Question: Let f : R2 > R be defined by f(x, y) = x4 - y3 - 2x2 + 3y a) Find the critical point of



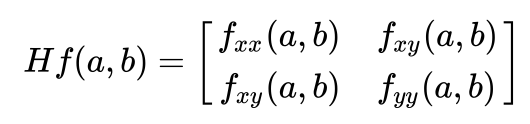


Let f : R2 > R be defined by f(x, y) = x4 - y3 - 2x2 + 3y a) Find the critical point of f, and identify them as a local minimum, maximum, and saddle points. b) Let S be the region in the xy-plane that lies inside the pentagon with vertices at (0,-1.5), (0,1), (1,1)l (15,0) and (15,-1.5). Find the global maximum and minimum values of f on S and the points at which they occur. Mark these points in a sketch of S. Example 4 Find and classify all critical points of the function f(x, y) = 23 - 4x2 + 4x - 4xy2. Solution: To find the critical points we solve the system 0 = fx(x, y) = 3x2- 8x + 4 - 4y 0 = fy(x, y) = -8xy From (**) we get that x = 0 or y = 0. If a = 0, then (*) gives 0 = 4 - 4y which then implies y = 11. If y = 0, then (*) gives 0 = 3x2 - 8x + 4 = (3x - 2) (x - 2) which then implies x = 2 and x = 2/3. Hence, we have critical points (0, 1), (0, -1), (2, 0), and (2/3, 0). The second partial derivatives are far (x, y) = 6x - 8, fry(x, y) = -8y, fy(x,y) = -8x At (2/3, 0), the Hessian matrix is Hf(2/3, 0) = -4 0 0 -16/3 , which is negative definite since the 16 corresponding quadratic form is Q(u, v) = -4u2 - U2. Thus, by the second partial derivative test, (2/3, 0) is a local maximum point. At (0, 1), we get H f(0, 1) = -8 -8 -8 0 . So det H f(0, 1) = -64 0 for all (u, v) * (0, 0), then Q(u, v) is positive definite. 2. If Q(u, v) 0 for some (w, z), then Q(u, v) is indefinite. 4. If Q(u, v) does not belong to classes 1) to 3), then Q(u, v) is semidefinite. Semidefinite quadratic forms may be split into two classes: a. If Q(u, v) 2 0 for all (u, v), then Q(u, v) is positive semidefinite. b. If Q(u, v) 0, for all (u, v) * (0, 0). B = 2 0 0 -3 is indefinite, since the associated quadratic form Q(u, v) = 2u2 - 302, and Q(u, 0) = 2u" > 0 for u * 0, and Q(0, v) = -302
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


