Question: la How to Manage Plant? Project Management aligned with Organizational Structure Jack Dorsey Make every detail perfect and limit the number of details to perfect
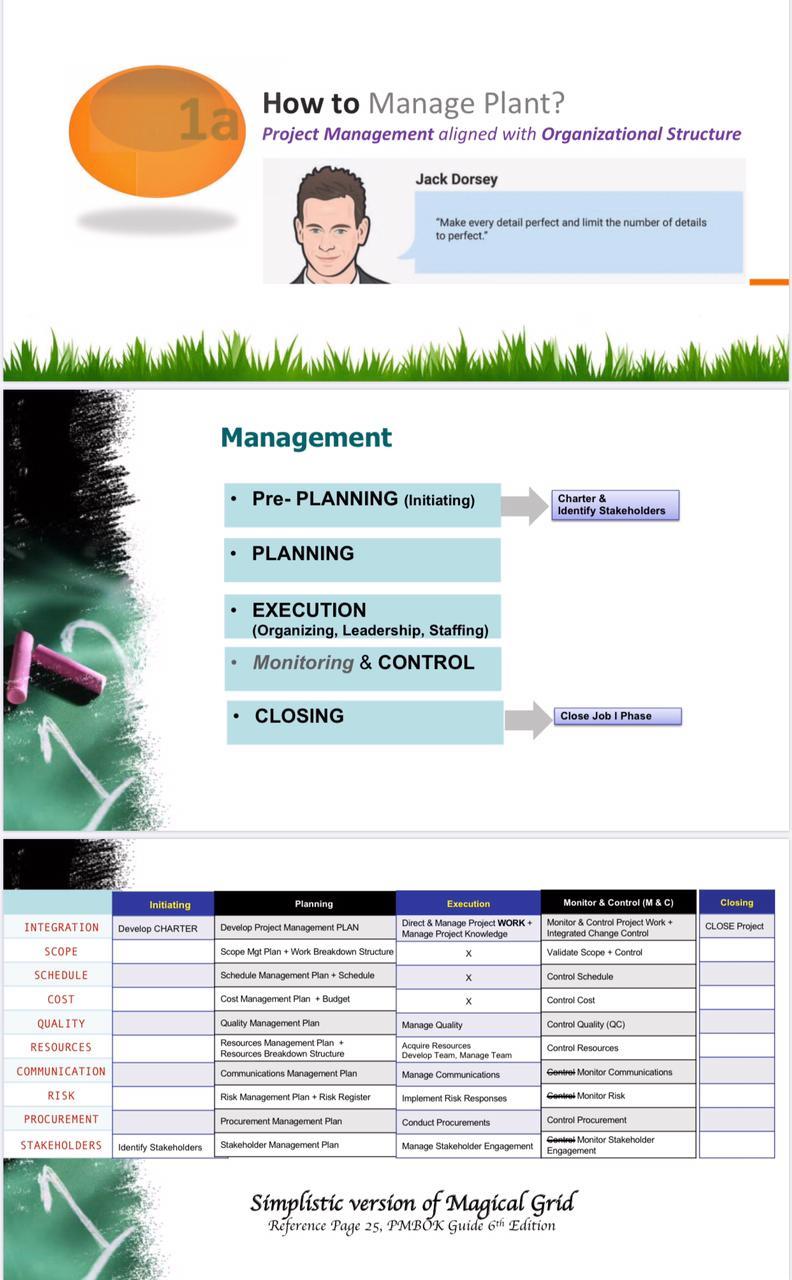
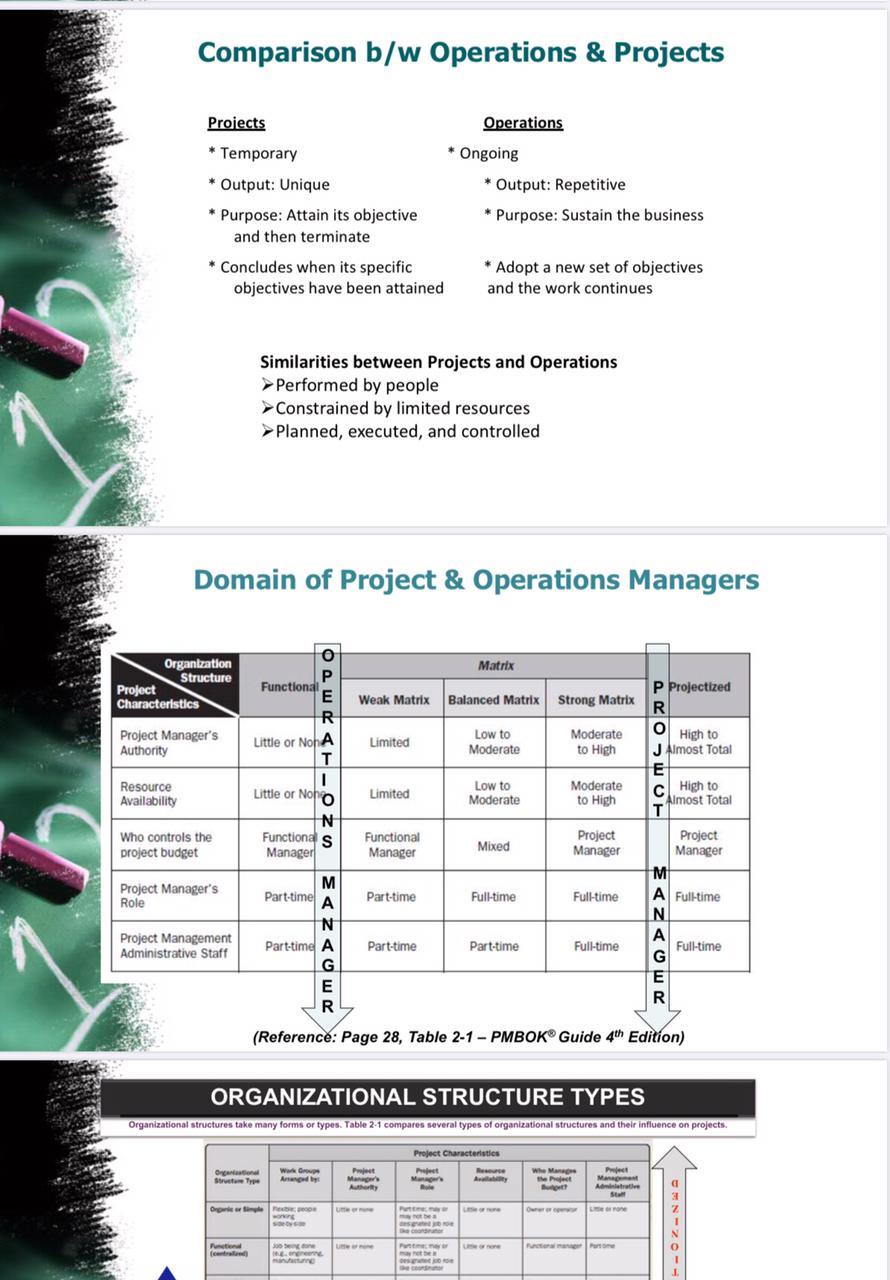
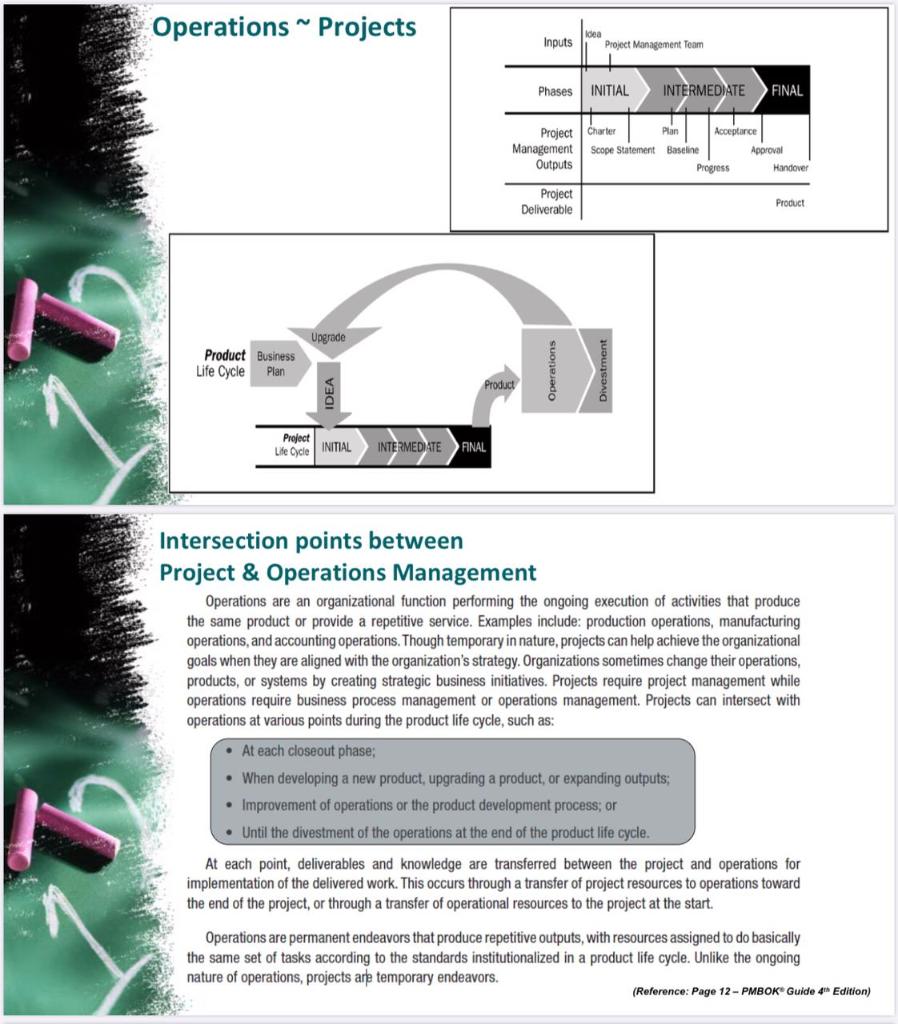
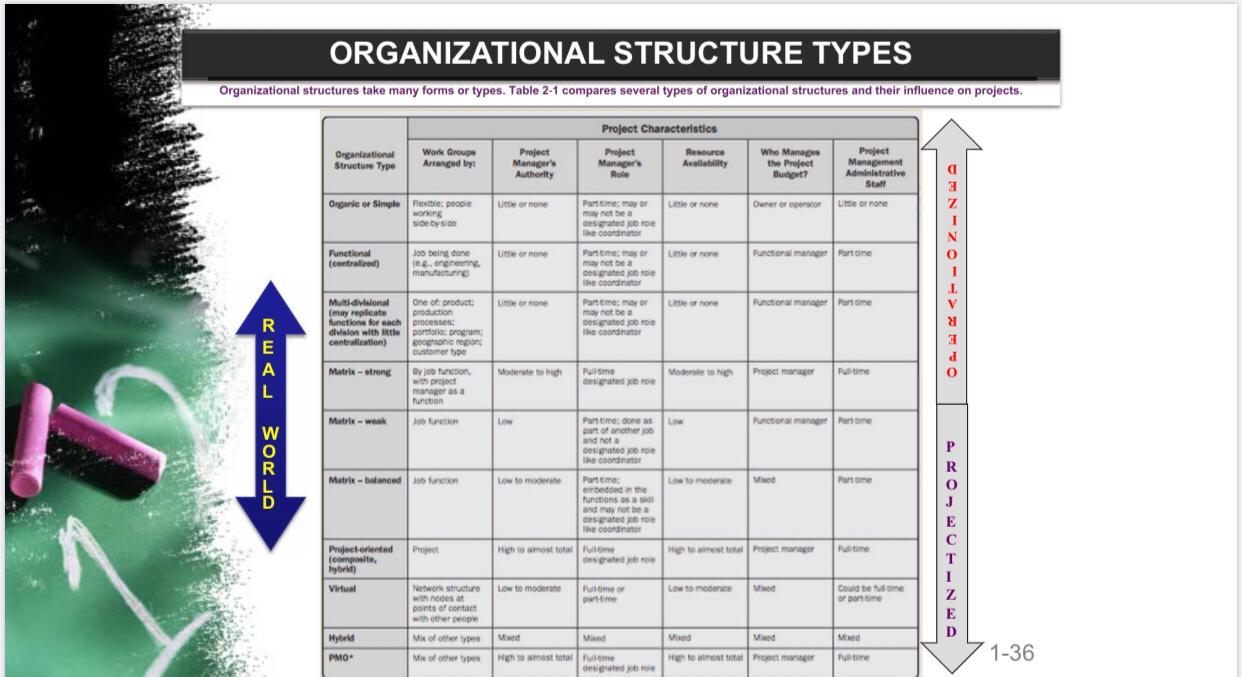
la How to Manage Plant? Project Management aligned with Organizational Structure Jack Dorsey "Make every detail perfect and limit the number of details to perfect Management Pre-PLANNING (Initiating) Charter & Identify Stakeholders PLANNING EXECUTION (Organizing, Leadership, Staffing) Monitoring & CONTROL CLOSING Close Job I Phase Initiating Planning Closing Execution Direct & Manage Project WORK Manage Project knowledge INTEGRATION Develop CHARTER Monitor & Control (M&C) Monitor & Control Project Work + Integrated Change Control Validate Scope + Control Develop Project Management PLAN Scope Mgt Plan + Work Breakdown Structure CLOSE Project SCOPE X SCHEDULE Control Schedule Schedule Management Plan + Schedule Cost Management Plan Budget COST Control Cost QUALITY Control Quality (QC) RESOURCES Quality Management Plan Resources Management Plan Resources Breakdown Structure Communications Management Plan Manage Quality Acquire Resources Develop Team Manage Team Manage Communications Control Resources COMMUNICATION Centre Monitor Communications RISK Risk Management Plan+Risk Register PROCUREMENT Procurement Management Plan Implement Risk Responses Conta Monitor Risk Conduct Procurements Control Procurement Cance Monitor Stakeholder Manage Stakeholder Engagement Engagement STAKEHOLDERS Identity Stakeholders Stakeholder Management Plan Simplistic version of Magical Grid Reference Page 25, PMBOK Guide 6th Edition Comparison b/w Operations & Projects Projects Operations * Temporary * Ongoing * Output: Unique * Output: Repetitive * Purpose: Attain its objective * Purpose: Sustain the business and then terminate * Concludes when its specific * Adopt a new set of objectives objectives have been attained and the work continues Similarities between Projects and Operations Performed by people Constrained by limited resources > Planned, executed, and controlled Domain of Project & Operations Managers Matrix Organization Structure