Question: Just i need the answer for requirement 4, It is a multiple choice question. thank you. Preferred Snacks produces snack mixes for the gourmet and
 Just i need the answer for requirement 4, It is a multiple choice question.
Just i need the answer for requirement 4, It is a multiple choice question.
thank you.
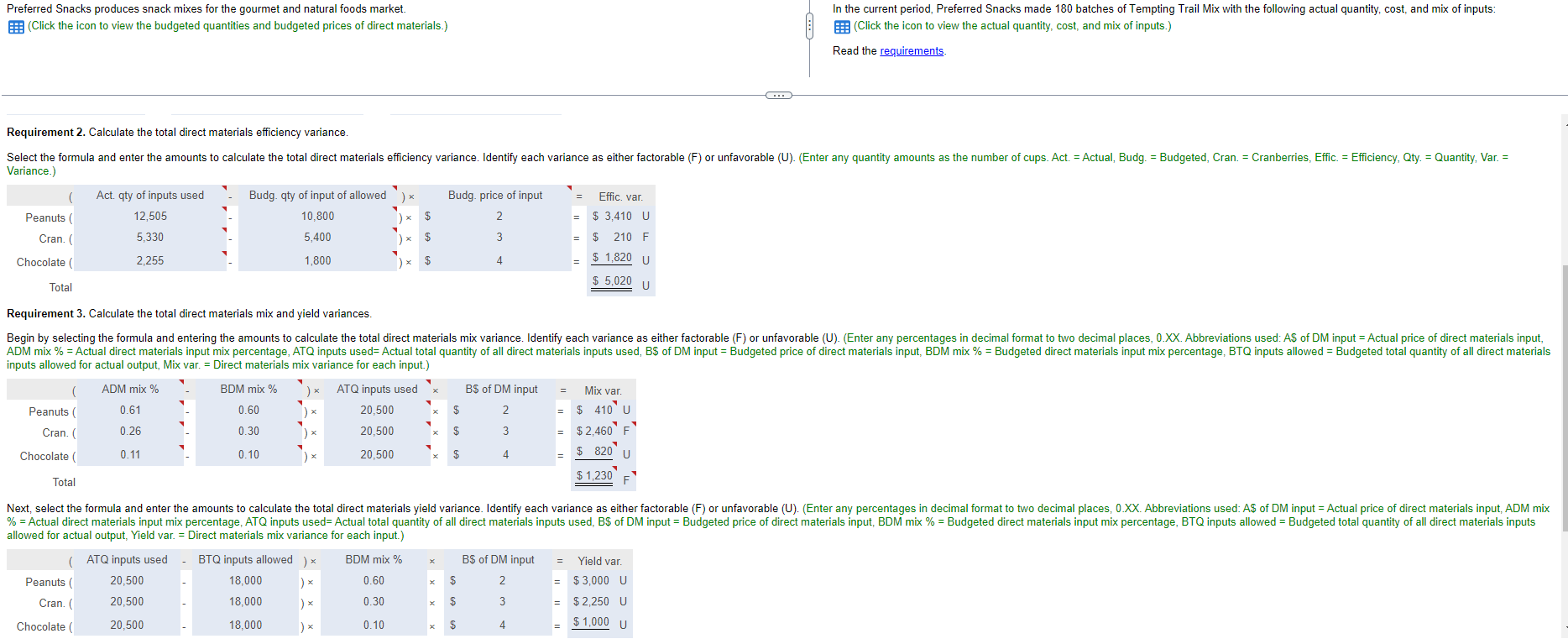
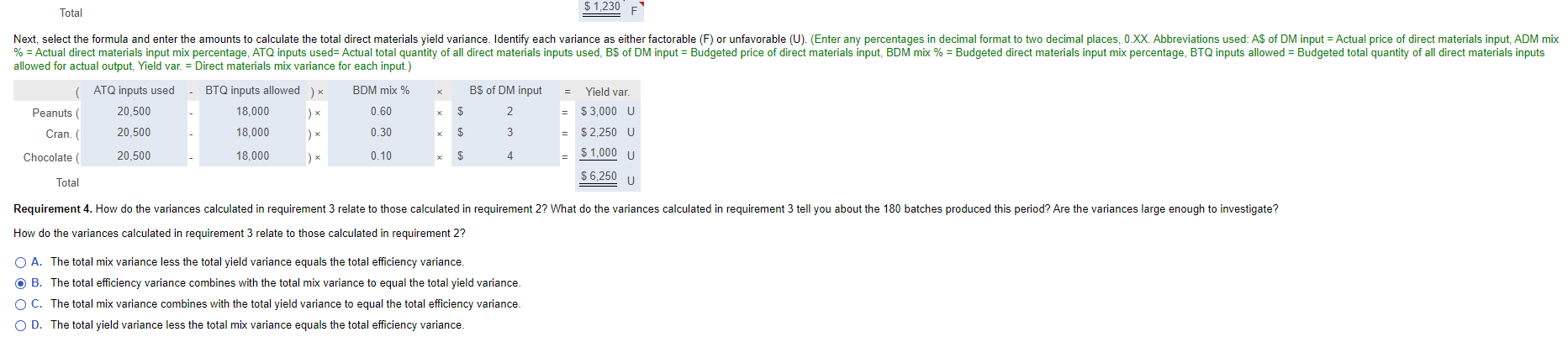
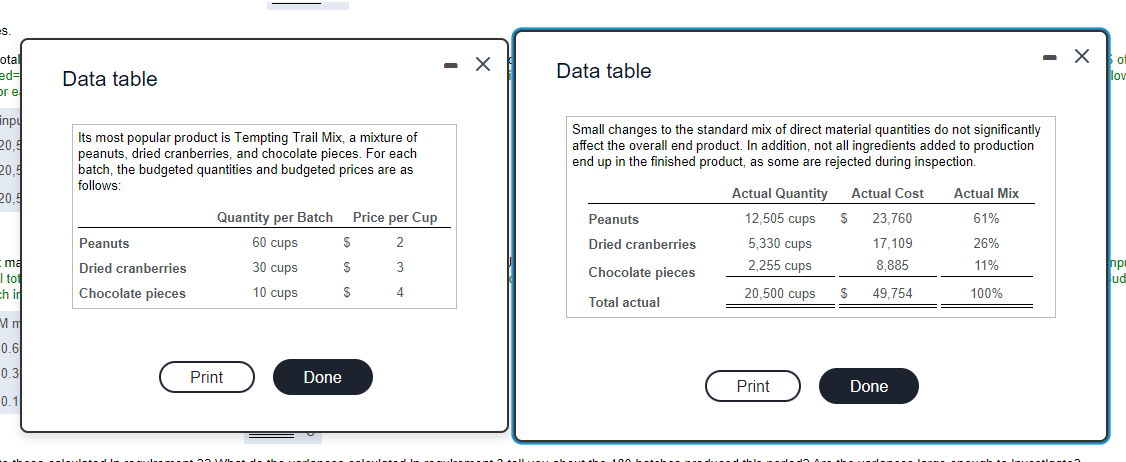
Preferred Snacks produces snack mixes for the gourmet and natural foods market. In the current period, Preferred Snacks made 180 batches of Tempting Trail Mix with the following actual quantity, cost, and mix of inputs: (Click the icon to view the actual quantity, cost, and mix of inputs.) (Click the icon to view the budgeted quantities and budgeted prices of direct materials.) Read the requirements. C Requirement 2. Calculate the total direct materials efficiency variance. Select the formula and enter the amounts to calculate the total direct materials efficiency variance. Identify each variance as either factorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Enter any quantity amounts as the number of cups. Act. = Actual, Budg. = Budgeted, Cran. = Cranberries, Effic. = Efficiency, Qty. = Quantity, Var. = Variance.) ( Act. qty of inputs used Budg. price of input Effic. var. = = Peanuts ( Budg. qty of input of allowed) * 10,800 5,400 ) x $ 2 12,505 5,330 $ 3,410 U $ 3 = $ 210 F Cran. ( Chocolate ( 2,255 1,800 $ 1,820 U 4 X $ = $ 5,020 Total U Requirement 3. Calculate the total direct materials mix and yield variances. Begin by selecting the formula and entering the amounts to calculate the total direct materials mix variance. Identify each variance as either factorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Enter any percentages in decimal format to two decimal places, 0.XX. Abbreviations used: A$ of DM input = Actual price of direct materials input, ADM mix % = Actual direct materials input mix percentage, ATQ inputs used= Actual total quantity of all direct materials inputs