Question: Let's compare PMO types and roles per your book, and consider the following question: Where do you see similarities and differences between the types and
Let's compare PMO types and roles per your book, and consider the following question:
Where do you see similarities and differences between the types and roles of the PMO?PMOTypesandRoles
TheliteraturesuggeststhatnotallPMOsarecreatedequalintermsoftheir types and the functions performed. The terms in some organiza-tions are used interchangeably to refer to activities that a PMO performs.Some organizations focus their PMO on only basic PMO-type func-tions; others are more mature with more advanced project and portfoliofunctions (Crawford 2004). Basic functions include: project method-ology, projectreporting, project tools, and project training. Advancedprojectandportfoliofunctionsinclude:portfolioanalysisandpriority,benefitrealization,andqualityriskmanagement.
The PMO often has a dual role of ensuring compliance in relation tousing the methodology, tools, and templates while also supporting indi-vidual business units. The PMO often monitors project progress andreports on this progress and accompanying risks to the organizations'senior managers. Another form of PMO finds the office actually manag-ing projects on behalf of the organization and forming project teams.In this structure, the PMO typically manages a project from initiationto closeout and is responsible for achieving successful project outcomes(Kerzner2004).
Letavec (2006) suggests that PMOs may work in any of the follow-ingroles:
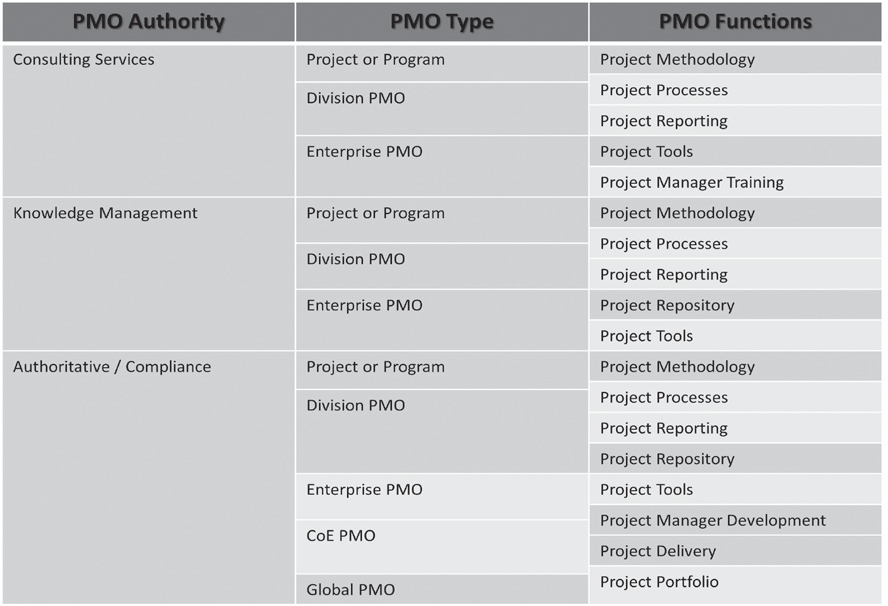
- ConsultingRole:advisortoproject/programteamsonhowtomanagetheirprojectsandprogramsthroughtoolsandmethodology
- KnowledgeManagementRole:capturerofproject-relatedinfor-mation,manageranddisseminatorofthisinformation
- ComplianceRole:setprocesses,tools,andreportingstandards
MANAGINGTHEPMOLIFECYCLE [17]
LightandBerg(2000)suggestthatPMOsmayhaveotherroles:
- ThePMOasarepository:custodianoftheprojectmethodologyandisnotinvolvedinthedecision-makingprocess
- The PMO as a coach:provides guidance on projects, performsproject reviews on request, establishes, supports project planning,monitorsandreportsonprojectsbutdoesnotordercorrectiveaction
- The PMO as manager:operates as an agent of senior management,manages the project portfolio, manages the master resource plan,reviewsprojectproposalsandisaccountablefortheportfolio
Kerzner(2004)detscribesthreetypesofPMOs.
