Question: MATLAB MATLAB MATLAB You must have access to MATLAB software in order to solve this question!!! PLEASE MODIFY THE GIVEN MATLAB CODE BELOW TO SOLVE
MATLAB MATLAB MATLAB You must have access to MATLAB software in order to solve this question!!!
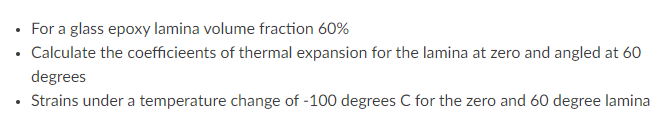 PLEASE MODIFY THE GIVEN MATLAB CODE BELOW TO SOLVE THE QUESTION ABOVE!
PLEASE MODIFY THE GIVEN MATLAB CODE BELOW TO SOLVE THE QUESTION ABOVE!
clc clear all
V_f =0.6; V_m =1-V_f; E_m=70e09; num_1=0.25; G_m=E_m/(2*(1+num_1)) ; nu_f=0.23; E1_f=73e09; E2f=73e09; G_12f=E1_f/(2*(1+nu_f)); E_1=V_f*E1_f+V_m*E_m; E_2=1/((V_f/E2f)/(V_m/E_m)); num_12= num_1*V_m-nu_f*V_f; G_12=1/((V_f/G_12f)/(V_m/G_m)); r_11= 1/E_1; r_12= num_12/E_1; r_22= 1/E_2; r_66=1/G_12; r_1=[r_11 r_12 0; r_12 r_22 0; 0 0 r_66] sig_1=[-46e6; 12e6; 19e6];
strain=[r_1*sig_1]; [A]=[1 0 0; 0 1 0; 0 0 21]; a = inv(A); ang= 60.00; m= cos (ang); n=sind (ang) ; [t]= [m^2 n^2 2*m*n; n^2 m^2 -2*m*n; -m*n m*n m^2-m^2]; e=inv(t); EndStr=[A]*[e]*[a]*[strain]
ang=60; m=cosd (ang) ; n=sind (ang) ; [t]= [m^2 n^2 2*m*n; n^2 m^2 -2*m*n; -m*n m*n m^2+n^2]; e=inv(t); EndStr=[A]*[e]*[a]*[ strain]
PLEASE USE MATLAB TO SOLVE! Please provide your modified code and a screenshot showing the code and result! thank you
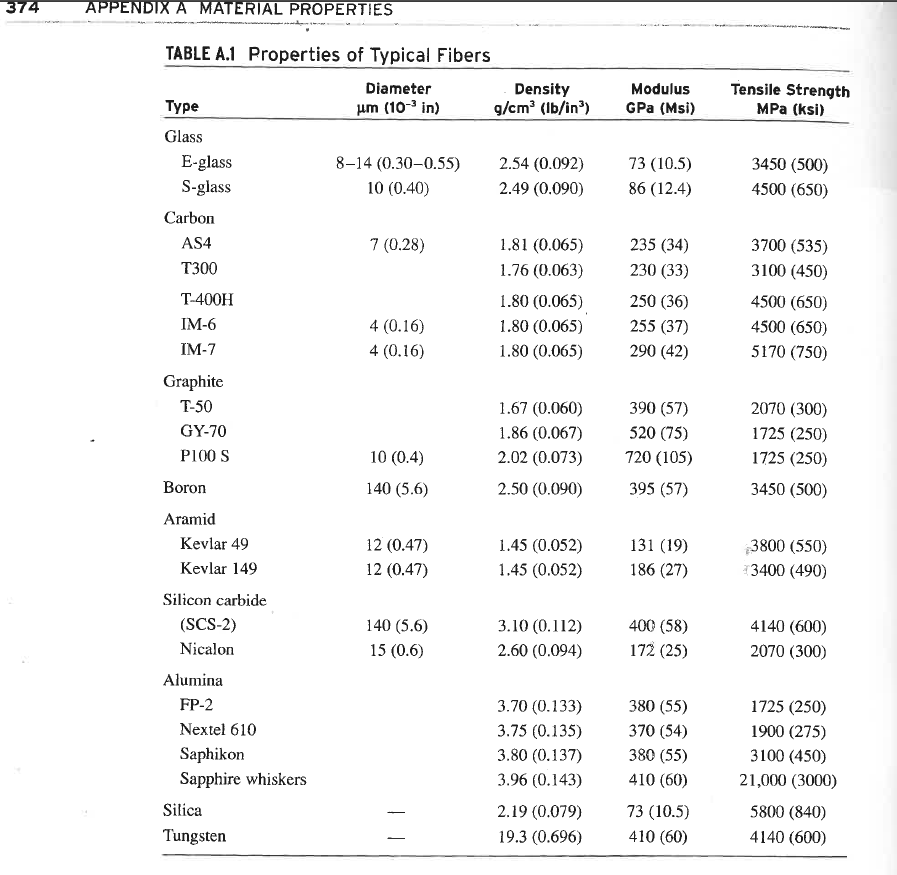
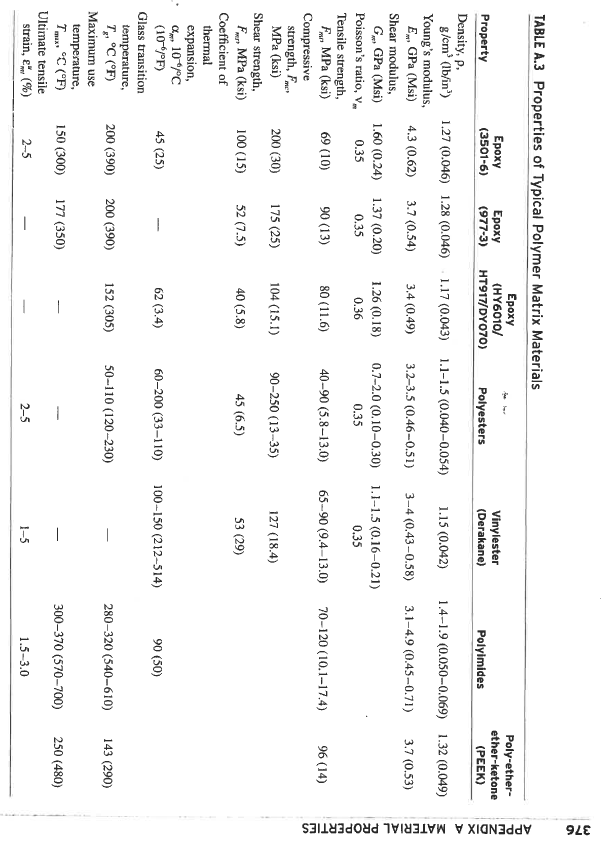
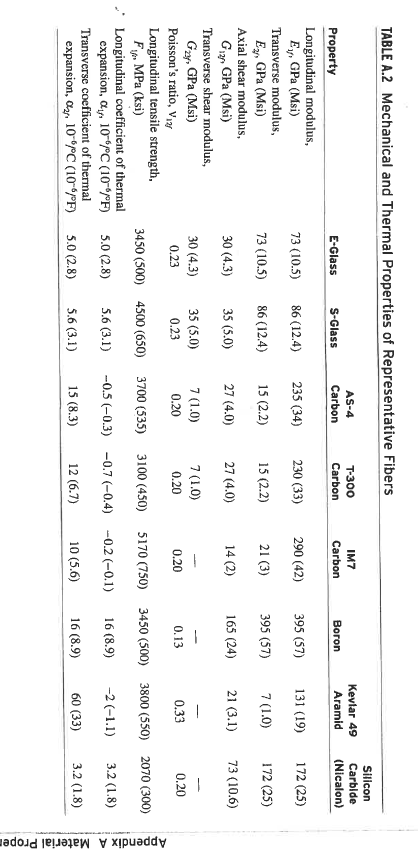
. . For a glass epoxy lamina volume fraction 60% Calculate the coefficieents of thermal expansion for the lamina at zero and angled at 60 degrees Strains under a temperature change of -100 degrees C for the zero and 60 degree lamina . 