used, B$ of DM input = Budgeted price of direct materials input, BDM mix % = Budgeted direct materials input mix percentage, BTQ inputs allowed = Budgeted total quantity of all direct materials inputs allowed for actual output, Mix var. = Direct materials mix variance for each input.) ( ) * ATQ inputs used BS of DM input = Mix var. ADM mix % 0.61 BDM mix % 0.60 Peanuts ( 20,500 $ 2 $ 410 U 0.26 0.30 20,500 $ 3 $2,460 F Cran. ( Chocolate ( 0.11 0.10 20,500 $ $ 820 U 4 $ 1,230 Total Next, select the formula and enter the amounts to calculate the total direct materials yield variance. Identify each variance as either factorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Enter any percentages in decimal format to two decimal places, 0.XX. Abbreviations used: A$ of DM input = Actual price of direct materials input, ADM mix % = Actual direct materials input mix percentage, ATQ inputs used= Actual total quantity of all direct materials inputs used, B$ of DM input = Budgeted price of direct materials input, BDM mix % = Budgeted direct materials input mix percentage, BTQ inputs allowed = Budgeted total quantity of all direct materials inputs allowed for actual output, Yield var. = Direct materials mix variance for each input.) (ATQ inputs used BDM mix % BS of DM input = Yield var. Peanuts ( 20,500 BTQ inputs allowed ) x 18,000 )x 18,000 0.60 2 X = $3,000 U 20,500 Cran. ( ) x 0.30 3 = $2,250 U $1,000 U Chocolate ( 20,500 18,000 0.10 = x $ $ $ 4 = = = $ 1,230 Total Next, select the formula and enter the amounts to calculate the total direct materials yield variance. Identify each variance as either factorable (F) or unfavorable (U). (Enter any percentages in decimal format to two decimal places, 0.XX. Abbreviations used: A$ of DM input = Actual price of direct materials input, ADM mix % = Actual direct materials input mix percentage, ATQ inputs used= Actual total quantity of all direct materials inputs used, B$ of DM input = Budgeted price of direct materials input, BDM mix % = Budgeted direct materials input mix percentage, BTQ inputs