- Functional PO:addresses functional area needs, such as IT typi-callyatthedepartmentallevel
- Customer Group PO:handles customer management and can actasacompanywithinacompany
- Corporate PO:services the entire organization and focuses on cor-poratestrategicalignment
Successful PMOs take on responsibility for different project-relatedfunctions and core tasks related to the development of shared methodol-ogy and processes for the handling of projects, training, and competencedevelopmentwithinprojectmanagement,proposingnewprojectsandquality assurance of projects. The success of a PMO is related to ensur-ingthenecessaryauthorityofthePMO?realorganizationalauthorityas well as academic and social credibility,top management support?and that the PMO covers true needs in the organization (Anderson etal.,2007).
Recent studies classify PMOs into two types: single-project organizationand multi-project organization. Within each are different setups, rangingfromaPMOcentralizedaroundasingleprojecttoacenterofexcellence
[18] WAFFA KARKUKLY, PH.D.
(CoE) that deals with many projects. Table 1.1 below illustrates thetype of functions performed and the expectations based on each type ofPMO. Each author has defined the type of PMO and different functionsfromtheperspectiveofanorganization'sneeds.
Table1.1TypesofPMOsandtheirroledefinitions
Author | PMO Type | Function/Role |
Hill(2004) | PO | Applies effective practices for project performance andoversightandemploysstandardlifecycleprocesseswhenavailable |
BasicPMO | Introducescriticalprocessesandpracticesofprojectmanagement | |
StandardPMO | Establishesandmonitorsuseofacompleteprojectmanagementmethodology | |
AdvancedPMO | Enhancescontentandmonitorsuseofacomprehensivemethodology | |
Center OfExcellence(CoE) | Analyzesprojectmanagementmethodologyandexaminesprocessvariationinbusinessunits | |
Rad andLevin(2002) | ProjectorProgram | Supportsasingleprojectoragroupofrelatedprojects |
DivisionPMO | Establishes standards and methodologies to follow inproject management, reviews and audits projects thatareunderway,andprovidesmentoringsupporttoprojectprofessionals | |
EnterprisePMO | Concerned with the enterprise of selection, prioritizing,andmonitoringthevaluefromtheorganization'sprojectportfolio |
MANAGINGTHEPMOLIFECYCLE [19]
Author | PMO Type | Function/Role |
Crawford(2002)w | Level1-PCO | Typicallyhandleslarge,complexsingleprojects(suchastheY2K project). It is focused specifically on one project, butthat one project is so large and so complex that it requiresmultiple schedules, which may need to be integrated intoanoverallprogramschedule. |
Level2 -BusinessUnitPO | The value of a level 2 PO is that it begins to integrateresourcesatanorganizationallevel.Theorganizationallevelis where resource control begins to play a much highervalueinthepaybackofaprojectmanagementsystem. | |
Level 3 -StrategicPO | Only a corporate-level organization can provide the coor-dinationandbroadperspectiveneededtoselect,prioritize,and monitor projects and programs that contribute toattaining corporate strategy, and this organization is thestrategicprojectoffice. | |
Kendalland Rollins(2003) | Repository | The PMO serves as a source of information on projects,methodology,andstandards.Thismodeloccursmostofteninorganizationsthatempowerdistributed,business-centricprojectownershiporthosewithweakcentralgovernance |
Coach | An extension of the Repository Model. It assumes awillingnesstosharesomeprojectmanagementpracticesacross functions and uses the PMO to coordinate thecommunication. | |
Enterprise | Thismodelusuallyimpliesamuchlargerinvestmentand,therefore, usually has a strongermission, charter, andsupport than the previous two models. The most consoli-dated version of this organizational model concentratesseniorprojectmanagementexpertiseandexecutionwithinthe PMO. Some or allproject managers are staffed withinthe shared service model and consigned to projects asneeded. This model assumes a governance process thatinvolvesthePMOinmostprojects,regardlessofsize. | |
Delivernow | This model emphasizes delivering measurable valuetotheexecutiveteamwithineachsix-monthperiod.Atinitialstartup,thePMO'sresourcesfocusonacceleratedproject deliveriesacrossallmajorprojects.Thismodelhassponsor-ship at a very high executive level (CEO or senior vicepresident). Its metrics are tied directly to senior manage-mentperformance |
[20] WAFFA KARKUKLY, PH.D.
