Question: Loan Amortization Schedule in Tabular Form An amortization table shows how monthly payments pays off the debt in the agreed duration of the loan. As
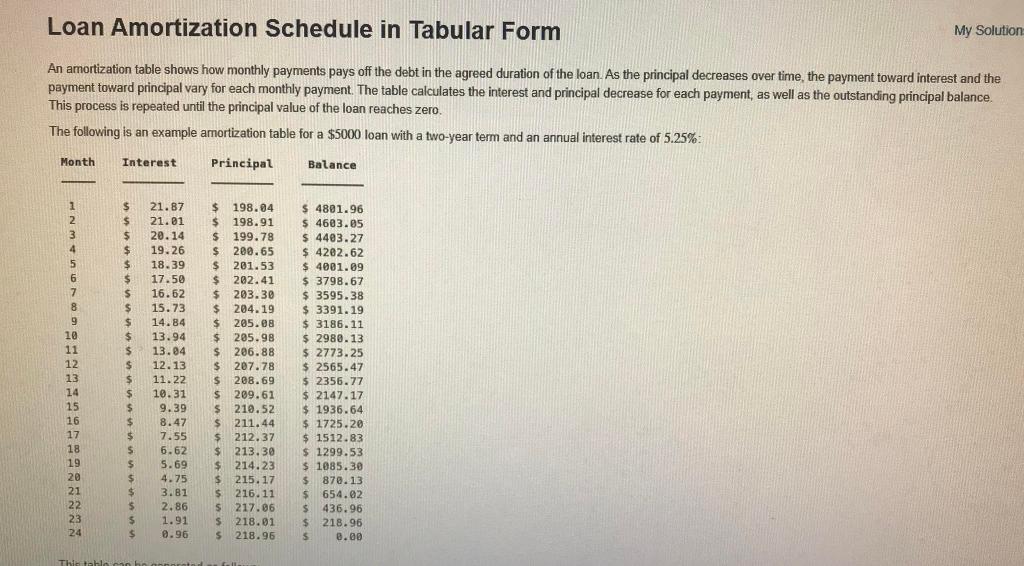

Loan Amortization Schedule in Tabular Form An amortization table shows how monthly payments pays off the debt in the agreed duration of the loan. As the principal decreases over time, the payment toward interest and the payment toward principal vary for each monthly payment. The table calculates the interest and principal decrease for each payment, as well as the outstanding principal balance. This process is repeated until the principal value of the loan reaches zero. The following is an example amortization table for a $5000 loan with a two-year term and an annual interest rate of 5.25%: Principal Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10. 11 12 13 HEERENNAN 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Interest $ 21.87 21.01 $ $ 20.14 $198.04 $198.91 $ 199.78 $ 200.65 $201.53 $ 19.26 18.39 $ 17.50 $ 202.41 16.62 $ 203.30 204.19 $ 205.08 15.73 $ 14.84 13.94 13.04 $ 205.98 $ 206.88 12.13 11.22 10.31 9.39 8.47 7.55 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ This table can $ 207.78 $ $ 209.61 208.69 $ 210.52 $ 211.44 $ 212.37. 6.62 $ 213.30 5.69 4.75 3.81 2.86 1.91 0.96 $ 214.23 $ 215.17 $ 216.11 S 217.06 $ 218.01 $ 218.96 Balance $ 4801.96 $ 4603.05 $ 4403.27 $ 4202.62 $ 4001.09 $ 3798.67 $ 3595.38 $ 3391.19 $3186.11 $ 2980.13 $ 2773.25 $ 2565.47 $ 2356.77 $ 2147.17 $ 1936.64 $ 1725.20 $ 1512.83 $ 1299.53 $ 1085.30 $ 870.13 $ 654.02 $ 436.96 $ 218.96 S 8.00 My Solution This table can be generated as follows: 1. Given a fixed-term loan with initial principal balance (total loan provided in year 0) value of B,, the monthly payment A can be computed with the formula: iB(14) (147-1 A- Where i is the monthly interest rate (decimal value), computed from an annual rate r as i-r/12, and n is the number of months in the term of the loan. For the example amortization table above, the monthly interest rate /-0.0525/12-0.004375. The monthly payment is calculated using the above formula to be $219.91. 2. For each month, the interest that accumulates must be paid in full before any portion of the payment is applied toward the principal balance. The interest due for the k month, M, is calculated using the monthly interest rate i and the principal balance from the previous month as M, -ix B_, For example in month 3 in the example table above the interest due is calculated using the principal balance from month 2 as M, -ix B.-0.004375 x 4603.05-20.14. 3. The remaining portion of the monthly payment is applied to reduce the principal balance using the formula B-B- (A-M) The portion of the payment applied to principal (P-A-M, from the formula above) is given in column 3 in the example table above. Continuing the example for month 3, the amount applied to principal is P-A-M, -219.91-20.14199.78 (off by 0.01 due to rounding). This amount is applied to reduce the principal balance to B, 4403.27. 4. Steps 2 and 3 are repeated each month for the duration of the term of the loan. The outstanding principal balance is $0.00 after the last payment is applied, as shown in the table above. In the given code, a function named amortization requires three input variables as in the ff. . The initial principal balance B, is assigned to the variable LoanAmount. . The annual interest rater is assigned to the variable Annual Interest Rate . The loan term (in years) is assigned to the variable TermYears Use the three input arguments to find the monthly payments using the provided equation and generate a single table assigned to Amortization Schedule as the output. It has the ff contents: . Column 1, having a label of Month, contains a column vector of integers. - Column 2, having a label of Interest, contains an 8-column character array showing the monthly interest with the appropriate currency format - Column 3. having a label of Principal, contains an 8-column character array of the amount applied toward principal each month with currency format Column 4, having a label of Balance, contains an 8-column character array of the outstanding loan balance at the end of each month with currency format The first test uses the same loan parameters as the example table above, so your function's output should be identical to the table shown. Note the values of LoanAmount, AnnualInterest Rate and Term Years are defined as inputs to the function. Do not overwrite