Question: Lab 2: Functions For this lab, you will use the two functions f(x) = 3r4 +5 and g(1) = 7x+10. You will write two functions

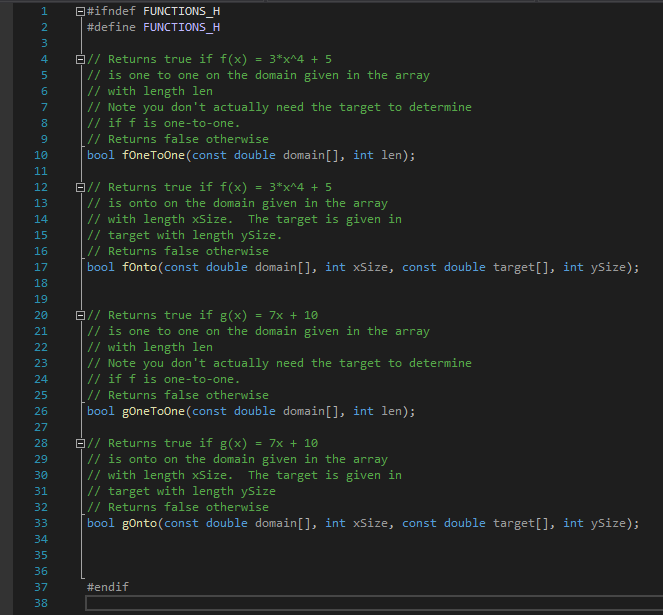
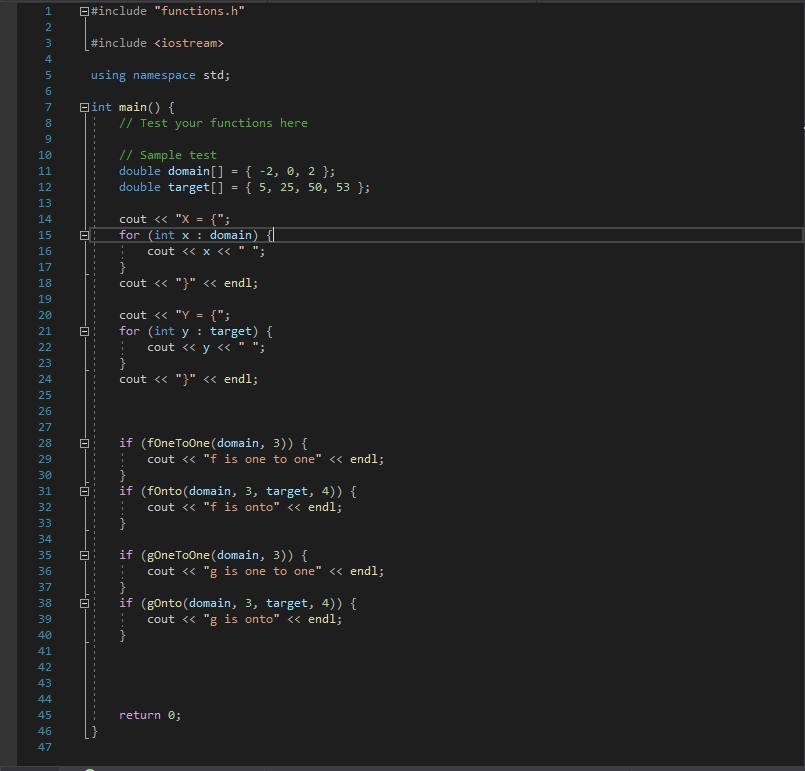
Lab 2: Functions For this lab, you will use the two functions f(x) = 3r4 +5 and g(1) = 7x+10. You will write two functions for f and two functions for g that will determine if each function is one-to-one or onto on the given domain. Functions You should implement the following functions: fOneToOne:Takes an array of doubles and the length of the array. It returns true if f, as defined above, is one-to-one on that particular domain. fonto:Takes two arrays of doubles and the length of each array. The first array is the domain: the second array is the target. It returns true if f, as defined above, is onto on that particular domain and target. gOneToOne:Takes an array of doubles and the length of the array. It returns true if g, as defined above, is one-to-one on that particular domain. gOnto:Takes two arrays of doubles and the length of each array. The first array is the domain; the second array is the target. It returns true if g, as defined above, is onto on that particular domain and target. The function declarations are given in functions.h. Do not modify the function signa- tures. Do not add other functions. I've also given you a main function that contains a sample test. Be sure to test your functions thoroughly. Hints . You'll probably want to store the output of the function and then check that the output matches the desired property. You can use an array or a vector to store the output. You can assume the parameters won't have any more than 20 elements. You can use the pow function from the math header The const array just means you can't modify that array. You don't have to implement anything specific in main. You won't turn in that file. Use it to test your functions. #ifndef FUNCTIONS_H #define FUNCTIONS_H // Returns true if f(x) = 3*x^4 + 5 // is one to one on the domain given in the array // with length len // Note you don't actually need the target to determine // if f is one-to-one. // Returns false otherwise bool foneToOne (const double domain[], int len); // Returns true if f(x) = 3*x^4 + 5 // is onto on the domain given in the array // with length xSize. The target is given in // target with length ysize. [// Returns false otherwise bool fonto(const double domain[], int xSize, const double target[], int ySize); 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 // Returns true if g(x) = 7x + 10 | 11 is one to one on the domain given in the array // with length len // Note you don't actually need the target to determine // if f is one-to-one. // Returns false otherwise bool gOneToOne(const double domain[], int len); // Returns true if g(x) = 7x + 10 // is onto on the domain given in the array // with length xSize. The target is given in // target with length ySize // Returns false otherwise bool gonto(const double domain[], int xSize, const double target[], int ySize); #endif #include "functions.h" #include
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


