Question: Let p be a positive integer. Recall that Zp = {0, 1,...,p-1} where addition and multiplication are mod p (i.e. p = 0 and
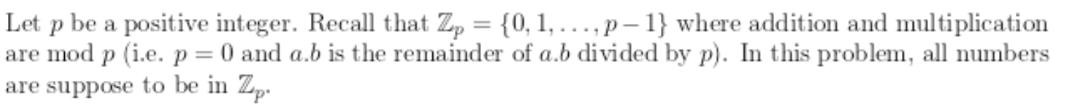

Let p be a positive integer. Recall that Zp = {0, 1,...,p-1} where addition and multiplication are mod p (i.e. p = 0 and a.b is the remainder of a.b divided by p). In this problem, all numbers are suppose to be in Zp. Show that if p is not prime, then there is a, b 0 such that a.b = 0. Show that if p is prime then, for all a, b 0 such that a.b #0 Show that if p is prime, a a' Zp and be Zp, b.ab.a', suppose b is not zero. Show that if p is prime, for all b Zp the map aab is a bijection from Zp to Zp. suppose b is not zero. E Show that if p is prime, we can define a division operation in Zp, i.e. to each a, b 0 there is a number (alb) Zp such that b.(a/b) = a). How many solutions does the following system have in Z5. Give the solution set using parameters. 2x1 + 2x-x3 = 2 3x1 - 22+4x3 = 3 What would be the issue to apply Gauss Jordan with this system in Z6?
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Here are the proofs of the statements about properties of prime numbers p in the ring Zp 1 Show that if p is not prime then there is ab 0 such that ab ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


