Question: Learning Objectives 2: Recall which vitamins work together to maintain physiological functions. 6: Recall the effects of megadoses of vitamins. 7: Recall the effects of

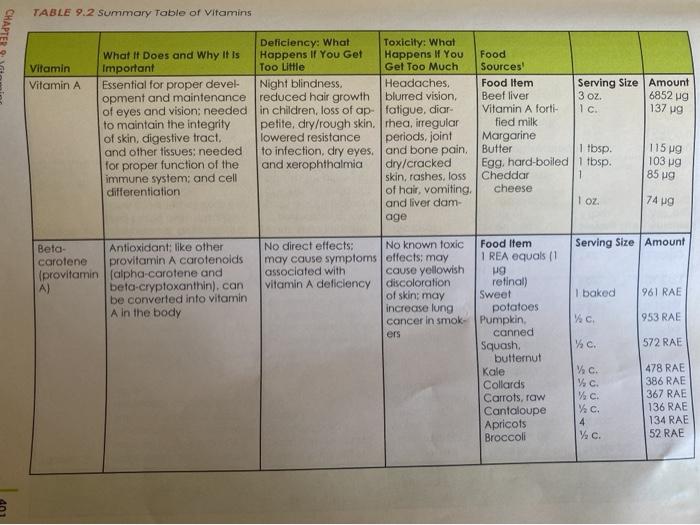
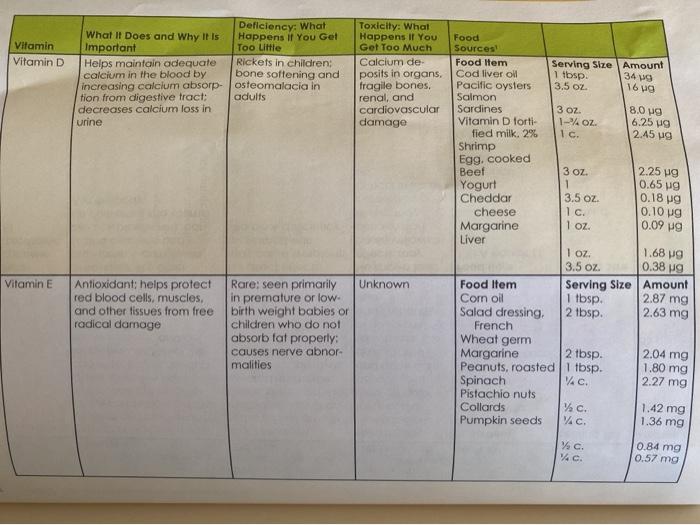
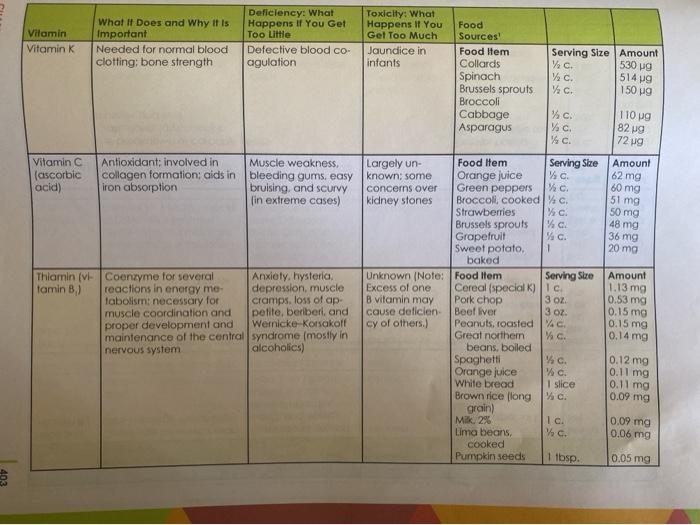
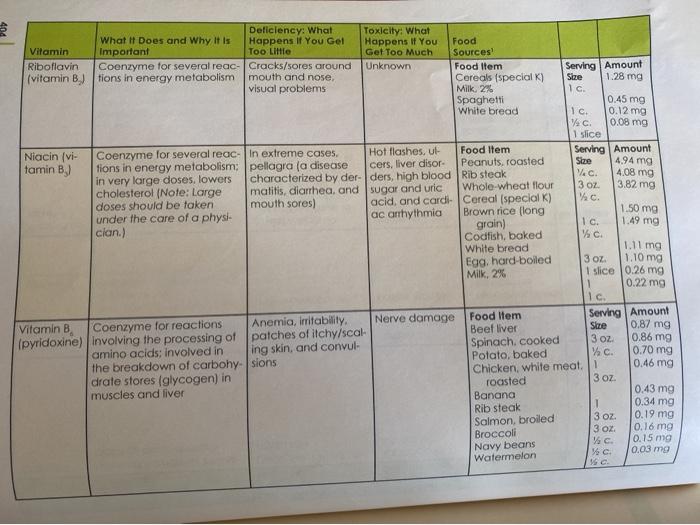
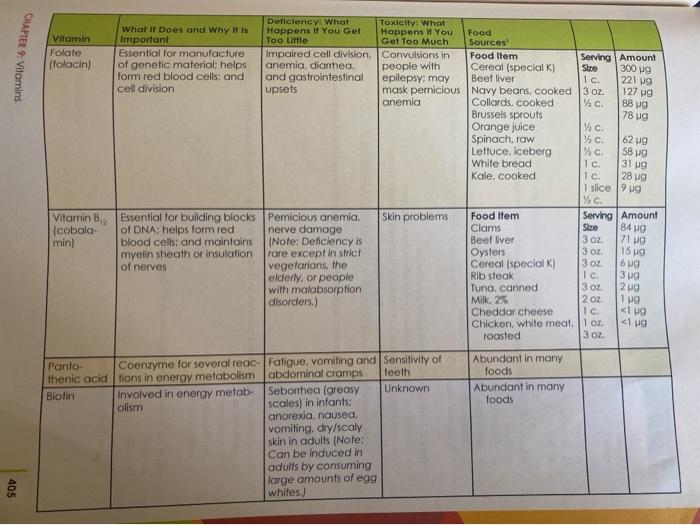
Learning Objectives 2: Recall which vitamins work together to maintain physiological functions. 6: Recall the effects of megadoses of vitamins. 7: Recall the effects of deficiency for each fat and water soluble vitamin and describe each deficiency condition. While you won't be reporting on or analyzing all these learning objectives, please keep them in mind as you assess the vitamin claim ad you're analyzing. 1. Find an advertisement about a vitamin supplement or product that makes a nutritional claim about a vitamin 2. Discuss the claim, giving information that supports or discredits the claim based on information about that vitamin from our text book. Be sure to focus on factual information about that vitamin(s) in relationship to the claim made in the ad. If you are evaluating a vitamin from a supplement, please list the potency for the vitamin/s in that particular supplement. Since some vitamins have an UL (Upper Limit) and can be toxic, be sure to include that in your analysis. For example, if your product has a large amount of Vitamin D, pay attention to the amount contained in the supplement, as Vitamin D has an UL of 2000 I.U. TABLE 9.2 Summary Table of Vitamins CHAPTER Vitamin Vitamin A 3 oz. I c 6852 137 g Deficiency: What Toxicity: What What It Does and Why It is Happens If You Get Happens If You Food Important Too Little Gel Too Much Sources Essential for proper devel- Night blindness Headaches, Food Item Serving Size Amount opment and maintenance reduced hair growth blurred vision, Beef liver of eyes and vision: needed in children, loss of ap fatigue, dior Vitamin A forti- to maintain the integrity petite, dry/rough skin. rhea, irregular fied milk of skin, digestive tract, lowered resistance periods, joint Margarine and other tissues: needed to infection, dry