374 APPENDIX A MATERIAL PROPERTIES Modulus GPa (Msi) Tensile Strength MPa (ksi) 73 (10.5) 86 (12.4) 3450 (500) 4500 (650) 235 (34) 230 (33) 250 (36) 255 (37) 290 (42) 3700 (535) 3100 (450) 4500 (650) 4500 (650) 5170 (750) TABLE A.1 Properties of Typical Fibers Diameter Density Type um (10-in) g/cm (lb/in) Glass E-glass 8-14 (0.30-0.55) 2.54 (0.092) S-glass 10 (0.40) 2.49 (0.090) Carbon AS4 7 (0.28) 1.81 (0.065) T300 1.76 (0.063) T-400H 1.80 (0.065) IM-6 4 (0.16) 1.80 (0.065) IM-7 4 (0.16) 1.80 (0.065) Graphite T-50 1.67 (0.060) GY-70 1.86 (0.067) P100 S 10 (0.4) 2.02 (0.073) Boron 140 (5.6) 2.50 (0.090) Aramid Kevlar 49 12 (0.47) 1.45 (0.052) Kevlar 149 12 (0.47) 1.45 (0.052) Silicon carbide (SCS-2) 140 (5.6) 3.10 (0.112) Nicalon 15 (0.6) 2.60 (0.094) Alumina FP-2 3.70 (0.133) Nextel 610 3.75 (0.135) Saphikon 3.80 (0.137) Sapphire whiskers 3.96 (0.143) Silica 2.19 (0.079) Tungsten 19.3 (0.696) 390 (57) 520 (75) 720 (105) 395 (57) 2070 (300) 1725 (250) 1725 (250) 3450 (500) 131 (19) 186 (27) 3800 (550) 3400 (490) 400 (58) 172 (25) 4140 (600) 2070 (300) 380 (55) 370 (54) 380 (55) 410 (60) 73 (10.5) 410 (60) 1725 (250) 1900 (275) 3100 (450) 21,000 (3000) 5800 (840) 4140 (600) 376 Vinylester (Derakane) Poly-ether- ether-ketone (PEEK) Polyimides 1.15 (0.042) 1.4-1.9 (0.050-0.069) 1.32 (0.049) 3-4 (0.43-0.58) 3.1-4.9 (0.45-0.71) APPENDIX A MATERIAL PROPERTIES 3.7 (0.53) 1.1-1.5 (0.16-0.21) 0.35 65-90 (9.4-13.0) 70-120 (10.1-17.4) 96 (14) TABLE A.3 Properties of Typical Polymer Matrix Materials Epoxy Epoxy Epoxy (HY6010/ Property (3501-6) (977-3) HT917/DY070) Polyesters Density, p. g/cm (lb/in) 1.27 (0.046) 1.28 (0.046) 1.17 (0.043) 1.1-1.5 (0.040-0.054) Young's modulus, E. GPa (Msi) 4.3 (0.62) 3.7 (0.54) 3.4 (0.49) 3.2-3.5 (0.46-0.51) Shear modulus, GGPa (Msi) 1.60 (0.24) 1.37 (0.20) 1.26 (0.18) 0.7-2.0 (0.10-0.30) Poisson's ratio, 0.35 0.35 0.36 0.35 Tensile strength, For MPa (ksi) 69 (10) 90 (13) 80 (11.6) 40-90 (5.8-13.0) Compressive strength, F MPa (ksi) 