Question: kindly solve these problems 11.13 An engineer determined the ESL of a new $80 000 piece of equipment and recorded the calculations shown below. [Note
kindly solve these problems


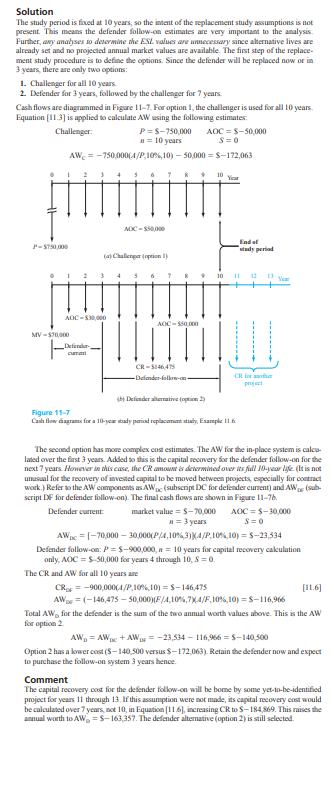
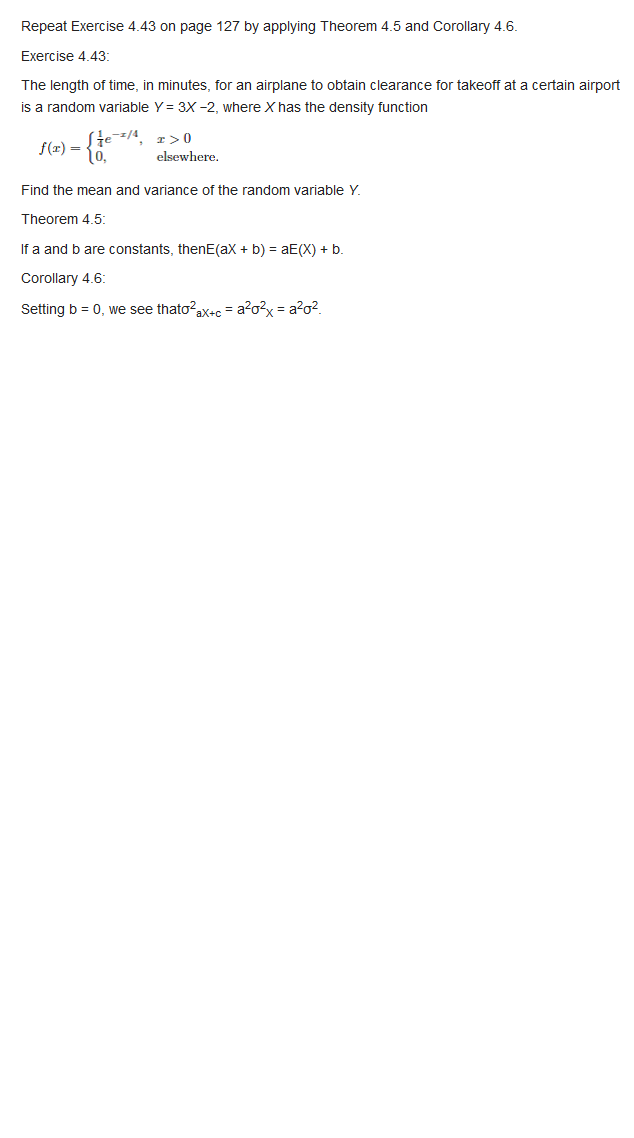

11.13 An engineer determined the ESL of a new $80 000 piece of equipment and recorded the calculations shown below. [Note that the num- bers are annual worth values associated with various years of retention; that is, if the equip- ment is kept for, say, 3 years, the AW (years I through 3) of the first cost is $32,169, the AW of the operating cost is $51,000, and the AW of the salvage value is $6042 ] The engineer forgot to enter the AW of the salvage value for 2 years of retention. From the information available, deter- mine the following: [a) The interest rate used in the ESL calculations. (b) The salvage value after 2 years, if the total AW of the equipment in year 2 was $78,762 Use the interest rate determined in part (a). Years AW of AW of AW of Retained First Cost, $ Operating Cost, $ Salvage Value, $ -45 000 -46 095 -46 000 7 -32,167 6042 11.14 A large, standby electricity generator in a hospital operating room has a first cost of $70,000 and may be used for a maximum of & years. Its salvage value, which decreases by 13%% per year, is de- scribed by the equation S = 70,000(1 - 0.15)- where a is the number of years after purchase. The operating cost of the generator will be constant at $75,000 per year At an interest rate of 12%% per year, what are the economic service life and the associated AW value?TABLE 12-4 IROR, P, and PW Values for Five Pro cts, Example 12.4 Projects vestment, NCE, $1000 - 15,00 matt per year Life , years PW an 15%, $1000 18 million. She has confirmed the computations and is ready to do the ranking and make the election. Help her by doing the Use the IROR measure to rank and select projects " Use the PI measure to rank and select projects. Compare the selected projects by the three methods and determine which one will maxi- mize the overall ROR value of the $18 million budgetSolution The study period is fixed at 10 years, so the intent of the replacement study assumptions is not present. This means the defender follow-on estimates are very important to the analysis. Further, any analyses to determine the ESL values are unnecessary since alternative lives are already set and no projected annual market values are available. The first step of the replace- ment study procedure is to define the options. Since the defender will be replaced now or in 3 years, there are only two options: 1. Challenger for all 10 years. 