Question: .......... Let O be a Bernoulli random variable that indicates which one of two hypotheses is true, and let P (0 = 1) = p.
..........
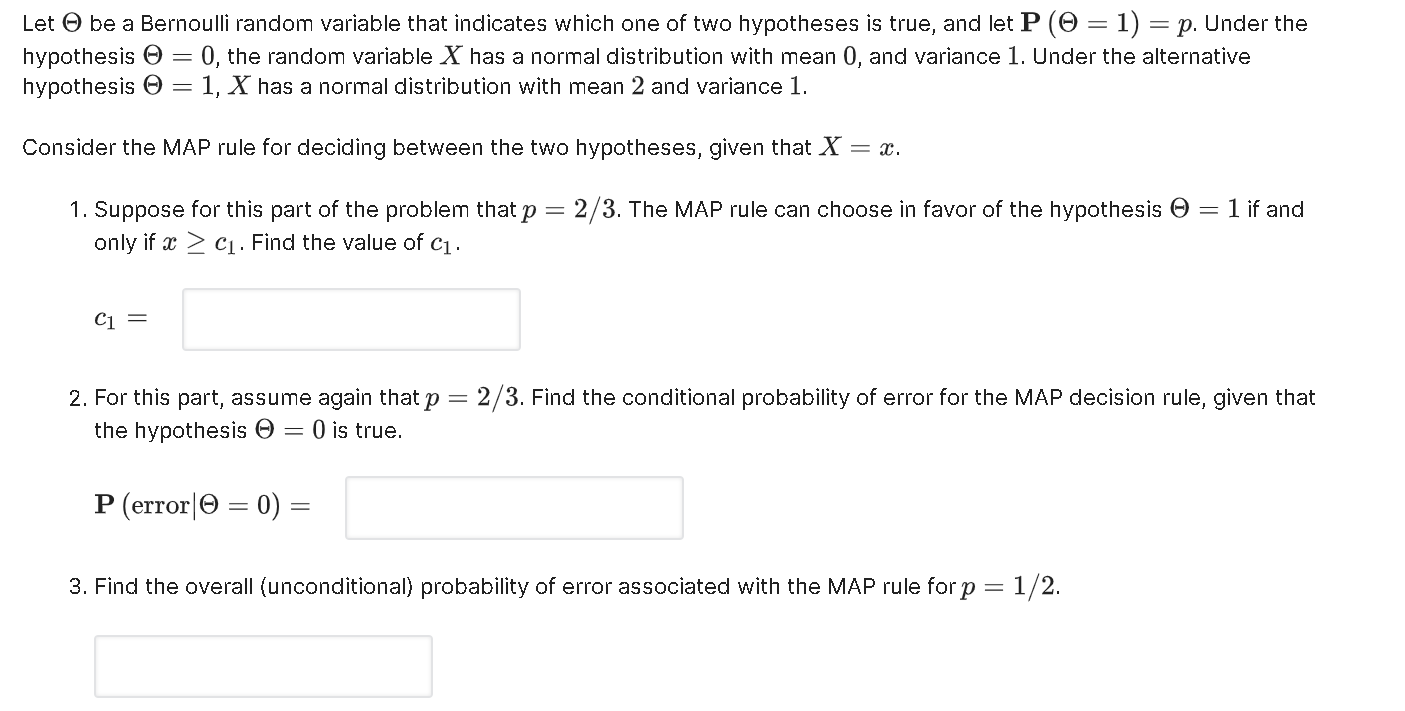
Let O be a Bernoulli random variable that indicates which one of two hypotheses is true, and let P (0 = 1) = p. Under the hypothesis O = 0, the random variable X has a normal distribution with mean 0, and variance 1. Under the alternative hypothesis O = 1, X has a normal distribution with mean 2 and variance 1. Consider the MAP rule for deciding between the two hypotheses, given that X = x. 1. Suppose for this part of the problem that p = 2/3. The MAP rule can choose in favor of the hypothesis O = 1 if and only if a > C1. Find the value of c1. C1 2. For this part, assume again that p = 2/3. Find the conditional probability of error for the MAP decision rule, given that the hypothesis O = 0 is true. P (error | 0 = 0) = 3. Find the overall (unconditional) probability of error associated with the MAP rule for p = 1/2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