eyes, and bone pain. Butter for proper function of the and xerophthalmia dry/cracked Egg, hard-boiled 1 tbsp. immune system and cell skin, rashes, loss Cheddar 1 differentiation of hair, vomiting, cheese and liver dam- 1 oz. age 1 tbsp. 115 g 1039 85 ug 74 g Serving Size Amount Beta- Antioxidant: like other carotene provitamin A carotenoids (provitamin (alpha-carotene and A) beta-cryptoxanthin), can be converted into vitamin A in the body I baked 961 RAE (1/C. 953 RAE ers No direct effects: No known toxic Food Item may cause symptoms offects: may 1 REA equals (1 associated with cause yellowish vitamin A deficiency discoloration retinal) of skin may Sweet increase lung potatoes cancer in smok- Pumpkin canned Squash butternut Kale Collards Carrots, raw Cantaloupe Apricots Broccoli 11/2c. 572 RAE c WC W c. Y c. 4 478 RAE 386 RAE 367 RAE 136 RAE 134 RAE 52 RAE Wc Vitamin Vitamin D Deficiency: What What It Does and Why It Is Happens if You Get Important Too Little Helps maintain adequate Rickets in children calcium in the blood by bone softening and increasing calcium absorp- osteomalacia in tion from digestive tract: adults decreases calcium loss in urine Toxicity: What Happens If You Get Too Much Calcium de posits in organs. fragile bones, renal, and cardiovascular damage 16 g Food Sources Food Item Serving Size Amount Cod liver oll 1 tbsp. 1340g Pacific oysters 3.5 Oz. Salmon Sardines 3 OZ. 8.0 g Vitamin D forti 1-4 OZ. 6.25 g fied milk. 2% Ic. 2.45 ug Shrimp Egg, cooked Beef 3 Oz 2.25 g 1 0.65 g Yogurt Cheddar 3.5 oz 0.18 cheese 10 0.10 g Margarine 1 oz 0.09 g Liver 1 oz. 1.68 g 3.5 oz 0.38 Food Item Serving Size Amount Com oil 1 tbsp. 2.87 mg Salad dressing 2 tbsp. 2.63 mg French Wheat germ Margarine 2 tbsp. 2.04 mg Peanuts, roasted 1 tbsp. 1.80 mg Spinach VAC 2.27 mg Pistachio nuts Collards % c. 1.42 mg Pumpkin seeds VAC 1.36 mg c. 0.84 mg 14c 0.57 mg Vitamin E Unknown Antioxidant: helps protect red blood cells, muscles. and other issues from free radical damage Rare: seen primarily in premature or low. birth weight babies or children who do not absorb fat properly; Causes nerve abnor malities Vitamin Vitamin K What If Does and Why it is Important Needed for