allowed = Budgeted total quantity of all direct materials inputs allowed for actual output, Yield var. = Direct materials mix variance for each input.) x BS of DM input Yield var. ( ATQ inputs used 20,500 BTQ inputs allowed ) x 18,000 18,000 BDM mix % 0.60 2 Peanuts ( $3,000 U 20,500 0.30 $ 3 Cran. ( $2,250 U $1,000 U 20,500 18,000 Chocolate ( 0.10 ) $ 4 $ 6,250 U Total Requirement 4. How do the variances calculated in requirement 3 relate to those calculated in requirement 2? What do the variances calculated in requirement 3 tell you about the 180 batches produced this period? Are the variances large enough to investigate? How do the variances calculated in requirement 3 relate to those calculated in requirement 2? O A. The total mix variance less the total yield variance equals the total efficiency variance. OB. The total efficiency variance combines with the total mix variance to equal the total yield variance. O C. The total mix variance combines with the total yield variance to equal the total efficiency variance. O D. The total yield variance less the total mix variance equals the total efficiency variance. $ = = = es. otal ed= or e npu 20.5 20.5 20.5 ma I tot ch in Mm 0.6 0.3 0.1 Data table Its most popular product is Tempting Trail Mix, a mixture of peanuts, dried cranberries, and chocolate pieces. For each batch, the budgeted quantities and budgeted prices are as follows: Quantity per Batch Price per Cup Peanuts 60 cups $ 2 Dried cranberries 30 cups 3 Chocolate pieces 10 cups 4 Print Done S S - X Data table Small changes to the standard mix of direct material quantities do not significantly affect the overall end product. In addition, not all ingredients added to production end up in the finished product, as some are rejected during inspection. Actual Mix Peanuts Actual Quantity 12,505 cups 5,330 cups Actual Cost $ 23,760 17,109 61% 26% Dried cranberries 2,255 cups 8,885 11% Chocolate pieces 20,500 cups 49,754 100% Total actual Print $ Done X of lov npi Jud
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


