Question: Let the operator: R=uu(Ri=ijkujuk) where u is a unit vector (i.e.: unun=1 ) Use index notation to calculate the following: a) R(u[Tu]) b) (u[Tu])Ruu where
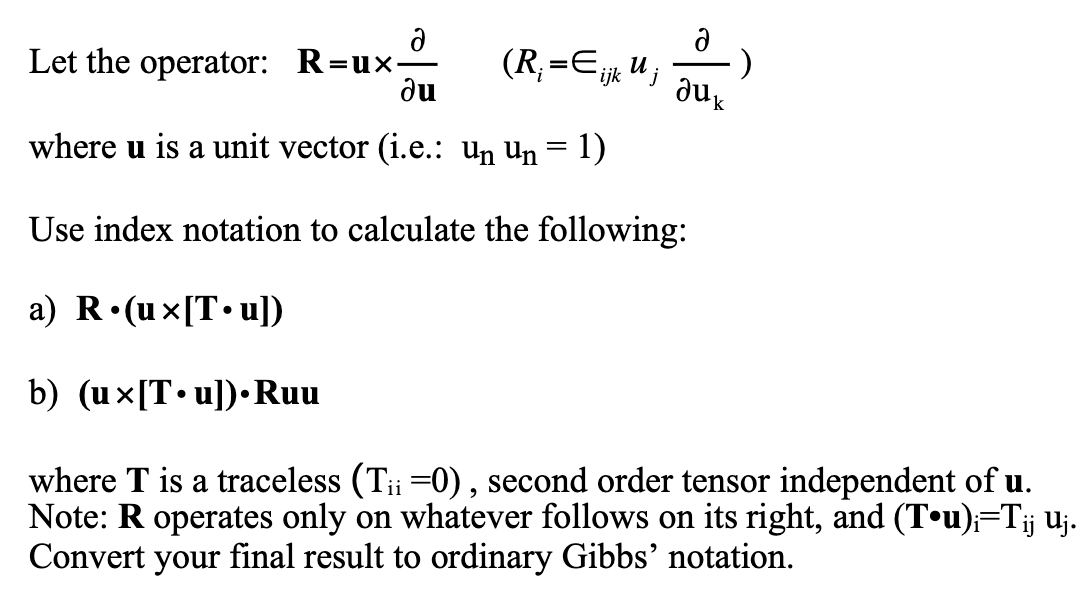
Let the operator: R=uu(Ri=ijkujuk) where u is a unit vector (i.e.: unun=1 ) Use index notation to calculate the following: a) R(u[Tu]) b) (u[Tu])Ruu where T is a traceless (Tii=0), second order tensor independent of u. Note: R operates only on whatever follows on its right, and (Tu)i=Tijuj. Convert your final result to ordinary Gibbs' notation. Let the operator: R=uu(Ri=ijkujuk) where u is a unit vector (i.e.: unun=1 ) Use index notation to calculate the following: a) R(u[Tu]) b) (u[Tu])Ruu where T is a traceless (Tii=0), second order tensor independent of u. Note: R operates only on whatever follows on its right, and (Tu)i=Tijuj. Convert your final result to ordinary Gibbs' notation
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


