Question: lQuestion 3 Consider a random sample X1, X21 X31, X4. where each random variable X.- corresponds to a coin toss that is equal to 1
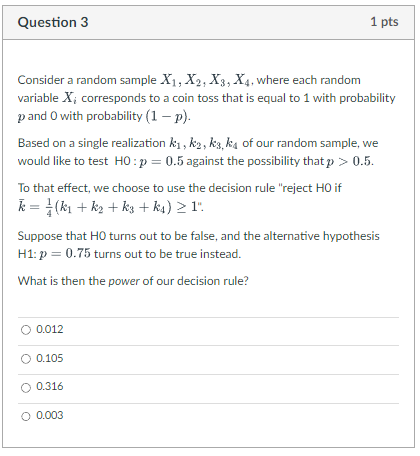
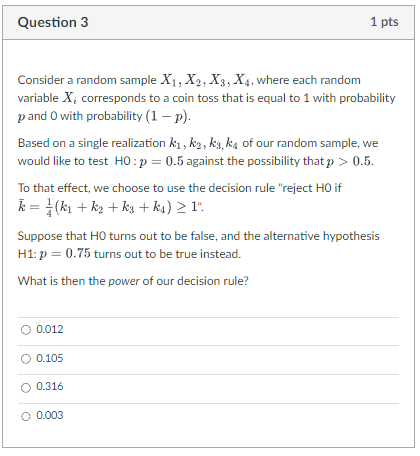
lQuestion 3 Consider a random sample X1, X21 X31, X4. where each random variable X.- corresponds to a coin toss that is equal to 1 with probability pand Dwith probability {1 11}. Based on a single realization la], , kg , k9,. liq of our random sample. we would like to test HCI :p = 0.5 against the possibility thatp :5 0.5. To that effect. we choose to use the decision rule "reject HCI if I: = %{k1+kg +k3, +k4} 2 1". Suppose that HID turns out to be false. and the alternative hypothesis H1: :5- = 0.75 turns out to be true instead. What is then the power of our decision rule
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


