Question: Let V be a two-dimensional vector space with basis (v1, v2), and T:V V the linear transformation such that T(v) 3v2v2, - = T(v2)
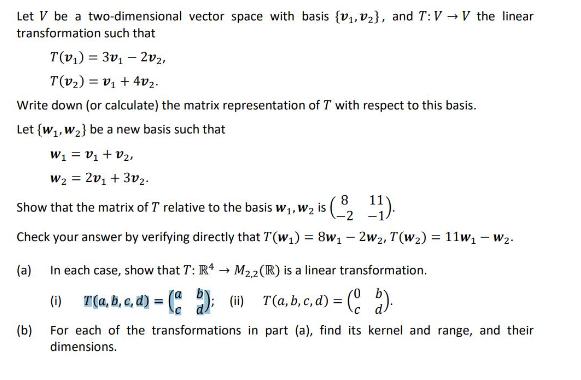
Let V be a two-dimensional vector space with basis (v1, v2), and T:V V the linear transformation such that T(v) 3v2v2, - = T(v2) v+4v2. = Write down (or calculate) the matrix representation of T with respect to this basis.. Let (w1, W2} be a new basis such that W = V + V2, W = 2v1 + 3v2. Show that the matrix of T relative to the basis w, W2 is ( 8 ). Check your answer by verifying directly that T(w) = 8w-2w2, T(w2) = 11w1 - W- (a) In each case, show that T: R4 M2,2 (R) is a linear transformation. (i) T (a, b, c, d) = (a); (ii) T(a,b,c,d) = ( (b). (b) For each of the transformations in part (a), find its kernel and range, and their dimensions.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


