Question: MATLAB problem. Would like detail The pressure drop delta p in Pa for a fluid flowing in a pipe with a sudden increase in diameter
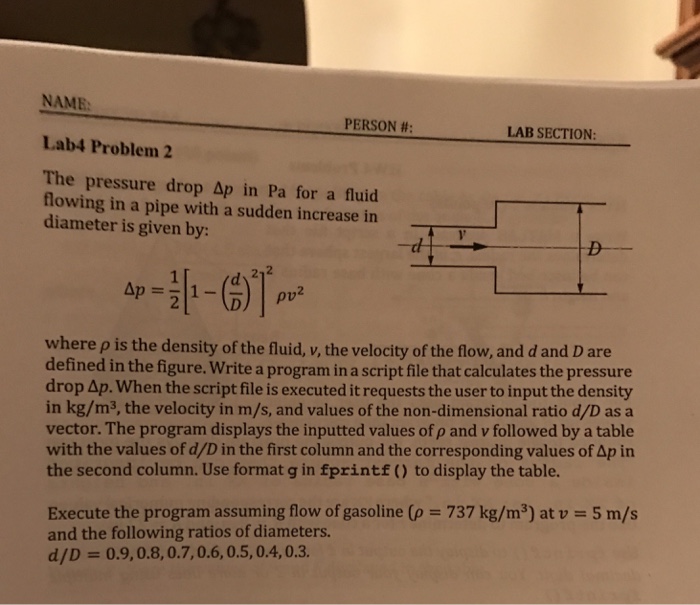
The pressure drop delta p in Pa for a fluid flowing in a pipe with a sudden increase in diameter is given by: delta p = 1/2[1 - (d/D)^2]^2 rho v^2 where rho is the density of the fluid, v, the velocity of the flow, and d and D are defined in the figure. Write a program in a script file that calculates the pressure drop delta p. When the script file is executed it requests the user to input the density in kg/m^3, the velocity in m/s, and values of the non-dimensional ratio d/D as a vector. The program displays the inputted values of rho and v followed by a table with the values of d/D in the first column and the corresponding values of delta p in the second column. Use format g in fprintf () to display the table. Execute the program assuming flow of gasoline (rho = 737 kg/m^3) at v = 5 m/s and the following ratios of diameters. d/D = 0.9, 0.8, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5, 0.4, 0.3
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