Project Characteristics Weak Matrix Balanced Matrix Strong Matrix P Projectized R o High to Project Manager's Authority Limited o Functional E R Little or Noha 1 Little or Not N Functional s Manager Low to Moderate Moderate to High Resource Availability Limited Low to Moderate Moderate to High Who controls the project budget Functional Manager Mixed Project Manager J Almost Total E cl. High to Almost Total T Project Manager M A Full-time N A Full-time G E R Project Manager's Role Part-time A Part-time Full-time Full-time Project Management Administrative Staff M N Part-time A G E R! Part-time Part-time Full-time (Reference: Page 28, Table 2-1 - PMBOK Guide 4th Edition) ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE TYPES Organizational structures take many forms or types. Table 2-1 compares several types of organizational structures and their influence on projects. Ong Sue Type Work And by Project Characteristics Pet Mag Pjet Manager's Author Man Annette SU a 31 Orale Or 1 fer 500 . 0 1 1 Operations Projects Inputs Idea Project Management Team Phases INITIAL INTERMEDIATE FINAL PL Acceptance Project Charter Management Scope Statement Outputs Baseline Approval Progress Handover Project Deliverable Product Upgrade Product Business Life Cycle Plan DI Product Project Life Cycle INITIAL INTERMEDIATE FINAL Intersection points between Project & Operations Management Operations are an organizational function performing the ongoing execution of activities that produce the same product or provide a repetitive service. Examples include: production operations, manufacturing operations, and accounting operations. Though temporary in nature, projects can help achieve the organizational goals when they are aligned with the organization's strategy. Organizations sometimes change their operations, products, or systems by creating strategic business initiatives. Projects require project management while operations require business process management or operations management. Projects can intersect with operations at various points during the product life cycle, such as: At each closeout phase; When developing a new product, upgrading a product, or expanding outputs: Improvement of operations or the product development process; or . Until the