Understandthe"P"inPMO
As a starting point, it is helpful to establish what type of PMO yourorganization requires, whether it is a project, program,or portfolioman-agementoffice.Figure1.3summarizesthefocusofeachPMOtype
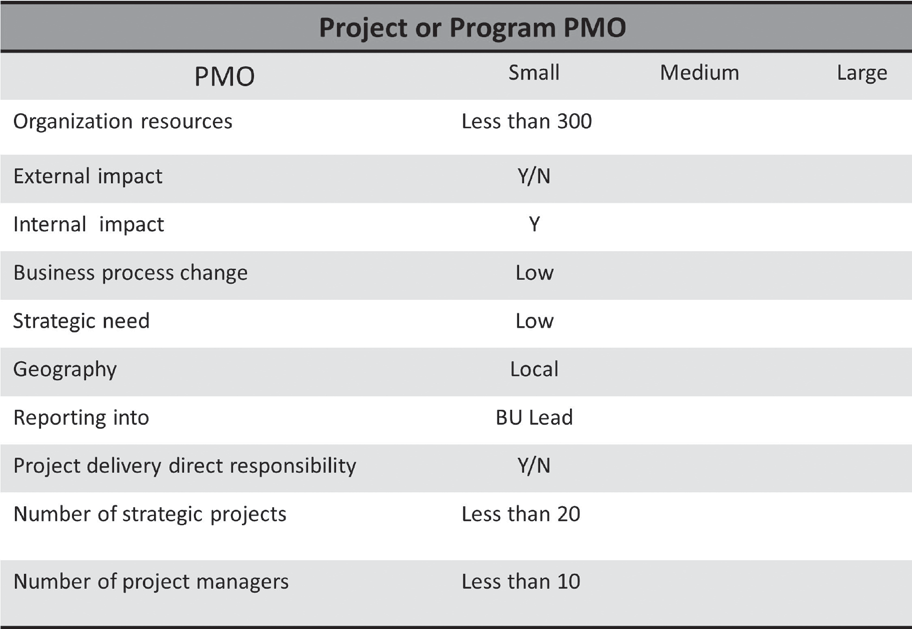
Project-basedPMOs
The focus of a project-based PMO is on project-level deliverables: howto initiate, plan, execute, monitor, control and close out a project.Attention is paid to project details pertaining to specific project mile-stonesanddeliverables.Areasoffocusinclude:
- Buildingtheprojectmanagementmethodology
- Promotingstandardprojectmanagementtemplatesandtools
- Ensuringstandardizationinprojectdelivery
- Improvingprojectdeliveryandperformance
- Allocatingandassigningprojectresources
- Planningtheprojectbudgetaswellastrackingvariances
- Monitoringprojectrisksandissues
- Projectstatusreporting,dashboard,andKPI(KeyProgressIndicator)
Project-based PMOs can be local or national, IT-based or business-based. In some organizations, IT reports to a business unit. For example,in some industries every business unit has its own IT function, while inotherorganizationsITisconsideredabusinessunit,muchlikefinanceor marketing. In large organizations, many project-based PMOs canbe found embedded in departments responsible for direct delivery ofprojects. Some organizations that have multiple PMOs will have anoverarchingPMOwithaspecificgovernanceroletoensurethatoverall
MANAGINGTHEPMOLIFECYCLE [21]
corporate standardization, communication,performance assessment,andmeasurementsareconsistent.
