Question: language is java Restrictions: You are not allowed to use anything from the String, StringBuilder, or Wrapper classes. In general, you may not use anything
language is java
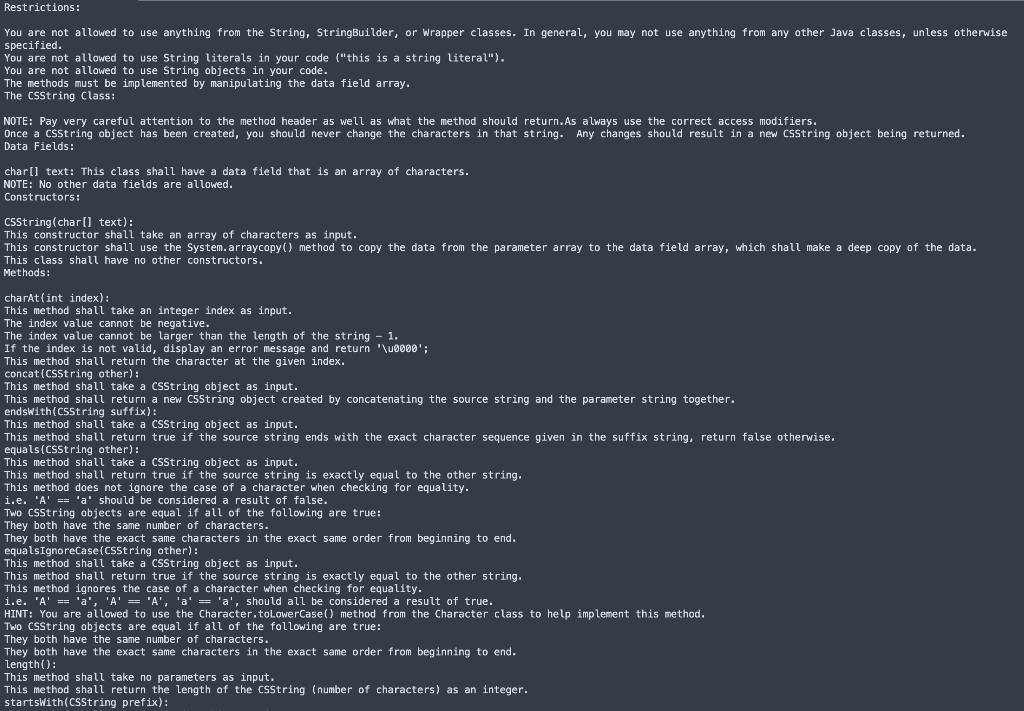
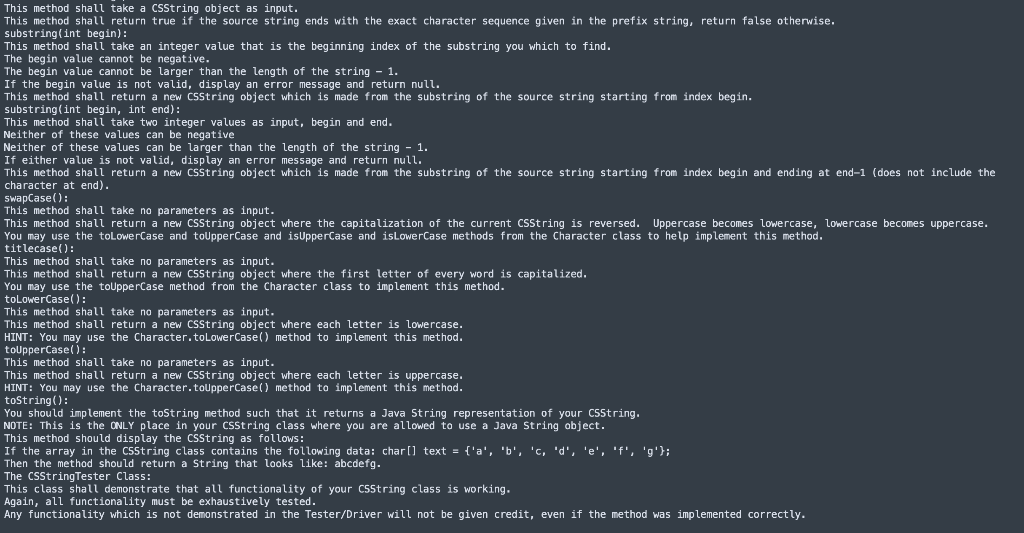
Restrictions: You are not allowed to use anything from the String, StringBuilder, or Wrapper classes. In general, you may not use anything from any other Java classes, unless otherwise specified. You are not allowed to use String literals in your code ("this is a string literal"). You are not allowed to use String objects in your code. The methods must be implemented by manipulating the data field array, The CSString Class: NOTE: Pay very careful attention to the method header as well as what the method should return. As always use the correct access modifiers, Once a CSString object has been created, you should never change the characters in that string. Any changes should result in a new CSString object being returned. Data Fields: char[] text: This class shall have a data field that is an array of characters. NOTE: No other data fields are allowed. Constructors: CSString(charl] text): This constructor shall take an array of characters as input. This constructor shall use the System. arraycopy() method to copy the data from the parameter array to the data field array, which shall make a deep copy of the data. This class shall have no other constructors. Methods: charAt(int index): This method shall take an integer index as input. The index value cannot be negative. The index value cannot be larger than the length of the string 1. If the index is not valid, display an error message and return '\00000': This method shall return the character at the given index. concat(CSString other): This method shall take a CSString object as input. This method shall return a new CSString object created by concatenating the source string and the parameter string together. endsWith(CSString suffix): This method shall take a CSString object as input. This method shall return true if the source string ends with the exact character sequence given in the suffix string, return false otherwise, equals(CSString other): This method shall take a CSString object as input. This method shall return true if the source string is exactly equal to the other string, This method does not ignore the case of a character when checking for equality. i.e. 'A' == 'a' should be considered a result of false. TWO CSString objects are equal if all of the following are true! They both have the same number of characters. They both have the exact same characters in the exact same order from beginning to end. equalsIgnoreCase (CSString other): This method shall take a csString object as input. This method shall return true if the source string is exactly equal to the other string. This method ignores the case of a character when checking for equality. 1.e. 