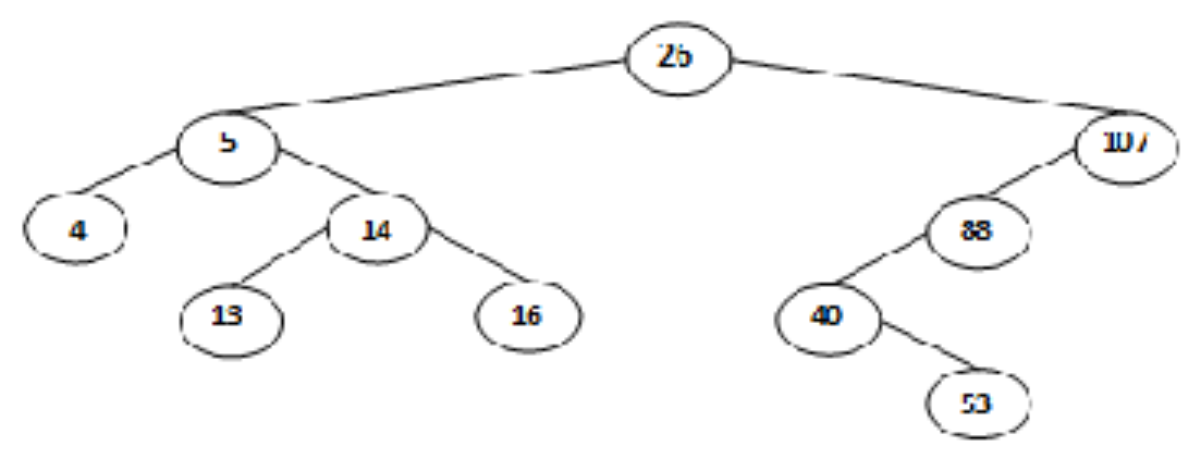
Question: List the values of the Binary Search Tree pictured below in the order in which in - order traversal of the tree will visit them.
List the values of the Binary Search Tree pictured below in the order in
which inorder traversal of the tree will visit them. Remember that this will also be
the sequence by which function BinarySearchTree::printElementssee BinarySearchTreeLabh prints out the values.
Show you listings.
We were told that no programming was needed, but here is BinarySearchTreeLabh anyway.
#ifndef BINARYSEARCHTREEH
#define BINARYSEARCHTREEH
#include
#include "Vector.h
using namespace std;
template
class BinarySearchTree
private:
struct BinaryNode
T element;
BinaryNode left;
BinaryNode right;
BinaryNodeconst T& theElement, BinaryNode lt BinaryNode rt
: elementtheElement leftlt rightrt
BinaryNodeconst T&& theElement, BinaryNode lt BinaryNode rt
: elementstd::movetheElement leftlt rightrt
;
public:
BinarySearchTree : root
~BinarySearchTree
makeEmpty;
bool isEmpty const
return root ;
void insertconst T& x
calls private insert
insertx root; LAB : add private fct from Module
LAB : print all elements values in line
void printElements const
if isEmpty
cout "Empty tree" endl;
else
printElementsroot; LAB : define private fct below
LAB : returns number of elements in BST
int size const
return sizeroot; LAB : define private fct below
void printInternal const
if isEmpty
cout "Empty tree" endl;
else
printInternalroot;
for destructor to call...
void makeEmpty
makeEmptyroot;
private:
BinaryNode root;
the private member fcts that do all the work...
void insertconst T& x BinaryNode& t
LAB : COMPLETE
void makeEmptyBinaryNode& t
if t
makeEmptytleft;
makeEmptytright;
delete t;
t ;
void printInternalBinaryNode t int offset const
for int i ; i offset; i
cout ;
if t
cout # endl;
return;
cout telement endl;
printInternaltleft, offset ;
printInternaltright, offset ;
return;
LAB : COMPLETE; to print inline all elements in BST rooted in t;
void printElementsBinaryNode t const
if t
print the elements of the left subtree
print the element under pointer t
print the elements of the right subtree
LAB : COMPLETE; returns the number of elements stored in BST
rooted in t;
Taking recursive view:
what is the size of the BST under pointer t if t is a nullptr? Must
be
what is the size of the BST under t if t is not a nullptr?
one Node t exists the one that t points to count
and add size of the left subtree of t
and add size of the right subtree of t
int sizeBinaryNode t const
return ; temp PLACE HOLDER for the actual code;
remove when adding the actual code
;
#endif
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


