Question: Language C CostOfDriving.c #include // main function definition. Execution begins here. int main( void ) { float dailyMiles; // float variable for storing the miles
Language C


CostOfDriving.c
#include// main function definition. Execution begins here. int main( void ) { float dailyMiles; // float variable for storing the miles driven per day. float costPerGallon; // float variable for storing the cost per gallon of gasoline. float milesPerGallon; // float variable for storing the miler per gallon obtained by the vehicle. float dailyParking; // float variable for storing daily parking fees. float dailyTolls; // float variable for storing daily tolls. float dailyCostOfDriving; // float variable for storing the total daily cost of driving. // The printf and scanf statements below prompt for each of the five values we need to obtain from the user, // then store the user's information in the associated variable. // Because we are reading in float data, we use the conversion specifier %f for a floating point value. // If we were instead using integers, it would be %d. // The lack of that follows each prompt means the insertion point is left after the question, and so // the user enters their values on the same line. To make this look a little nicer, I leave a single space // after each question mark. printf("How many miles do you drive daily? "); scanf("%f", &dailyMiles); printf("How much does gas cost per gallon? "); scanf("%f", &costPerGallon); printf("How many miles per gallon does your vehicle get? "); scanf("%f", &milesPerGallon); printf("How much do you spend on parking fees daily? "); scanf("%f", &dailyParking); printf("How much do you spend on road tolls daily? "); scanf("%f", &dailyTolls); // The following statement calculates the daily cost of driving. The formula for obtaining this information is: // daily parking fees + daily tolls + (the cost of gas per gallon * the numbers of gallons used per day). // The number of gallons used per day is, in turn, the result of dividing the miles driven per day by the MPG of the vehicle. dailyCostOfDriving = dailyParking + dailyTolls + (costPerGallon * (dailyMiles / milesPerGallon)); // We use puts to print out the next string, as it automatically includes the new line. puts("Calculating your total daily cost of driving..."); // The following statement displays the actual formula being used, substituting in the values for the five variables. // Because all of our variables are floats, we use the %f conversion specifier here. // In the printf statements below, the conversion specifiers are more complicated than the ones we've seen. // Because we are working with currency, we want to restrict the output to two decimal places. // The %f conversion specifiers becomes %.2f to indicate that we only want two decimal places visible. // You will NOT need to use syntax similar to this in your lab. Your conversion specifiers will be the basic ones we've discussed. printf("%.2f + %.2f + (%.2f * (%.2f / %.2f)) ", dailyParking, dailyTolls, costPerGallon, dailyMiles, milesPerGallon); // And, finally, we print out the daily cost of driving. printf("Your total daily cost of driving is $%.2f", dailyCostOfDriving); printf(" "); return 0; } // end of the main function
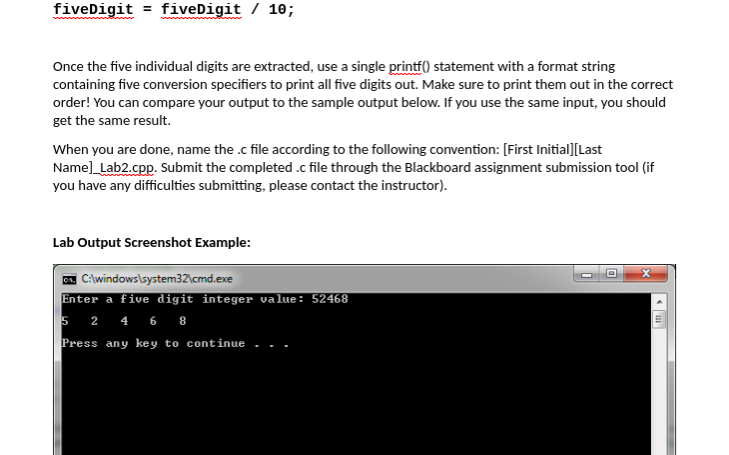
In this lab, you will experiment more with basic console output using printf, user input via scanf_s, and variable declaration and assignment via arithmetic expressions and the assignment operator EXAMPLE PROGRAM The sample program for this lab is a simple calculator to determine your total cost of driving per day. It asks the user to enter five values, and then uses those values to calculate the total cost. We use float variables to store these values, because we want to be able to support fractional parts (less than whole dollar amounts) Download the CostofDriving.c source file, create a project in Visual Studio, and add the source file to your project. The one provided is similar, but not identical to, the one completed in the demo video. Take some time to explore it and understand what is going on, and I encourage you to make changes and see what happens. When you feel confident, proceed to your program below. YOUR PROGRAM Now you will write code that is similar to what you have just seen. This is the code that you will submit to be graded for this lab. Create a new source file for this lab. For your lab, you will write a program that allows the user to enter a five-digit integer (for now, we will assume the user gives us the correct number of digits when requested). After storing the user's input in an integer variable, you will use the arithmetic operators (specifically division and modulus) to extract the five individual values from the number, and print them out, separated by 3 spaces each. While it is possible to achieve this goal without storing the individual digits, for the purposes of this lab you should create five additional integer variables to store the digits. As you remove digits from the number, you should store the values in the corresponding variable that you created. Names for these variables are up to you, but remember to follow meaningful naming conventions. For the right-most digit, as an example, you might choose "ones", to signify that it is the ones place In order to extract the digits, you will use a combination of the modulus and division operators. First, take the modulus of the number divided by 10, which will extract the ones place. Then, divide the number by 10 to remove the ones place entirely (we are exploiting the behavior of integer division truncating fractional components to achieve this goa 89503 % 10-3 89503/10 8950 8950 % 10-0 8950 10 895 and so on TIP: You can use the value of a variable as part of an expression in an assignment statement to that same variable. The expression will use its original value, and the result of that expression will overwrite the previous value with the new value. In this way, you can continually update the variable that stores the user input, instead of needing to create new variables at each step. See the example syntax below. int fiveDigit - 895e3; fiveDigit fiveDigit / 10; Once the five individual digits are extracted, use a single printf0 statement with a format string containing five conversion specifiers to print all five digits out. Make sure to print them out in the correct order! You can compare your output to the sample output below. If you use the same input, you should get the same result. When you are done, name the .c file according to the following convention: [First Initial] [Last Name]_Lab2.cpp. Submit the completed .c file through the Blackboard assignment submission tool (if you have any difficulties submitting, please contact the instructor) Lab Output Screenshot Example: Enter a five digit integer value: 52468 Press any key to continue
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


