Question: Machine Learning Problem Suppose we flip a coin N times and observe N, tails and N, heads. We believe the outcome of a flip is
Machine Learning Problem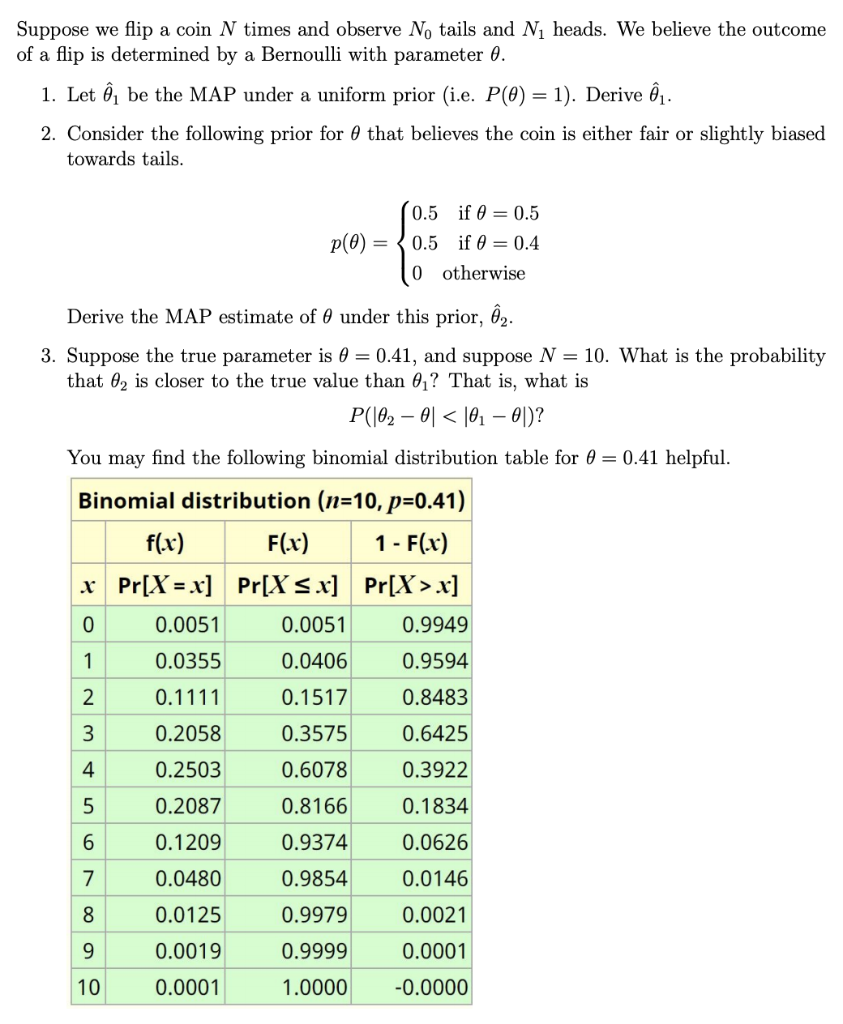
Suppose we flip a coin N times and observe N, tails and N, heads. We believe the outcome of a flip is determined by a Bernoulli with parameter 0. 1. Let , be the MAP under a uniform prior (i.e. P(0) = 1). Derive n. 2. Consider the following prior for that believes the coin is either fair or slightly biased towards tails. p(0) 0.5 if 0 = 0.5 0.5 if = 0.4 0 otherwise Derive the MAP estimate of 6 under this prior, 2. 3. Suppose the true parameter is 0 = 0.41, and suppose N = 10. What is the probability that 62 is closer to the true value than 0,? That is, what is P(|02 01 x] 0 0.0051 0.0051 0.9949 1 0.0355 0.0406 0.9594 2 0.1111 0.1517 0.8483 3 0.2058 0.3575 0.6425 4 0.2503 0.6078 0.3922 5 0.2087 0.8166 0.1834 6 0.1209 0.9374 0.0626 7 0.0480 0.9854 0.0146 8 0.9979 0.0021 0.0125 0.0019 9 0.9999 0.0001 10 0.0001 1.0000 -0.0000 Suppose we flip a coin N times and observe N, tails and N, heads. We believe the outcome of a flip is determined by a Bernoulli with parameter 0. 1. Let , be the MAP under a uniform prior (i.e. P(0) = 1). Derive n. 2. Consider the following prior for that believes the coin is either fair or slightly biased towards tails. p(0) 0.5 if 0 = 0.5 0.5 if = 0.4 0 otherwise Derive the MAP estimate of 6 under this prior, 2. 3. Suppose the true parameter is 0 = 0.41, and suppose N = 10. What is the probability that 62 is closer to the true value than 0,? That is, what is P(|02 01 x] 0 0.0051 0.0051 0.9949 1 0.0355 0.0406 0.9594 2 0.1111 0.1517 0.8483 3 0.2058 0.3575 0.6425 4 0.2503 0.6078 0.3922 5 0.2087 0.8166 0.1834 6 0.1209 0.9374 0.0626 7 0.0480 0.9854 0.0146 8 0.9979 0.0021 0.0125 0.0019 9 0.9999 0.0001 10 0.0001 1.0000 -0.0000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