normal blood clotting; bone strength Deficiency: What Happens If You Get Too Little Defective blood co- agulation 110 pg 82 g 72 9 Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) Antioxidant; involved in collagen formation: aids iron absorption Muscle weakness, bleeding gums. easy bruising, and sCurvy in extreme cases) Toxicity: What Happens If You Food Gel Too Much Sources Jaundice in Food Item Serving Size Amount infants Collards Yc 530 g Spinach W c. 5149 Brussels sprouts c 150 g g Broccoli Cabbage % c. Asparagus % Largely un- Food Item Serving Size Amount known: some Orange juice VC concerns over Green peppers c kidney stones Broccoli, cooked Strawberries %c. Brussels sprouts Y Grapefruit %c. Sweet potato, 1 baked Unknown (Note: Food Item Serving Size Amount Excess of one Cereal (specialK) Ic 1.13 mg B vitamin may Pork chop 3 OZ. 0.53 mg cause deficien Beef liver 0.15 mg cy of others.) Peanuts, roasted VG. 0.15 mg Great northern 0.14 mg beans, boiled Spaghetti c. 0.12 mg Orange juice %c. 0.11 mg White bread 1 slice Brown rice flong % 0. 0.09 mg grain) Milk, 2% 1 c. Lima beans /c. 0.06 mg cooked Pumpkin seeds 0.05 mg 62 mg 60 mg 51 mg 50 mg 48 mg 36 mg 20 mg Thiamin (v Coenzyme for several Anxiety, hysteria tamin B.) reactions in energy me depression, muscle labolism: necessary for cramps, loss of ap. muscle coordination and petite, berberi, and proper development and Wernicke Korsakoff maintenance of the central syndrome (mostly in nervous system alcoholics) 3 Oz 0.11 mg 0.09 mg 1 tbsp. 1/C. 1.50 mg 1.49 mg Deficiency: What Toxicity: What What It Does and Why It Is Happens If You Get Happens If You Food Vitamin Important Too Little Get Too Much Sources Riboflavin Coenzyme for several reac-Cracks/sores around Unknown Food Item Serving Amount (vitamin B tions in energy metabolism mouth and nose, Cereals (special) Stre 1.28 mg visual problems Milk. 2% 10 Spaghetti 0.45 mg White bread 1 c. 0.12 mg VC 0.08 mg 1 slice Niacin (vi- Coenzyme for several reac- in extreme cases, Hot flashes. Food Item Serving Amount Size tamin B.) cers, liver disor Peanuts roasted 4.94 mg tions in energy metabolism; pellagra (a disease Vec. characterized by derders, high