Question: Knowledge Base of the Tool The tool's knowledge base consists of several key components, including technical best practices, ethical AI principles, legal regulations, and AI
Knowledge Base of the Tool
The tool's knowledge base consists of several key components, including technical best practices, ethical AI principles, legal regulations, and AIspecific guidelines like the EU AI Act. Here's an analytical description of the tool's knowledge base:
Technical Knowledge:
Bias Mitigation:
The tool uses wellestablished machine learning principles that recommend the use of diverse datasets to reduce bias in AI models. This comes from research in natural language processing NLP which shows that models trained on biased data can unfairly discriminate against certain groups.
Privacy and Security:
The tools knowledge base includes data privacy principles, especially from frameworks like GDPR which are essential for any system handling sensitive personal data. Privacypreserving techniques like data anonymization, encryption, and access control are embedded in the tool's assessment.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations:
GDPR: The tool integrates key privacy principles from GDPR General Data Protection Regulation which is a cornerstone of data privacy law in Europe. GDPR provides rules for collecting, processing, and storing personal data, especially when that data includes personally identifiable information PIIMitigations are based on AI development best practices for dataset diversity and privacy and legal regulations GDPR and AI Act
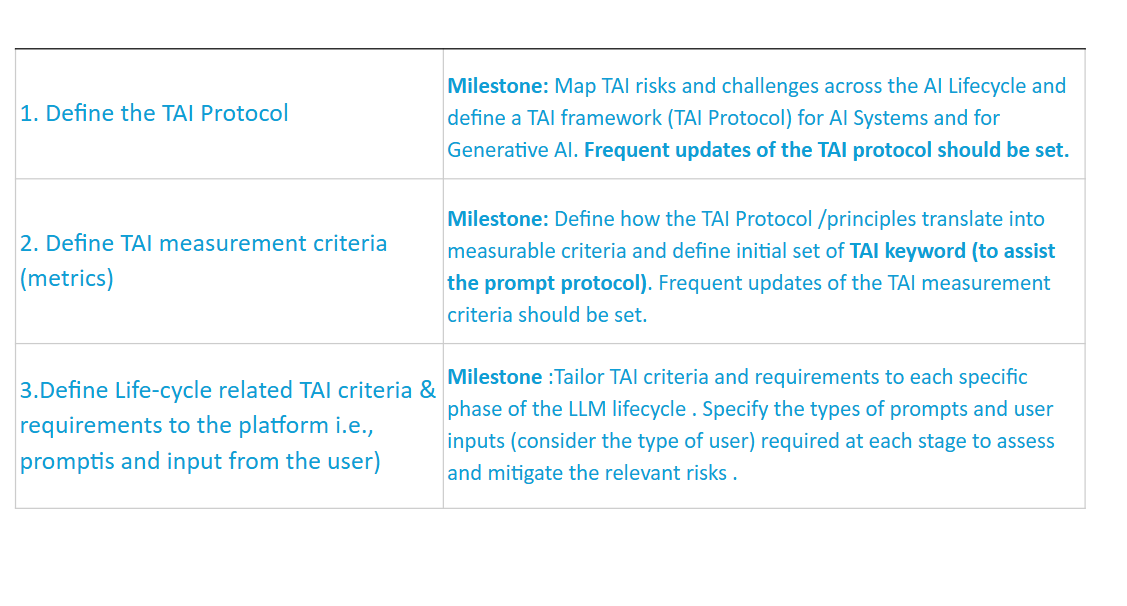
Knowledge Base includes technical research on bias and fairness in AI legal requirements from GDPR and the AI Act, and ethical AI principlesDefine the TAI Protocol
LLM Risk Mapping Source:
Associate Risks with Lifecycle phases
Associate Risks with TAI principles HLEG Risk Mapping & Mitigation Measures proposition
User Input:
User feedback:
Potential RisksRisk Categories
Potential Mitigation Measures
Prompts for further analysis Customised prompts from our prompt library & user input
Potential Benchmarks Scenario Description:
A law enforcement agency deploys a realtime facial recognition system to monitor and identify potential criminal suspects in a busy urban environment eg a train station, airport, or public square The system analyzes live video feeds from public cameras and processes biometric data facial images to match individuals against a criminal database in realtime. The system aims to improve public safety by flagging individuals with active arrest warrants and preventing potential security threats.
However, this deployment introduces significant privacy, data governance, and bias concerns as it involves the processing of sensitive biometric data on a large scale.
User Inputs for the Tool:
AI System Lifecycle Phase:
Operation Phase The system is already deployed and actively being used in realtime
TAI Principle for Testing:
Privacy and Data Governance Due to the sensitive nature of biometric data processing in public spaces
Domain of Application:
Law Enforcement The system is deployed by law enforcement agencies to monitor and secure public spaces
Type of Input Data:
Biometric Data Facial recognition data collected from realtime video feeds
Type of AI System:
Predictive Models, Facial Recognition The system uses facial recognition algorithms to identify individuals and predict potential threats based on their movements and matches with the criminal database
Intended Use:
To monitor and track individuals in realtime by law enforcement in a public space to identify potential security risks, flag criminal suspects, and enhance public safety.
Expected Results from the Tool:
Summary:
Lifecycle Phase: Operation Phase
TAI Principle: Privacy and Data Governance
Domain: Law Enforcement
Input Data: Biometric Data Facial Recognition
AI System: Predictive Models, Facial Recognition
Intended Use: To monitor and track individuals in realtime, identifying potential threats and enhancing public safety.
Identified Risks:
Risk : Potential Bias in Facial Recognition
Facial recognition systems have been shown to exhibit bias, particularly against individuals from certain demographic groups eg ethnic minorities, gender This could lead to disproportionate false positives, especially in hightraffic public spaces.
Risk : Data Privacy Concerns
The realtime collection and processing of biometric data in public spaces pose significant privacy concerns, particularly under the GDPR as facial images are considered sensitive personal data.
There is a risk of oversurveillance and potential misuse of personal data by authorities.
Mitigation Measures:
Mitigation : Regular Bias Audits and Dataset Improvements
Conduct regular bias audits on the facial recognition system and improve the diversity of the training datasets to reduce errors and ensure fairness across demographic groups.
Mitigation : Data Encryption and Access Controls
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


