Question: MATLAB: d. Extract the columns corresponding to time, windspeed, and waveheight from the imported data and store them in cell arrays as defined below. Note
MATLAB:
d. Extract the columns corresponding to time, windspeed, and waveheight from the imported data and store them in cell arrays as defined below. Note that the datasets will
likely be incomplete, with perhaps many hours of data missing. Thus, the length of the time and windspeed and waveheight vectors will differ from year to year. Also, the time
is given in the data files in MM:DD:HH format.



 This is what I have so far, completed part 1a,1b, and 1c. Need extreme help on 1d.
This is what I have so far, completed part 1a,1b, and 1c. Need extreme help on 1d.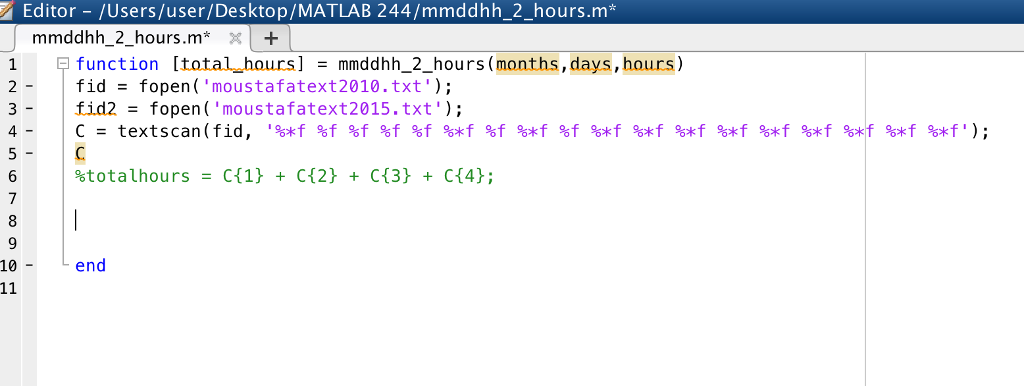
Problem 1: The National Data Buov Center collects and makes public measurements of offshore conditions worldwide. a) Visit http://www.ndbc.noaa.gov and explore b) Select one monitoring station worldwide and download the data for any 2 individual years. Download the 'standard meteorological data' from the historical Data measurements part of each buov record. Download and save as a .txt file a. Best not to choose a leap year b. NDBC places a string of '9's in places where no data was recorded. Try to find data files that have a minimum of such data gaps for the windspeed and c) Import the data into MATLAB. There are several ways to do this, but the recommended he result of this operation will be an array variable in d) Extract the columns corresponding to time, windspeed, and waveheight from the waveheight columns way is to delete the text header lines from the file (use notepad, the matlab editor, ...) and then use the load command. T MATLAB in which each column is a column from the text data file imported data and store them in cell arrays as defined below. Note that the datasets will likely be incomplete, with perhaps many hours of data missing. Thus, the length of the time and windspeed and waveheight vectors will differ from year to year. Also, the time is given in the data files in MM:DD:HH format. You must convert these to hours that range from 1 to 8760 for a standard (non-leap) year. For example, if a time is recorded as 03 22 04, the 4th hour of the 22nd day of the 3rd month, this time instant would be recorded as (31*24 + 28*24 + 21 *24 + 4) 1924 hrs. Note that this can be a little tricky since different months have different numbers of days. You should probably consider writing a function to do this calculation for you. function [total hours]-mmddhh 2 hours(months,days,hours) Variable definitions: time - cell array in which each cell holds the vector of time instants for one of the years of data. This variable should contain time in hours, not in MM:DD:HH format. cell array in which each cell holds the vector of windspeeds for one year of windspeed data waveheight cell array in which each cell holds the vector of waveheights for one year Problem 1: The National Data Buov Center collects and makes public measurements of offshore conditions worldwide. a) Visit http://www.ndbc.noaa.gov and explore b) Select one monitoring station worldwide and download the data for any 2 individual years. Download the 'standard meteorological data' from the historical Data measurements part of each buov record. Download and save as a .txt file a. Best not to choose a leap year b. NDBC places a string of '9's in places where no data was recorded. Try to find data files that have a minimum of such data gaps for the windspeed and c) Import the data into MATLAB. There are several ways to do this, but the recommended he result of this operation will be an array variable in d) Extract the columns corresponding to time, windspeed, and waveheight from the waveheight columns way is to delete the text header lines from the file (use notepad, the matlab editor, ...) and then use the load command. T MATLAB in which each column is a column from the text data file imported data and store them in cell arrays as defined below. Note that the datasets will likely be incomplete, with perhaps many hours of data missing. Thus, the length of the time and windspeed and waveheight vectors will differ from year to year. Also, the time is given in the data files in MM:DD:HH format. You must convert these to hours that range from 1 to 8760 for a standard (non-leap) year. For example, if a time is recorded as 03 22 04, the 4th hour of the 22nd day of the 3rd month, this time instant would be recorded as (31*24 + 28*24 + 21 *24 + 4) 1924 hrs. Note that this can be a little tricky since different months have different numbers of days. You should probably consider writing a function to do this calculation for you. function [total hours]-mmddhh 2 hours(months,days,hours) Variable definitions: time - cell array in which each cell holds the vector of time instants for one of the years of data. This variable should contain time in hours, not in MM:DD:HH format. cell array in which each cell holds the vector of windspeeds for one year of windspeed data waveheight cell array in which each cell holds the vector of waveheights for one year
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