blood Rib steak 4,08 mg in very large doses, lowers 3 OL Whole-wheat flour cholesterol (Note: Large matitis, diarrhea, and sugar and uric 3.82 mg doses should be taken mouth sores) acid, and cardi Cereal (special K) under the care of a physi- ac arrhythmia Brown rice (long grain) 1 c. clan.) Codfish, baked 1/2 c. White bread 1.11 mg Egg, hard-boiled 3 Oz 1.10 mg Milk, 2% 1 slice 0.26 mg 1 0.22 mg 1 c Nerve damage Food Item Serving Amount Anemia, irritability, Vitamin B. Coenzyme for reactions Size Beef liver 0.87 mg (pyridoxine) involving the processing of patches of itchy/scal |3oz Spinach, cooked 0.86 mg amino acids: Involved in ing skin, and convul- Potato, baked c. 0.70 mg the breakdown of carbohysions Chicken, white meat. 0.46 mg drate stores (glycogen) in roasted 3 Oz muscles and liver Banana 0.43 mg 1 Rib steak 0.34 mg Salmon, broiled 3 oz 0.19 mg Broccoli 3 OZ 0.16 mg VC 0.15 mg Navy beans Wc 0.03 mg Watermelon We CHAPTER 9: Vitamins 221 g 127 g 88 9 78 g g VC Wc Deficiency: What Toxicity: What What It Does and Why It Is Happens If You Get Happens If You Food Vitamin Important Too Little Get Too Much Sources Folate Essential for manufacture Impaired cell division. Convulsions in Food Item Serving Amount Yolacin) of genetic material: helps anemia, diarrhea people with Cereal (special ) Size 300 g form red blood cells: and and gastrointestinal epilepsy: may Beef liver 16. cell division upsets mask pernicious Navy beans, cooked 3 oz. anemia Collards, cooked Wc Brussels sprouts Orange juice c. Spinach, raw Lettuce, iceberg White bread 10. Kale, cooked 1 c. 1 slice 9 ug Yc Vitamin B, Essential for building blocks Pemicious anemia. Skin problems Food Item Serving Amount (cobala Size of DNA helps form red nerve damage Clams min) blood cells and maintains (Note: Deficiency is Beef liver 3 Oz myelin sheath or insulation Tore except in strict Oysters 3oz of nerves vegetarians, the Cereal (special) 3. OZ elderly, or people Rib steak I c. with malabsorption Tuna, canned disorders.) Milk. 296 2 oz Cheddar cheese Ic. Chicken, white meat.1 oz roasted 3 02. 62 wg 58 19 31 g 28 g 84 wg 71 g 15 6 g 3 g 2 g 19
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


