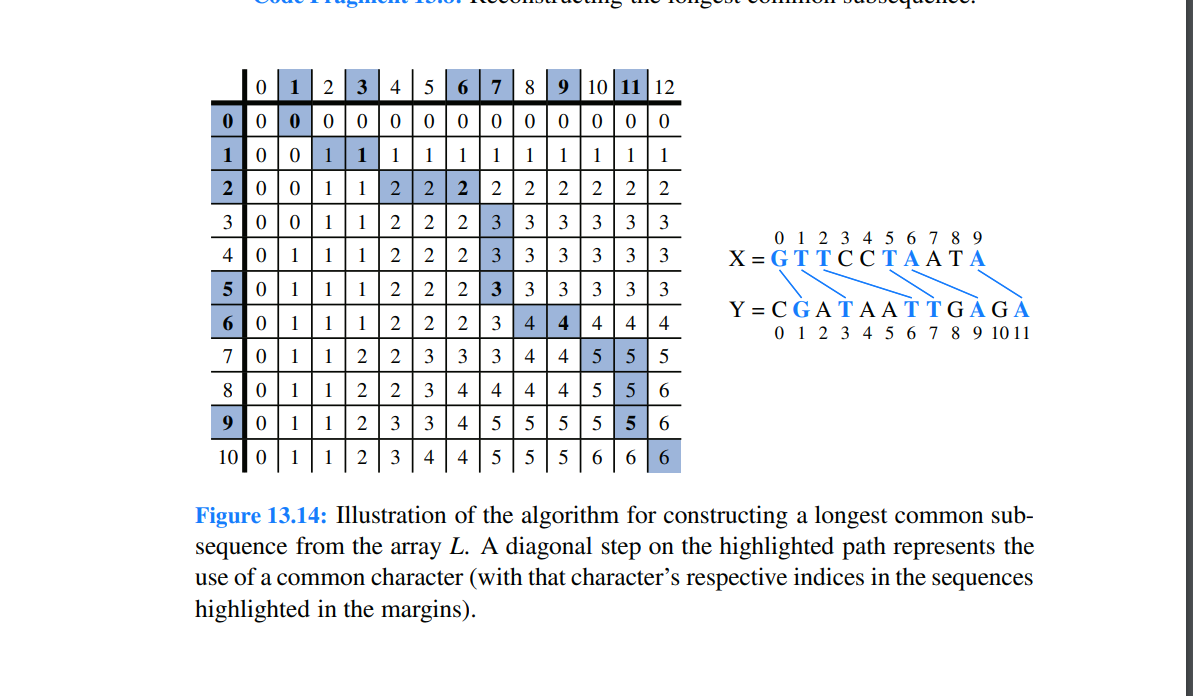
The LCS Algorithm The definition of Lj,k satisfies subproblem optimization, for we cannot have a longest common subsequence without also having longest common subsequences for the subproblems. Also, it uses subproblem overlap, because a subproblem solution Lj,k can be used in several other problems (namely, the problems Lj+1,k, Lj,k+1, and Lj+1,k+1 ). Turning this definition of Lj,k into an algorithm is actually quite straightforward. We create an (n+1)(m+1) array, L, defined for 0jn and 0km. We initialize all entries to 0 , in particular so that all entries of the form Lj,0 and L0,k are zero. Then, we iteratively build up values in L until we have Ln,m, the length of a longest common subsequence of X and Y. We give a Java implementation of this algorithm in Code Fragment 13.7. 123456789101112/ReturnstablesuchthatL[j][k]islengthofLCSforX[0..j1]andY[0..k1]./publicstaticint[][]LCS(char[]X,char[]Y){intn=X.length;intm=Y.length;int[][]L=newint[n+1][m+1];for(intj=0;j
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