1. Defender for 3 years, followed by the challenger for 7 years. Cash flows are diagrammed in Figure 11-7. For option I, the challenger is used for all 10 years. Equation [1 1.3] is applied to calculate AW using the following estimates: Challenger: P =$-750,000 AOC = $-50,000 # = 10 years S=0 AW, = -750,000(4/P,10%,10) - 507000 = $-172,063 10 ADC - $56000 End of study period fat Challenger |option IF 11 Year AOC -30 0U _Defender- current CR - 5146475 -Defender-fallow-an 4hy Defender alternative [option ?) Figure 11-7 Cash flow diagrams for a 10-year mudy period replacement study, Example II.6. The second option has more complex cost estimates. The AW for the in-place system is calcu- lated over the first 3 years. Added to this is the capital recovery for the defender follow-on for the next 7 years. However is this case, the CR amown is determined over its full 10-year Me. (It is not unusual for the recovery of invested capital to be moved between projects, especially for contract work.) Refer to the AW components as AWp (subscript DC for defender current) and AW (sub- script DF for defender follow-on). The final cash flows are shown in Figure 11-76. Defender current market value = $-70,000 AOC =$-30,000 a =3 years AWac = [-70,000 - 30,000(P/4, 10%,3) (4/P.10%,10) = $-23,534 Defender follow-on: P = $-900,000, a = 10 years for capital recovery calculation only, AOC = $-50,000 for years 4 through 10, 8 = 0. The CR and AW for all 10 years are CROF = -900,00014/P,10%%,101 = $-146,475 [11.6] AWDE =(-146,475 - 50,000)(F/4,10%,7)(4/F,10%,10) = $-116,966 Total AW, for the defender is the sum of the two annual worth values above. This is the AW for option 2 AW = AWac + AW = -23,534 - 116,956 =$-140,500 Option 2 has a lower cost ($-140,300 versus $-172,063). Retain the defender now and expect to purchase the follow-on system 3 years hence. Comment The capital recovery cost for the defender follow-on will be home by some yet-to-be-identified project for years 10 through 13. If this assumption were not made, its capital recovery cost would be calculated over 7 years, not 10, in Equation [1 1 6], increasing CR to $-184,869. This raises the annual worth to AW,, = $-163,357. The defender alternative (option 2) is still selected.\f\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


