Question: k - Nearest Neighbor The learning technique we have seen so far ( i . e . Naive Bayes ) has involved the analysis of
kNearest Neighbor
The learning technique we have seen so far ie Naive Bayes has involved the analysis of a training set of examples in order to build a model for the task at hand. New examples were then classified using the learned model. We now consider the k nearest neighbor algorithm, which does not explicitly build a model from training data. Instead, it stores the training instances so that they can be used to analyze new instances later As its name implies, the k nearest neighbor algorithm searches the training examples to find those that are "closest" to a new example to be classified. It then uses these to determine the appropriate output for the new instance. knearest neighbor is an example of a class of learning techniques called instancebased methods. These methods are sometimes referred to as "lazy", because they put off the processing of examples until a new test instance is considered.
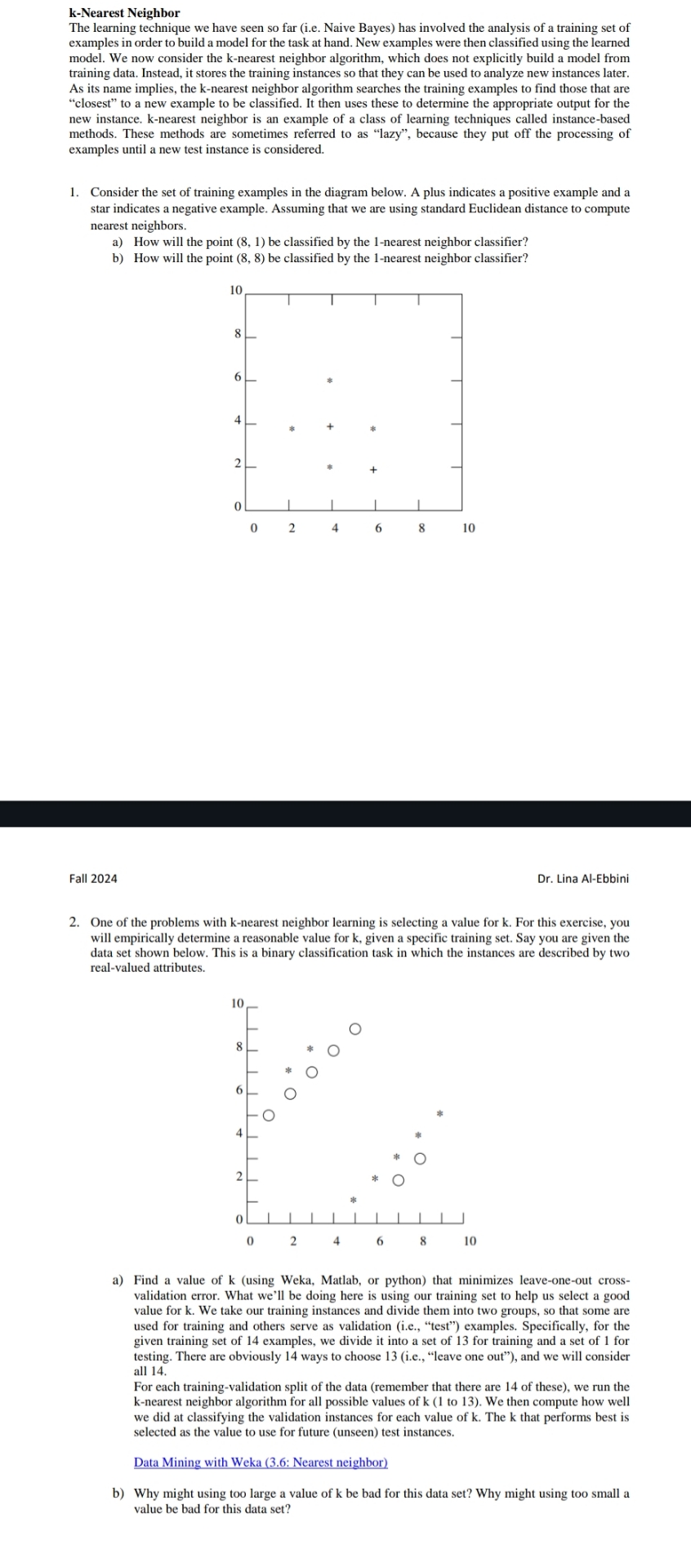
Consider the set of training examples in the diagram below. A plus indicates a positive example and a star indicates a negative example. Assuming that we are using standard Euclidean distance to compute nearest neighbors.
a How will the point be classified by the nearest neighbor classifier?
b How will the point be classified by the nearest neighbor classifier?
Fall
Dr Lina AlEbbini
One of the problems with k nearest neighbor learning is selecting a value for k For this exercise, you will empirically determine a reasonable value for given a specific training set. Say you are given the data set shown below. This is a binary classification task in which the instances are described by two realvalued attributes.
a Find a value of k using Weka, Matlab, or python that minimizes leaveoneout crossvalidation error. What we'll be doing here is using our training set to help us select a good value for k We take our training instances and divide them into two groups, so that some are used for training and others serve as validation ie "test" examples. Specifically, for the given training set of examples, we divide it into a set of for training and a set of for testing. There are obviously ways to choose ie "leave one out" and we will consider all
For each trainingvalidation split of the data remember that there are of these we run the nearest neighbor algorithm for all possible values of to We then compute how well we did at classifying the validation instances for each value of k The k that performs best is selected as the value to use for future unseen test instances.
Data Mining with Weka : Nearest neighbor
b Why might using too large a value of k be bad for this data set? Why might using too small a value be bad for this data set?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