these values in your code. Be sure to assign values to each of the function output variables Loan Amortization Schedule in Tabular Form An amortization table shows how monthly payments pays off the debt in the agreed duration of the loan. As the principal decreases over time, the payment toward interest and the payment toward principal vary for each monthly payment. The table calculates the interest and principal decrease for each payment, as well as the outstanding principal balance. This process is repeated until the principal value of the loan reaches zero. The following is an example amortization table for a $5000 loan with a two-year term and an annual interest rate of 5.25%: Principal Month 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10. 11 12 13 HEERENNAN 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Interest $ 21.87 21.01 $ $ 20.14 $198.04 $198.91 $ 199.78 $ 200.65 $201.53 $ 19.26 18.39 $ 17.50 $ 202.41 16.62 $ 203.30 204.19 $ 205.08 15.73 $ 14.84 13.94 13.04 $ 205.98 $ 206.88 12.13 11.22 10.31 9.39 8.47 7.55 $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ $ This table can $ 207.78 $ $ 209.61 208.69 $ 210.52 $ 211.44 $ 212.37. 6.62 $ 213.30 5.69 4.75 3.81 2.86 1.91 0.96 $ 214.23 $ 215.17 $ 216.11 S 217.06 $ 218.01 $ 218.96 Balance $ 4801.96 $ 4603.05 $ 4403.27 $ 4202.62 $ 4001.09 $ 3798.67 $ 3595.38 $ 3391.19 $3186.11 $ 2980.13 $ 2773.25 $ 2565.47 $ 2356.77 $ 2147.17 $ 1936.64 $ 1725.20 $ 1512.83 $ 1299.53 $ 1085.30 $ 870.13 $ 654.02 $ 436.96 $ 218.96 S 8.00 My Solution This table can be generated as follows: 1. Given a fixed-term loan with initial principal balance (total loan provided in year 0) value of B,, the monthly payment A can be computed with the formula: iB(14) (147-1 A- Where i is the monthly interest rate (decimal value), computed from an annual rate r as i-r/12, and n is the number of months in the term of the loan. For the example amortization table above, the monthly interest rate /-0.0525/12-0.004375. The monthly payment is calculated using the above formula to be $219.91. 2. For each month, the interest that accumulates must be paid in full before any portion of the payment is applied toward the principal balance. The interest due for the k month, M, is calculated using the monthly interest rate i and the principal balance from the previous month as M, -ix B_, For example in month 3 in the example table above the interest due is calculated using the principal balance from month 2 as M, -ix B.-0.004375 x 4603.05-20.14. 3. The remaining portion of the monthly payment is applied to reduce the principal balance using the formula B-B- (A-M) The portion of the payment applied to principal (P-A-M, from the formula above) is given in column 3 in the example table above. Continuing the example for month 3, the amount applied to principal is P-A-M, -219.91-20.14199.78 (off by 0.01 due to rounding). This amount is applied to reduce the principal balance to B, 4403.27. 4. Steps 2 and 3 are repeated each month for the duration of the term of the loan. The outstanding principal balance is $0.00 after the last payment is applied, as shown in the table above. In the given code, a function named amortization requires three input variables as in the ff. . The initial principal balance B, is assigned to the variable LoanAmount. . The annual interest rater is assigned to the variable Annual Interest Rate . The loan term (in years) is assigned to the variable TermYears Use the three input arguments to find the monthly payments using the provided equation and generate a single table assigned to Amortization Schedule as the output. It has the ff contents: . Column 1, having a label of Month, contains a column vector of integers. - Column 2, having a label of Interest, contains an 8-column character array showing the monthly interest with the appropriate currency format - Column 3. having a label of Principal, contains an 8-column character array of the amount applied toward principal each month with currency format Column 4, having a label of Balance, contains an 8-column character array of the outstanding loan balance at the end of each month with currency format The first test uses the same loan parameters as the example table above, so your function's output should be identical to the table shown. Note the values of LoanAmount, AnnualInterest Rate and Term Years are defined as inputs to the function. Do not overwrite these values in your code. Be sure to assign values to each of the function output variables