200 (30) 175 (25) 104 (15.1) 90-250 (13-35) Shear strength, FMPa (ksi) 100 (15) 52 (7.5) 40 (5.8) 45 (6.5) Coefficient of thermal expansion, C., 10*/C (10/F) 45 (25) 62 (3.4) 60-200 (33-110) Glass transition temperature, TC (F) 200 (390) 200 (390) 152 (305) 50-110 (120-230) Maximum use temperature, TxC (F) 150 (300) 177 (350) Ultimate tensile strain, (%) 2-5 2-5 me 127 (18.4) 53 (29) 100--150 (212-514) 90 (50) 280-320 (540-610) 143 (290) 300-370 (570-700) 250 (480) 1-5 1.5-3.0 TABLE A.2 Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Representative Fibers AS-4 Carbon T-300 Carbon IM7 Carbon Kevlar 49 Aramid Silicon Carbide (Nicalon) Boron 235 (34) 230 (33) 290 (42) 395 (57) 131 (19) 172 (25) 15 (2.2) 15 (2.2) 21 (3) 395 (57) 7 (1.0) 172 (25) 27 (4.0) 27 (4.0) 14 (2) 165 (24) 21 (3.1) 73 (10.6) Property E-Glass S-Glass Longitudinal modulus, E, GPa (Msi) 73 (10.5) 86 (12.4) Transverse modulus, E, GPa (Msi) 73 (10.5) 86 (12.4) Axial shear modulus, Gin GPa (Msi) 30 (4.3) 35 (5.0) Transverse shear modulus, Gz, GPa (Msi) 30 (4.3) 35 (5.0) Poisson's ratio, Vizy 0.23 0.23 Longitudinal tensile strength, F.MPa (ksi) 3450 (500) 4500 (650) Longitudinal coefficient of thermal expansion, air, 10-6C (10/F) 5.0 (2.8) 5.6 (3.1) Transverse coefficient of thermal expansion, Oz, 10-6C (10/F) 5.0 (2.8) 5.6 (3.1) 7 (1.0) 0.20 7(1.0) 0.20 0.20 0.13 0.33 0.20 3700 (535) 3100 (450) 5170 (750) 3450 (500) 3800 (550) 2070 (300) -0.5 (-0.3) -0.7 (-0.4) -0.2 -0.1) 16 (8.9) -2 (-1.1) 3.2 (1.8) 15 (8.3) 12 (6.7) Appendix A Material Prope. 10 (5.6) 16 (8.9) 60 (33) 3.2 (1.8) . . For a glass epoxy lamina volume fraction 60% Calculate the coefficieents of thermal expansion for the lamina at zero and angled at 60 degrees Strains under a temperature change of -100 degrees C for the zero and 60 degree lamina . 