Question: LAB 5: Acceleration of gravity Objectives: 1) we will analyze constant acceleration motion. 2) We will find experimentally the magnitude of the acceleration due to
LAB 5: Acceleration of gravity
Objectives:
1) we will analyze constant acceleration motion.
2) We will find experimentally the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravitational force (acceleration of free fall).
Introduction
When an object moves under the influence of gravity only, its motion is called free fall. Near the Earth's surface acceleration of free fall is about g = 9.80 m/s2. Its direction is downward.
A ball dropped from small heights can be considered as being in free fall since the air drag force is much smaller than its weight at small speeds. In today's experiment, we will examine how a ball moves in a free fall and determine from the analysis the experimental value of g.
Calculation of g
For an object that starts from rest and speeds up at a constant rate (constant acceleration), the distance covered (d) the object covers depends on time (t) as a quadratic function:
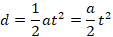
= at 2 2\f
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