'A' == 'a', 'A' == 'A', 'a' == 'a', should all be considered a result of true. HINT: You are allowed to use the Character.toLowerCase() method from the Character class to help implement this method. TWO CSString objects are equal if all of the following are true: They both have the same number of characters. They both have the exact same characters in the exact same order from beginning to end. Length(): This method shall take no parameters as input. This method shall return the length of the csString (number of characters) as an integer. startsWith(CSString prefix): This method shall take a CSString object as input, This method shall return true if the source string ends with the exact character sequence given in the prefix string, return false otherwise, substring(int begin): This method shall take an integer value that is the beginning index of the substring you which to find. The begin value cannot be negative. The begin value cannot be larger than the length of the string - 1. If the begin value is not valid, display an error message and return null. This method shall return a new CSString object which is made from the substring of the source string starting from index begin. substring(int begin, int end) : This method shall take two integer values as input, begin and end. Neither of these values can be negative Neither of these values can be larger than the length of the string - 1. If either value is not valid, display an error message and return null. This method shall return a new csString object which is made from the substring of the source string starting from index begin and ending at end-1 (does not include the character at end). SwapCase(): This method shall take no parameters as input. This method shall return a new CSString object where the capitalization of the current CSString is reversed. Uppercase becomes lowercase, Lowercase becomes uppercase. You may use the toLowerCase and toUpperCase and is Uppercase and is LowerCase methods from the Character class to help implement this method. titlecase(): This method shall take no parameters as input. This method shall return a new CSString object where the first letter of every word is capitalized. You may use the touppercase method from the Character class to implement this method. toLowerCase(): This method shall take no parameters as input. This method shall return a new CSString object where each letter is lowercase. HINT: You may use the Character.toLowerCase() method to implement this method. toupperCase(): This method shall take no parameters as input. This method shall return a new CSString object where each letter is uppercase, HINT: You may use the Character.toupperCase() method to implement this method. toString(): You should implement the toString method such that it returns a Java String representation of your C55tring, NOTE: This is the ONLY place in your CSString class where you are allowed to use a Java String object. This method should display the CSString as follows: If the array in the C55tring class contains the following data: charl) text = ['a', 'b', 'c, 'd', 'e', 'f', '': Then the method should return a String that looks like: abcdefg. The CSStringTester Class: This class shall demonstrate that all functionality of your csString class is working. Again, all functionality must be exhaustively tested. Any functionality which is not demonstrated in the Tester/Driver will not be given credit, even if the method was implemented correctly
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