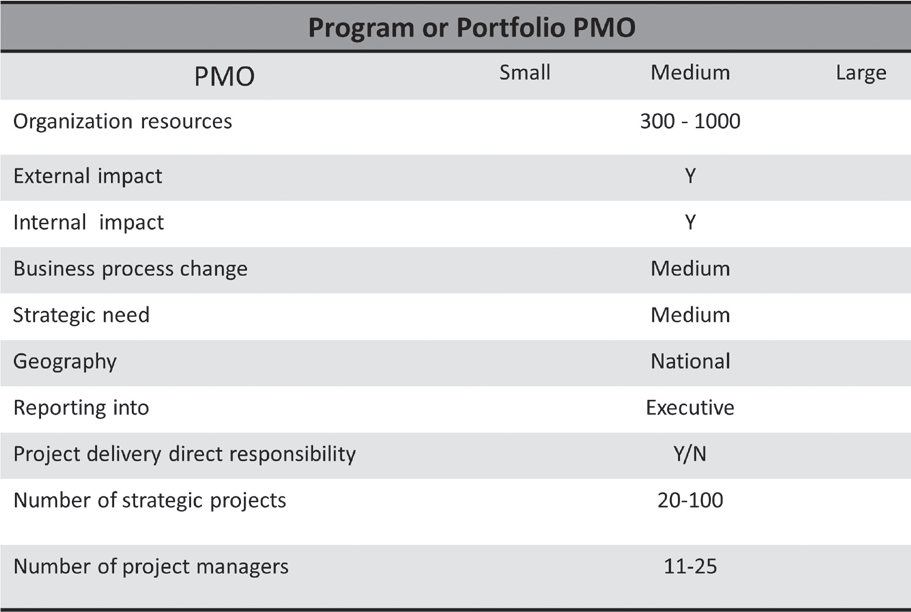
Program-basedPMOs
The focus of program-based PMOs is, as the title suggests, on program-level outcomes, how to integrate projects and sequence them, resourcemanagement, stakeholders change impact management, and rollup ofgroupsofprojects.Attentionispaidtoprogramdeliverables,includingbusinesscaseandprogrambase benefits.Theareasoffocus include:
- Promotingstandardprogrammanagementmethodology
- Ensuringstandardizationinprojectdeliveryacrossdependentandindependentprojects
- Performingprojectbenefitsaswellaslookingatprogrambenefitrealization
- Budgetingandtrackingprogramlevelcost/valueandROI
- Addressingresourceplanningacrossmultipleprojectswiththeaimtoensureappropriateallocation
- Monitoringrisksandissuesattheprogramlevel
These PMOs can be local but are more frequently national- or enter-prise-level. They are most common in large organizations where variousprojects are either cross-geographic or cross-departmental and there arestrong dependencies between these projects; including securing deliveryas part of a specific program. Hence, a PMO may run single or mul-tipleprograms.
[22] WAFFA KARKUKLY, PH.D.
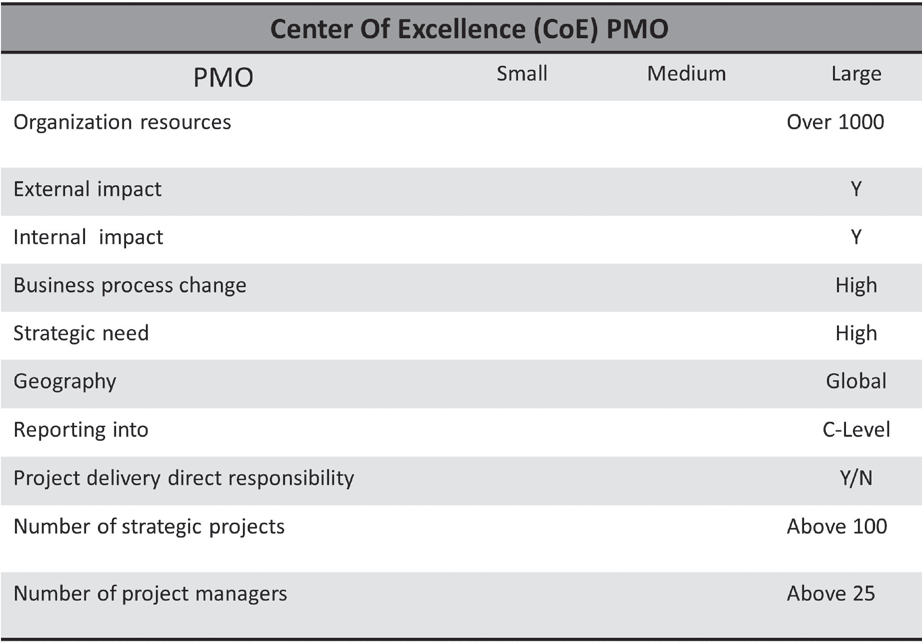
Portfolio-basedPMOs
Because of the way some organizations are structured politically, someportfolio-based PMOs encompass a project and program deliverycomponent while others retain a portfolio function only. These kindsofPMOsmayhavevariousnamesiftheyfunctionseparatelyfromthePMO (e.g. EnterpriseStrategy, Corporate Strategy, Strategic PortfolioOffice, CorporatePortfolio Office, or Portfolio Management Office).ThesePMOsfocusonportfolio-leveloutcomesandhowtoalignorga-nizationalstrategicinitiativestorealizebenefits.Areasoffocusinclude:
- Creatinganorganizationportfolioprocess
- PromotingstandardsacrossPPMselection,monitoring,andcontrolling
- Evaluatingandprioritizingallinitiativesagainststrategickeyindicators
- Performingdemandmanagement
- Aligninganorganization'sbudgetrequestsandapprovalsalongwithPPMinitiatives
- ImplementingongoinggovernancemodelstomonitorandcontrolPPMhealthchecks
- PerformingbenefitrealizationandmonitoringKPIsandreporting
- Monitoringrisksandissuesataportfoliolevel
ThesePMOsoperatepredominantlyatthenationalorenterpriselevel.Manyofthemcanbefoundinlargeorganizationsinwhicheachbusinessunithasadelivery-basedPMOthatoverseestheexecutionofmultipleprojects or programs. While delivery-based PMOs are involved in car-ryingoutprojects,theyreporttotheportfolio-basedPMO.ThisPMOhasoversightatthemacrolevelofallinitiativesgeneratedbythevariousbusinessunitsandtheirobjectivestomoreofaportfoliooversightforselecting and prioritizing projects across the entire organization as wellastrackingbenefitrealization.
MANAGINGTHEPMOLIFECYCLE [23]
