Question: M is below 1. Consider the Turing machine M in the JFLAP file: IHW5.TM.1.jff. (a) If you run M on 1111, what will the contents

M is below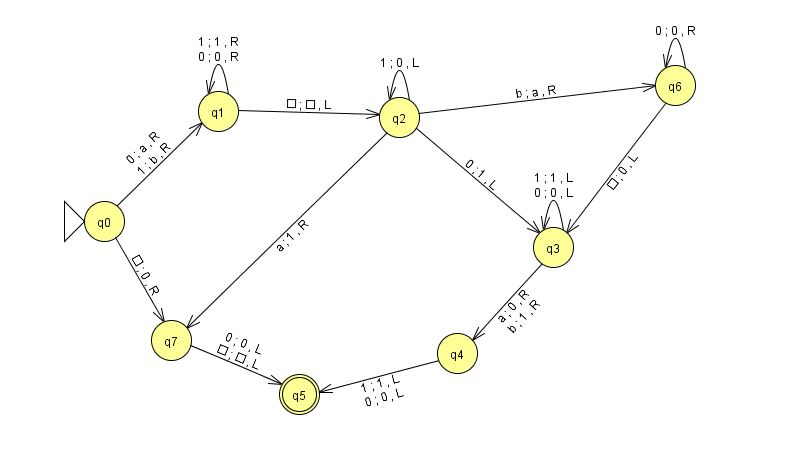
1. Consider the Turing machine M in the JFLAP file: IHW5.TM.1.jff. (a) If you run M on 1111, what will the contents of the tape be when it accepts. Where will the tapehead be when it accepts? be when it accepts? tapehead be when it accepts? state to the accept state. (Hint: think about binary strings as integers in base 2.) (b) If you run M on e, what will the contents of the tape be when it accepts. Where will the tapehead (c) If you run M on 1011, what will the contents of the tape be when it accepts. Where will the (e) Make a conjecture about the language of M (f) Consider the following definition of an enumerator. An enumerator is a deterministic Turing machine that does not have an accept state or a reject state. A subset of the states are print states. Whenever a computation enters a print state, the enumerator "prints" the string of all symbols on the current content of the tape before the first blank symbol. The only allowable input to the enumerator is the empty string. Describe how to alter the given machine M so that the result is an enumerator that follows the above rules and enumerates 0, 1)* 1. Consider the Turing machine M in the JFLAP file: IHW5.TM.1.jff. (a) If you run M on 1111, what will the contents of the tape be when it accepts. Where will the tapehead be when it accepts? be when it accepts? tapehead be when it accepts? state to the accept state. (Hint: think about binary strings as integers in base 2.) (b) If you run M on e, what will the contents of the tape be when it accepts. Where will the tapehead (c) If you run M on 1011, what will the contents of the tape be when it accepts. Where will the (e) Make a conjecture about the language of M (f) Consider the following definition of an enumerator. An enumerator is a deterministic Turing machine that does not have an accept state or a reject state. A subset of the states are print states. Whenever a computation enters a print state, the enumerator "prints" the string of all symbols on the current content of the tape before the first blank symbol. The only allowable input to the enumerator is the empty string. Describe how to alter the given machine M so that the result is an enumerator that follows the above rules and enumerates 0, 1)*
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


