Question: Math correction 14) By using the T -F Conditional Strategy method what do you find the truth value of the statement W ? A True
Math correction


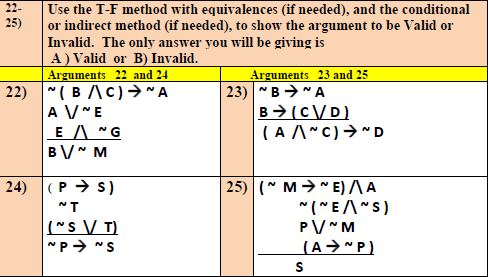
14) By using the T -F Conditional Strategy method what do you find the truth value of the statement W ? A True B False C Cannot determine 15-16) With the argument below you could use the T-F Indirect Method Approach -B VW BAZ (-WVZ)ZA ( ~ PVA ) 15) What additional statement would you assume to be a true premise in order to use the T-F Indirect Method Approach on the statement above? A (-PVA) A C - (-PVA ) D 16) If you rewrote the conclusion by the conditional equivalence, you could have (P ) A) as the conclusion. In that case, you might try to use the T -F Conditional Strategy method. What additional statement would you assume to be a true premise in order to use a Conditional Strategy T -F method on the argument above? A -(P) A ) B P C (P) A) D A17 - 20 Directions: In each of the arguments below an equivalence ( either DeMorgan, Conditional or Contrapositive Equivalence) needs to be used to show the argument to be valid. Which equivalence : Use A) Conditional B) Contrapositive () DeMorgan Arguments 17 and 19 Arguments 18 and 20 17) Which equivalence could be used 18) Which equivalence could be on (~ R V - Q ) in order to more used on (- R > P ) in order to easily show the argument valid with more easily show the argument T- F method? valid with T-F method? -P> (R /\\Q) -PV - (-P> R) "R V -Q -R > P P N P 19) Which equivalence could be used 20) Which equivalence could be on - (PVR) in order to more easily used on (~ R > - P ) in order to show the argument valid with T-F more easily show the argument method valid with T-F method? Q - (-P-R) Q9 -(P- R) "( PVR) R > -P - Q - Q 21) Under which condition below is an argument considered invalid? A) Only when the premises are True B) When all the premises are assumed to be True, then the conclusion is also True C) Only when the conclusion is False D) When all the premises are assumed to be True, then the conclusion is also False.12- Use the T-F method with equivalences (if needed), and the conditional 15) or indirect method (if needed), to show the argument to be Valid or Invalid. The only answer you will be giving is A ) Valid or B) Invalid. Arguments 22 and 24 Arguments 23 and 25 22) " ( B /C)- NA 23) NBONA AVE B - (CV/D) EA ( A /~C) - ND 24) (P)) 25) ( ~ M ) ~E) MA NT " ( "E/\\"S ) ( "S \\/ T) PV~M (A ) ~P ) S
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


