Question: Linear interpolation is a method of curve fitting using linear polynomials. It is heavily employed in mathematics (particularly numerical analysis), and numerous applications including computer
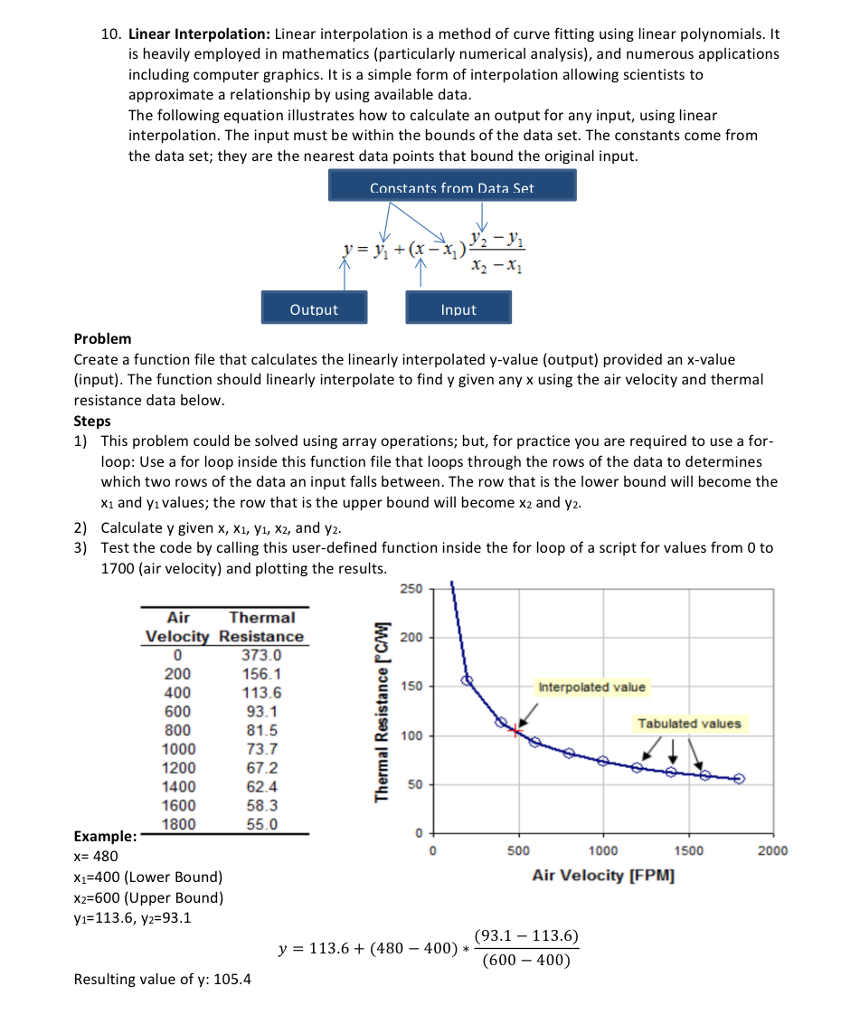
Linear interpolation is a method of curve fitting using linear polynomials. It is heavily employed in mathematics (particularly numerical analysis), and numerous applications including computer graphics. It is a simple form of interpolation allowing scientists to approximate a relationship by using available data. The following equation illustrates how to calculate an output for any input, using linear interpolation. The input must be within the bounds of the data set. The constants come from the data set; they are the nearest data points that bound the original input. Create a function file that calculates the linearly interpolated y-value (output) provided an x-value (input). The function should linearly interpolate to find y given any x using the air velocity and thermal resistance data below. Steps This problem could be solved using array operations; but, for practice you are required to use a for-loop: Use a for loop inside this function file that loops through the rows of the data to determines which two rows of the data an input falls between. The row that is the lower bound will become the x_1 and y_1 values; the row that is the upper bound will become x_2 and y_2. Calculate y given x, x_1, y_1, x_2, and y_2. Test the code by calling this user-defined function inside the for loop of a script for values from 0 to 1700 (air velocity) and plotting the results. Example: x= 480 x_1=400 (Lower Bound) x_2=600 (Upper Bound) y_1=113.6, y_2=93.1 y = 113.6 + (480 - 400) * (93.1 - 113.6)/(600 - 400) Resulting value of y: 105.4
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


