Question: kindly help write this program using python Part II - Assemblers In this part you will play the role of the assembler and assign a
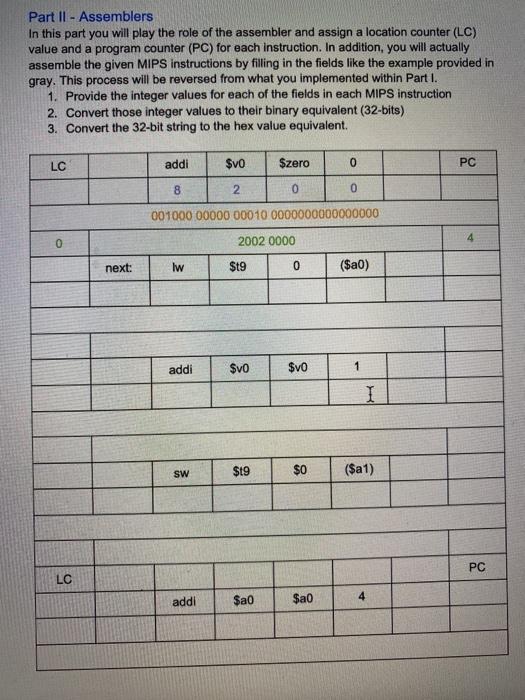
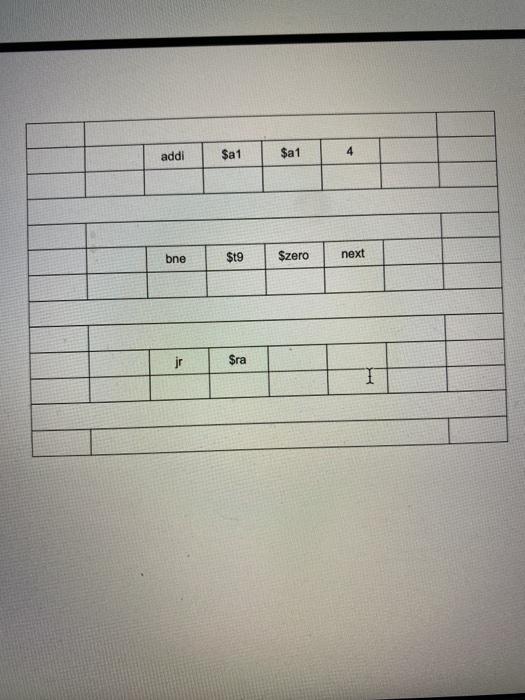

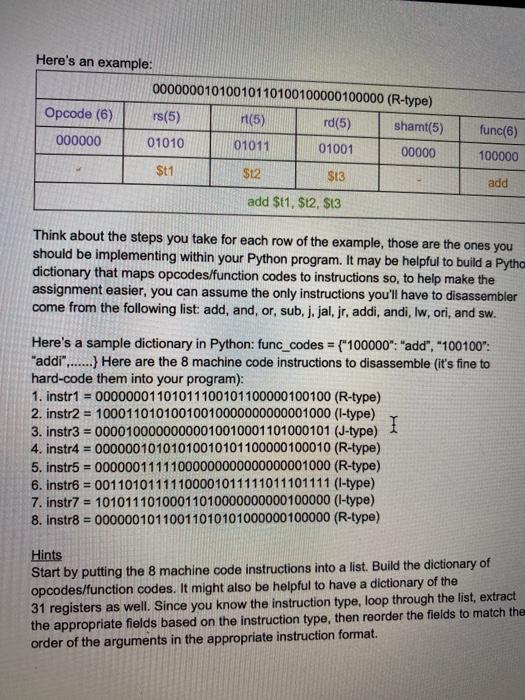
Part II - Assemblers In this part you will play the role of the assembler and assign a location counter (LC) value and a program counter (PC) for each instruction. In addition, you will actually assemble the given MIPS instructions by filling in the fields like the example provided in gray. This process will be reversed from what you implemented within Part I. 1. Provide the integer values for each of the fields in each MIPS instruction 2. Convert those integer values to their binary equivalent (32-bits) 3. Convert the 32-bit string to the hex value equivalent. LC addi $vo Szero 0 PC 8 2 0 0 001000 00000 00010 0000000000000000 0 2002 0000 next: lw $t9 0 ($a0) addi $vo $vo 1 I SW $19 $0 ($a1) PC LC addi $a0 $a0 addi Sa1 $a1 4 bne $t9 Szero next jr $ra Here's an example: 00000001010010110100100000100000 (R-type) Opcode (6) rs(5) (5) rd(5) shamt(5) 000000 01010 01011 01001 00000 func(6) 100000 $t1 $12 $13 add add $t1, $12, $t3 Think about the steps you take for each row of the example, those are the ones you should be implementing within your Python program. It may be helpful to build a Pytho dictionary that maps opcodes/function codes to instructions so, to help make the assignment easier, you can assume the only instructions you'll have to disassembler come from the following list: add, and, or, sub, j.jal, jr, addi, andi, Iw, ori, and sw. Here's a sample dictionary in Python: func_codes = {"100000": "add", "100100": "addi".......} Here are the 8 machine code instructions to disassemble (it's fine to hard-code them into your program): 1. instr1 = 00000001101011100101100000100100 (R-type) 2. instr2 = 10001101010010010000000000001000 (1-type) 3. instr3 = 00001000000000010010001101000101 (J-type) I 4. instr4 = 00000010101010010101100000100010 (R-type) 5. instr5 = 00000011111000000000000000001000 (R-type) 6. instr6 = 00110101111100001011111011101111 (I-type) 7. instr7 = 10101110100011010000000000100000 (1-type) 8. Instr8 = 00000010110011010101000000 100000 (R-type) Hints Start by putting the 8 machine code instructions into a list. Build the dictionary of opcodes/function codes. It might also be helpful to have a dictionary of the 31 registers as well. Since you know the instruction type, loop through the list, extract the appropriate fields based on the instruction type, then reorder the fields to match the order of the arguments in the appropriate instruction format
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