divestment of the operations at the end of the product life cycle. At each point, deliverables and knowledge are transferred between the project and operations for implementation of the delivered work. This occurs through a transfer of project resources to operations toward the end of the project, or through a transfer of operational resources to the project at the start. Operations are permanent endeavors that produce repetitive outputs with resources assigned to do basically the same set of tasks according to the standards institutionalized in a product life cycle. Unlike the ongoing nature of operations, projects are temporary endeavors. (Reference: Page 12 - PMBOK Guide 4 Edition) ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE TYPES Organizational structures take many forms or types. Table 2-1 compares several types of organizational structures and their influence on projects. Organizational Structure Type Work Group Arranged by: Project Manager's Project Project Characteristics Resource Manager's Availability Role Who Manage the Project Budget? Authority Project Management Administrative Stall a Une or more Owner or operator Lorone Organic or Simple Flexible people woning side by side Une or mone Punctional manager Partime Functional (centralized) Jo being done 10.8. grein manufacturing Part time mayor terrone may not be desenated job the coordinator Pame, mayor errone may not be a designated job too The coordinator Partime mayor no one may not be a Designated for The coordinator Uterone Punctional manager Portime R E A L Multivisional One of product may replicate production functions for each processes vision with the portfolio program : centralation) geographic region customer type Matrix - strong by function w project manager as a function Moderate to Pull time designated to Pret manager Pultime O Matrix - weak L Function manager Parme W Part time done part of the and not a bestede The coordinator P Matrie balanced Jouretion - Low to Moed M Parttime D Low to morate Parttime embedded in the functions as a and may not be designated obro The coordinator High to most time dewater to most romanager time Project-oriented Projet (composite hy Virtual Network structure with nodes at points of contact J E 1 z E D Low to moderate imeo Dome