Question: Main Concepts: Enhanced Entity Relationship Diagrams ( EERD ) : ii . Completeness Constraint: Total Specialization Rule ( An instance of the supertype must also
Main Concepts:
Enhanced Entity Relationship Diagrams EERD:
ii Completeness Constraint:
Total Specialization Rule An instance of the supertype must also belong to either of the
subtypes; Use double line
Partial Specialization Rule An instance of an entity could belong to either of the subtypes of
none of them; Use single line
i Disjointness Constraints:
Disjoint Rule Instance of Supertype could be only ONE of the subtypes; write a within circle
Overlap Rule Instance of Supertype could be more than one subtype; write an o within circle
i Subtype Discriminator attribute of the supertype that describes to which subtype an
instance of the entity belongs
If Disjoint: a simple attribute is created with different categories for each subtype
If Overlapping: a composite attribute is created with subparts indicating whether or not an
instance of the entity belongs to each separate subtype
i Entity Clusters If model gets too complex, we can group it into "clusters" by replacing
them with an abstract entity type
ii Packaged Models the search for best practices means that rather than build our
models entirely from the ground up we can acquire data models from vendors
Universal data model generic model template that can be reused with ease in multiple
scenarios
Industryspecific data model predefined models for specific scenarios
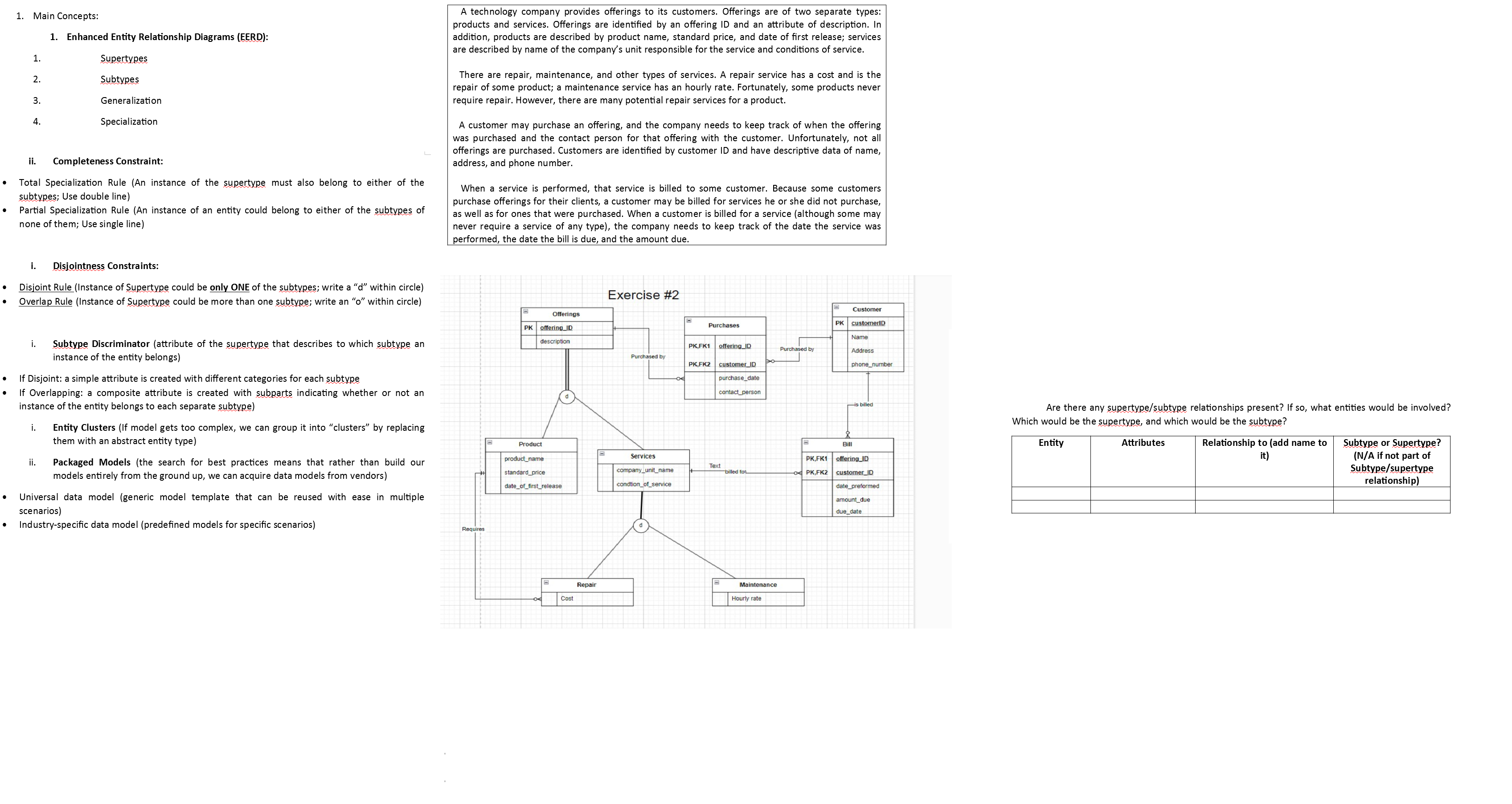
A technology company provides offerings to its customers. Offerings are of two separate types:
products and services. Offerings are identified by an offering ID and an attribute of description. In
addition, products are described by product name, standard price, and date of first release; services
are described by name of the company's unit responsible for the service and conditions of service.
There are repair, maintenance, and other types of services. A repair service has a cost and is the
repair of some product; a maintenance service has an hourly rate. Fortunately, some products never
require repair. However, there are many potential repair services for a product.
A customer may purchase an offering, and the company needs to keep track of when the offering
was purchased and the contact person for that offering with the customer. Unfortunately, not all
offerings are purchased. Customers are identified by customer ID and have descriptive data of name,
address, and phone number.
When a service is performed, that service is billed to some customer. Because some customers
purchase offerings for their clients, a customer may be billed for services he or she did not purchase,
as well as for ones that were purchased. When a customer is billed for a service although some may
never require a service of any type the company needs to keep track of the date the service was
performed, the date the bill is due, and the amount due.
Are there any supertypesubtype relationships present? If so what entities would be involved?
Which would be the supertype, and which would be the subtype?
fill in the blank and fix any error on diagram please
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