374 APPENDIX A MATERIAL PROPERTIES Modulus GPa (Msi) Tensile Strength MPa (ksi) 73 (10.5) 86 (12.4) 3450 (500) 4500 (650) 235 (34) 230 (33) 250 (36) 255 (37) 290 (42) 3700 (535) 3100 (450) 4500 (650) 4500 (650) 5170 (750) TABLE A.1 Properties of Typical Fibers Diameter Density Type um (10-in) g/cm (lb/in) Glass E-glass 8-14 (0.30-0.55) 2.54 (0.092) S-glass 10 (0.40) 2.49 (0.090) Carbon AS4 7 (0.28) 1.81 (0.065) T300 1.76 (0.063) T-400H 1.80 (0.065) IM-6 4 (0.16) 1.80 (0.065) IM-7 4 (0.16) 1.80 (0.065) Graphite T-50 1.67 (0.060) GY-70 1.86 (0.067) P100 S 10 (0.4) 2.02 (0.073) Boron 140 (5.6) 2.50 (0.090) Aramid Kevlar 49 12 (0.47) 1.45 (0.052) Kevlar 149 12 (0.47) 1.45 (0.052) Silicon carbide (SCS-2) 140 (5.6) 3.10 (0.112) Nicalon 15 (0.6) 2.60 (0.094) Alumina FP-2 3.70 (0.133) Nextel 610 3.75 (0.135) Saphikon 3.80 (0.137) Sapphire whiskers 3.96 (0.143) Silica 2.19 (0.079) Tungsten 19.3 (0.696) 390 (57) 520 (75) 720 (105) 395 (57) 2070 (300) 1725 (250) 1725 (250) 3450 (500) 131 (19) 186 (27) 3800 (550) 3400 (490) 400 (58) 172 (25) 4140 (600) 2070 (300) 380 (55) 370 (54) 380 (55) 410 (60) 73 (10.5) 410 (60) 1725 (250) 1900 (275) 3100 (450) 21,000 (3000) 5800 (840) 4140 (600) 376 Vinylester (Derakane) Poly-ether- ether-ketone (PEEK) Polyimides 1.15 (0.042) 1.4-1.9 (0.050-0.069) 1.32 (0.049) 3-4 (0.43-0.58) 3.1-4.9 (0.45-0.71) APPENDIX A MATERIAL PROPERTIES 3.7 (0.53) 1.1-1.5 (0.16-0.21) 0.35 65-90 (9.4-13.0) 70-120 (10.1-17.4) 96 (14) TABLE A.3 Properties of Typical Polymer Matrix Materials Epoxy Epoxy Epoxy (HY6010/ Property (3501-6) (977-3) HT917/DY070) Polyesters Density, p. g/cm (lb/in) 1.27 (0.046) 1.28 (0.046) 1.17 (0.043) 1.1-1.5 (0.040-0.054) Young's modulus, E. GPa (Msi) 4.3 (0.62) 3.7 (0.54) 3.4 (0.49) 3.2-3.5 (0.46-0.51) Shear modulus, GGPa (Msi) 1.60 (0.24) 