Low to Med could be tume forme Hybrid Mis of the Med Mixed Med Med Med Hinto a most total Poet maar PMO" Mother Puntime 1-36 High to most totaluome designated obro la How to Manage Plant? Project Management aligned with Organizational Structure Jack Dorsey "Make every detail perfect and limit the number of details to perfect Management Pre-PLANNING (Initiating) Charter & Identify Stakeholders PLANNING EXECUTION (Organizing, Leadership, Staffing) Monitoring & CONTROL CLOSING Close Job I Phase Initiating Planning Closing Execution Direct & Manage Project WORK Manage Project knowledge INTEGRATION Develop CHARTER Monitor & Control (M&C) Monitor & Control Project Work + Integrated Change Control Validate Scope + Control Develop Project Management PLAN Scope Mgt Plan + Work Breakdown Structure CLOSE Project SCOPE X SCHEDULE Control Schedule Schedule Management Plan + Schedule Cost Management Plan Budget COST Control Cost QUALITY Control Quality (QC) RESOURCES Quality Management Plan Resources Management Plan Resources Breakdown Structure Communications Management Plan Manage Quality Acquire Resources Develop Team Manage Team Manage Communications Control Resources COMMUNICATION Centre Monitor Communications RISK Risk Management Plan+Risk Register PROCUREMENT Procurement Management Plan Implement Risk Responses Conta Monitor Risk Conduct Procurements Control Procurement Cance Monitor Stakeholder Manage Stakeholder Engagement Engagement STAKEHOLDERS Identity Stakeholders Stakeholder Management Plan Simplistic version of Magical Grid Reference Page 25, PMBOK Guide 6th Edition Comparison b/w Operations & Projects Projects Operations * Temporary * Ongoing * Output: Unique * Output: Repetitive * Purpose: Attain its objective * Purpose: Sustain the business and then terminate * Concludes when its specific * Adopt a new set of objectives objectives have been attained and the work continues Similarities between Projects and Operations Performed by people Constrained by limited resources > Planned, executed, and controlled Domain of Project & Operations Managers Matrix Organization Structure Project Characteristics Weak Matrix Balanced Matrix Strong Matrix P Projectized R o High to Project Manager's Authority Limited o Functional E R Little or Noha 1 Little