Question: LD- B . $ % 9 BIU AAE *E-AA- pard Font Format as Table Cell Styles - Alignment Number Styles fa =B20/C35 Fixed Variable $2.30
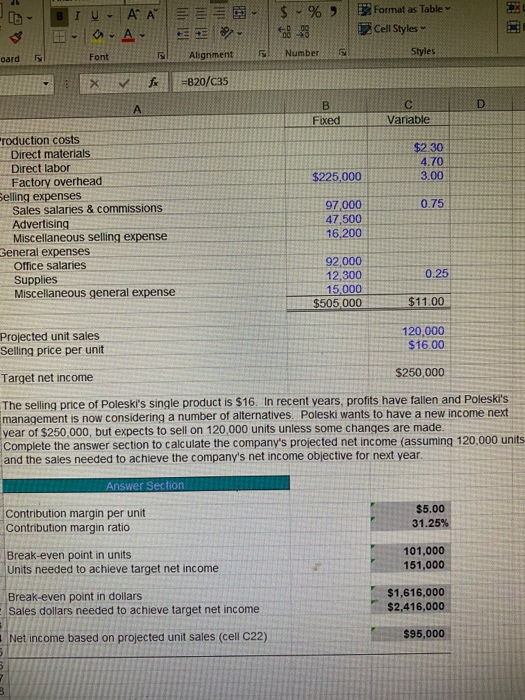
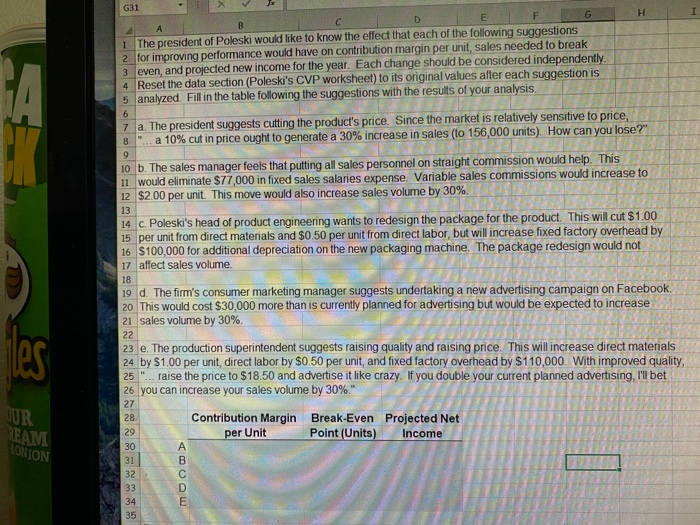
LD- B . $ % 9 BIU AAE *E-AA- pard Font Format as Table Cell Styles - Alignment Number Styles fa =B20/C35 Fixed Variable $2.30 4.70 3.00 $225,000 0.75 roduction costs Direct materials Direct labor Factory overhead Selling expenses Sales salaries & commissions Advertising Miscellaneous selling expense Beneral expenses Office salaries Supplies Miscellaneous general expense 97,000 47,500 16,200 92,000 12,300 15,000 $505 000 0.25 $11.00 Projected unit sales Selling price per unit 120,000 $16.00 Target net income $250,000 The selling price of Poleski's single product is $16. In recent years, profits have fallen and Poleski's management is now considering a number of alternatives Poleski wants to have a new income next year of $250,000, but expects to sell on 120,000 units unless some changes are made. Complete the answer section to calculate the company's projected net income (assuming 120,000 units and the sales needed to achieve the company's net income objective for next year. Answer Section Contribution margin per unit Contribution margin ratio $5.00 31.25% Break-even point in units Units needed to achieve target net income 101.000 151,000 Break-even point in dollars Sales dollars needed to achieve target net income $1,616,000 $2,416,000 Net income based on projected unit sales (cell C22) $95,000 Bco ELF G H 1 The president of Poleski would like to know the effect that each of the following suggestions 2 for improving performance would have on contribution margin per unit, sales needed to break 3 leven, and projected now income for the year. Each change should be considered independently 4 Reset the data section (Poleski's CVP worksheet) to its original values after each suggestion is 5 analyzed. Fill in the table following the suggestions with the results of your analysis 7 a. The president suggests cutting the product's price. Since the market is relatively sensitive to price, 8 "...a 10% cut in price ought to generate a 30% increase in sales (to 156,000 units) How can you lose?" 10 b. The sales manager feels that putting all sales personnel on straight commission would help. This 11 would eliminate $77,000 in fixed sales salaries expense. Variable sales commissions would increase to 12 $2.00 per unit. This move would also increase sales volume by 30% 14 C. Poleski's head of product engineering wants to redesign the package for the product. This will cut $1.00 15 per unit from direct materials and $0.50 per unit from direct labor, but will increase fixed factory overhead by 16 $100,000 for additional depreciation on the new packaging machine. The package redesign would not 17 affect sales volume. 19 d. The firm's consumer marketing manager suggests undertaking a new advertising campaign on Facebook 20 This would cost $30,000 more than is currently planned for advertising but would be expected to increase 21 sales volume by 30% 22 23 e. The production superintendent suggests raising quality and raising price. This will increase direct materials 24 by $1.00 per unit, direct labor by $0.50 per unit, and fixed factory overhead by $110,000. With improved quality. 25 raise the price to $18.50 and advertise it like crazy. If you double your current planned advertising, I bet 26 you can increase your sales volume by 30%. JUR TEAM Contribution Margin per Unit Break-Even Projected Net Point (Units) Income LONTON
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


