Question: [Linear and Nonlinear Waves, 'hitham (1974), Section 4.5] .J Please give detailed solution (derivation) of the following. Also, please give MATLAB code to reproduce Fig.
![[Linear and Nonlinear Waves, \"'hitham (1974), Section 4.5] .J Please give](https://s3.amazonaws.com/si.experts.images/answers/2024/06/66792824671b0_164667928243c4f2.jpg)


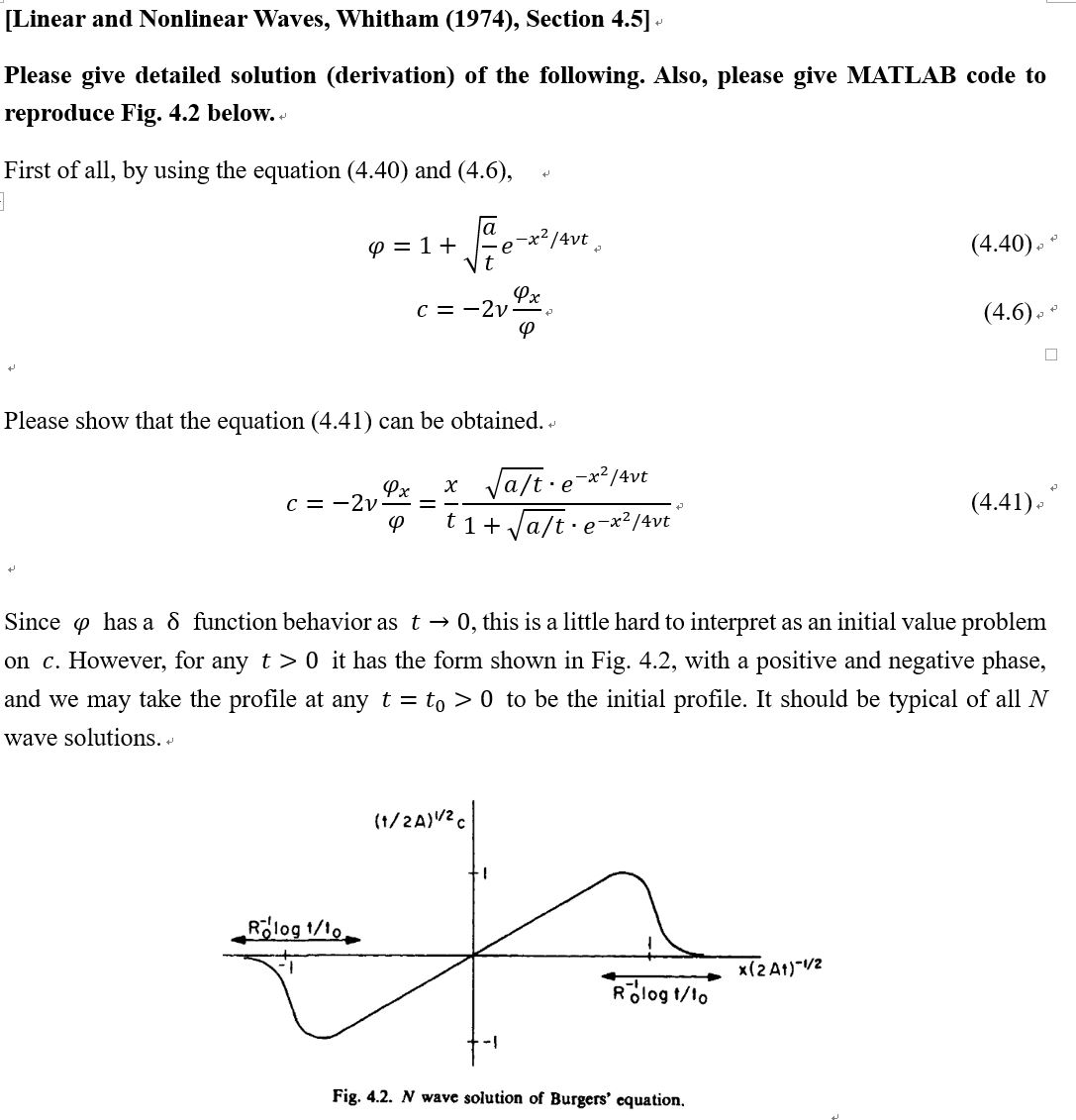


[Linear and Nonlinear Waves, \"'hitham (1974), Section 4.5] .J Please give detailed solution (derivation) of the following. Also, please give MATLAB code to reproduce Fig. 4.2 below. a First of all, by using the equation (4.40) and (4.6), (p = 1 + Eff/W. (4.40). J as. C = -2vo 4.6 .3 J (p i i .4 Please show that the equation (4.41) can be obtained. .J E" x2/4vt ,3 C = -2v XL (4.41). (P t 1 + 'fa/t -ex2/4W .4 Since (p has a 6 function behavior as t > 0, this is a little hard to interpret as an initial value problem on C. However, for any t > 0 it has the form shown in Fig. 4.2, with a positive and negative phase, and we may take the prole at any t = to > 0 to be the initial prole. It should be typical of all N wave solutions. .J \"Marne R'Q'log mg ._,____, idem?\" R'giog mo Fig. 4.2. N wave solution of Burgera' equation. The area under the positive phase of the profile is + cdx = -2v[logo]8 = 2vlog|1+ +1 21 + (4.42) - The magnitude of the area of the negative phase is the same. Thus in marked contrast with the previous case, the area of the positive phase tends to zero as t - co. If the value of (4.42) at the initial time to is denoted by A, we may introduce a Reynolds number Ro= = log 1 + (4.43) ." But as times goes on the effective Reynolds number will be " R (t ) = 2 So cdx = log (1 + ]:) (4.44) ." In terms of Ro and to, a = to(eRo - 1)2; hence (4.41) may be written - -1 t ex2 / 4vt C= 1+ (4.45) + to eRo - 1For Ro >> 1 (corresponding to to V2At This is exactly the inviscid solution. However, for any fixed a and v we see directly from (4.41) [and it may be verified also from (4.46)] that + C = e 4vt as t - 00 . (4.47) - + This is the dipole solution of the heat equation. The diffusion dominates the nonlinear term in the final decay
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