or Not N Functional s Manager Low to Moderate Moderate to High Resource Availability Limited Low to Moderate Moderate to High Who controls the project budget Functional Manager Mixed Project Manager J Almost Total E cl. High to Almost Total T Project Manager M A Full-time N A Full-time G E R Project Manager's Role Part-time A Part-time Full-time Full-time Project Management Administrative Staff M N Part-time A G E R! Part-time Part-time Full-time (Reference: Page 28, Table 2-1 - PMBOK Guide 4th Edition) ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE TYPES Organizational structures take many forms or types. Table 2-1 compares several types of organizational structures and their influence on projects. Ong Sue Type Work And by Project Characteristics Pet Mag Pjet Manager's Author Man Annette SU a 31 Orale Or 1 fer 500 . 0 1 1 Operations Projects Inputs Idea Project Management Team Phases INITIAL INTERMEDIATE FINAL PL Acceptance Project Charter Management Scope Statement Outputs Baseline Approval Progress Handover Project Deliverable Product Upgrade Product Business Life Cycle Plan DI Product Project Life Cycle INITIAL INTERMEDIATE FINAL Intersection points between Project & Operations Management Operations are an organizational function performing the ongoing execution of activities that produce the same product or provide a repetitive service. Examples include: production operations, manufacturing operations, and accounting operations. Though temporary in nature, projects can help achieve the organizational goals when they are aligned with the organization's strategy. Organizations sometimes change their operations, products, or systems by creating strategic business initiatives. Projects require project management while operations require business process management or operations management. Projects can intersect with operations at various points during the product life cycle, such as: At each closeout phase; When developing a new product, upgrading a product, or expanding outputs: Improvement of operations or the product development process; or . Until the divestment of the operations at the end of the product life cycle. At each point, deliverables and knowledge are transferred between the project and operations for implementation