1.37 (0.20) 1.26 (0.18) 0.7-2.0 (0.10-0.30) Poisson's ratio, 0.35 0.35 0.36 0.35 Tensile strength, For MPa (ksi) 69 (10) 90 (13) 80 (11.6) 40-90 (5.8-13.0) Compressive strength, F MPa (ksi) 200 (30) 175 (25) 104 (15.1) 90-250 (13-35) Shear strength, FMPa (ksi) 100 (15) 52 (7.5) 40 (5.8) 45 (6.5) Coefficient of thermal expansion, C., 10*/C (10/F) 45 (25) 62 (3.4) 60-200 (33-110) Glass transition temperature, TC (F) 200 (390) 200 (390) 152 (305) 50-110 (120-230) Maximum use temperature, TxC (F) 150 (300) 177 (350) Ultimate tensile strain, (%) 2-5 2-5 me 127 (18.4) 53 (29) 100--150 (212-514) 90 (50) 280-320 (540-610) 143 (290) 300-370 (570-700) 250 (480) 1-5 1.5-3.0 TABLE A.2 Mechanical and Thermal Properties of Representative Fibers AS-4 Carbon T-300 Carbon IM7 Carbon Kevlar 49 Aramid Silicon Carbide (Nicalon) Boron 235 (34) 230 (33) 290 (42) 395 (57) 131 (19) 172 (25) 15 (2.2) 15 (2.2) 21 (3) 395 (57) 7 (1.0) 172 (25) 27 (4.0) 27 (4.0) 14 (2) 165 (24) 21 (3.1) 73 (10.6) Property E-Glass S-Glass Longitudinal modulus, E, GPa (Msi) 73 (10.5) 86 (12.4) Transverse modulus, E, GPa (Msi) 73 (10.5) 86 (12.4) Axial shear modulus, Gin GPa (Msi) 30 (4.3) 35 (5.0) Transverse shear modulus, Gz, GPa (Msi) 30 (4.3) 35 (5.0) Poisson's ratio, Vizy 0.23 0.23 Longitudinal tensile strength, F.MPa (ksi) 3450 (500) 4500 (650) Longitudinal coefficient of thermal expansion, air, 10-6C (10/F) 5.0 (2.8) 5.6 (3.1) Transverse coefficient of thermal expansion, Oz, 10-6C (10/F) 5.0 (2.8) 5.6 (3.1) 7 (1.0) 0.20 7(1.0) 0.20 0.20 0.13 0.33 0.20 3700 (535) 3100 (450) 5170 (750) 3450 (500) 3800 (550) 2070 (300) -0.5 (-0.3) -0.7 (-0.4) -0.2 -0.1) 16 (8.9) -2 (-1.1) 3.2 (1.8) 15 (8.3) 12 (6.7) Appendix A Material Prope. 10 (5.6) 16 (8.9) 60 (33) 3.2 (1.8)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