Figure1.3Summarizesthefocusofproject-based,program-based,andportfolio-basedPMOs.
     |
PMO Small Medium Large Organization resources Less than 300 External impact Y/N Internal impact Y Business process change Low Strategic need Low Geography Local Reporting into BU Lead Project delivery direct responsibility VIN Number of strategic projects Less than 20 Number of project managers Less than 10 PMO Small Medium Large Organization resources 300 - 1000 External impact Y Internal impact Y Business process change Medium Strategic need Medium Geography National Reporting into Executive Project delivery direct responsibility YIN Number of strategic projects 20-100 Number of project managers 11-25 pMQ Small Medium Large Organization resources Over 100-0 External impact Y Internal impact Y Business process change High Strategic need High Geography Global Reporting into CLevel Project delivery direct responsibility YIN Number of strategic projects Above 100 Number of project managers Above 25 PMO Authority PMO Type PMO Functions Consulting Services Project or Program Project Methodology Division PMO Project Processes Project Reporting Enterprise PMO Project Tools Project Manager Training Knowledge Management Project or Program Project Methodology Project Processes Division PMO Project Reporting Enterprise PMO Project Repository Project Tools Authoritative / Compliance Project or Program Project Methodology Division PMO Project Processes Project Reporting Project Repository Enterprise PMO Project Tools Project Manager Development COE PMO Project Delivery Global PMO Project PortfolioPortfolio management focuses on: o Translating business strategy into manageable initiatives (programs and projects) organized into portfolios Portfolio o Managing and tracking the portfolio of initiatives (manage resources, Management dollars, and capital rationalization o Regular "checkpoints" at which the benefits and results of the initiatives are reviewed to understand their impact on the realization of the business strategy Program management focuses on: Program o Creation and management of key program deliverables, including business Management case and other base lined documents o Identify, manage, and address interdependencies between projects in terms of activities, deliverables, risks, issues, and resources o Program benefits tracking and realization Project management focuses on: Project o Execution and delivery of planned project deliverables and milestones Management o Management of project schedules, budgets, issues, risks, and change requests using defined project management processes and tools o Escalation of project issues and change requests and risks, where necessary
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