of the delivered work. This occurs through a transfer of project resources to operations toward the end of the project, or through a transfer of operational resources to the project at the start. Operations are permanent endeavors that produce repetitive outputs with resources assigned to do basically the same set of tasks according to the standards institutionalized in a product life cycle. Unlike the ongoing nature of operations, projects are temporary endeavors. (Reference: Page 12 - PMBOK Guide 4 Edition) ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE TYPES Organizational structures take many forms or types. Table 2-1 compares several types of organizational structures and their influence on projects. Organizational Structure Type Work Group Arranged by: Project Manager's Project Project Characteristics Resource Manager's Availability Role Who Manage the Project Budget? Authority Project Management Administrative Stall a Une or more Owner or operator Lorone Organic or Simple Flexible people woning side by side Une or mone Punctional manager Partime Functional (centralized) Jo being done 10.8. grein manufacturing Part time mayor terrone may not be desenated job the coordinator Pame, mayor errone may not be a designated job too The coordinator Partime mayor no one may not be a Designated for The coordinator Uterone Punctional manager Portime R E A L Multivisional One of product may replicate production functions for each processes vision with the portfolio program : centralation) geographic region customer type Matrix - strong by function w project manager as a function Moderate to Pull time designated to Pret manager Pultime O Matrix - weak L Function manager Parme W Part time done part of the and not a bestede The coordinator P Matrie balanced Jouretion - Low to Moed M Parttime D Low to morate Parttime embedded in the functions as a and may not be designated obro The coordinator High to most time dewater to most romanager time Project-oriented Projet (composite hy Virtual Network structure with nodes at points of contact J E 1 z E D Low to moderate imeo Dome Low to Med could be tume forme Hybrid Mis of the Med Mixed Med Med Med Hinto a most total Poet maar PMO" Mother Puntime 1-36 High to most totaluome designated obro








